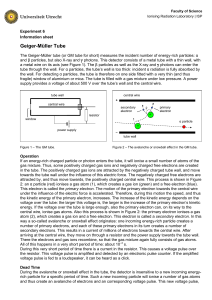
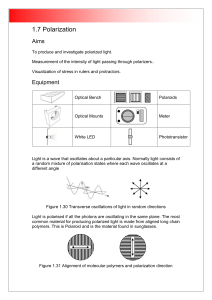
Chapter 4 - TeacherJeff
... • The shinier and smoother the surface the better the reflection. • Plane Mirrors – flat mirrors – will allow for the clearest of reflections ...
... • The shinier and smoother the surface the better the reflection. • Plane Mirrors – flat mirrors – will allow for the clearest of reflections ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first covalently then through ionic bonding • Oxidation number – the number of ...
... • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first covalently then through ionic bonding • Oxidation number – the number of ...
Chapter 5
... Resistance • Symbol: R Unit: Ohms (Ω) • is the ability of a material within an electrical circuit to hinder the flow of electric current. • Formula: R = V/I • Measured with a device called an OHMMETER, which must be disconnected in from the circuit to take a measurement! • Resistance is dependent o ...
... Resistance • Symbol: R Unit: Ohms (Ω) • is the ability of a material within an electrical circuit to hinder the flow of electric current. • Formula: R = V/I • Measured with a device called an OHMMETER, which must be disconnected in from the circuit to take a measurement! • Resistance is dependent o ...
Radiation in a Medium
... entirely from Maxwell’s equations. • But for atmospheric applications, a number of simplifying assumptions can be made that eliminate the need to work from first principles: 1. Far field, time-averaged solutions are sought. 2. Medium is sparsely populated with discrete, randomly-oriented and randoml ...
... entirely from Maxwell’s equations. • But for atmospheric applications, a number of simplifying assumptions can be made that eliminate the need to work from first principles: 1. Far field, time-averaged solutions are sought. 2. Medium is sparsely populated with discrete, randomly-oriented and randoml ...
valence electrons
... Valence Electrons Review • In order to be stable, atoms must empty or fill their outermost level. • Since the outer level contains two s electrons and six p electrons (d & f are always in lower levels), the optimum number of electrons is eight. • This is called the octet rule. ...
... Valence Electrons Review • In order to be stable, atoms must empty or fill their outermost level. • Since the outer level contains two s electrons and six p electrons (d & f are always in lower levels), the optimum number of electrons is eight. • This is called the octet rule. ...
Exam # 3 Fall 2009
... 16.) A 16.8-kg boy is riding in a 4.50-kg wagon. A 14.0-kg girl pushes the wagon and exerts a constant force of 2.60 N over a distance of 3.50 m. What is the change in energy of the boy and the wagon? (9.10 J) 17.) An elevator lifts a total mass of 1.1x103 kg a distance of 40.0 m in 12.5 s. How muc ...
... 16.) A 16.8-kg boy is riding in a 4.50-kg wagon. A 14.0-kg girl pushes the wagon and exerts a constant force of 2.60 N over a distance of 3.50 m. What is the change in energy of the boy and the wagon? (9.10 J) 17.) An elevator lifts a total mass of 1.1x103 kg a distance of 40.0 m in 12.5 s. How muc ...
15.2 Energy Conversion and Conservation
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. This happens constantly Batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy, then the light bulb converts the electrical energy to electromagnetic energy (light) and thermal energy. I convert kinetic energy to potential energy by pulling back the ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. This happens constantly Batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy, then the light bulb converts the electrical energy to electromagnetic energy (light) and thermal energy. I convert kinetic energy to potential energy by pulling back the ...
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
... The distance from the crest of a wave or the trough to the resting position of a wave. ...
... The distance from the crest of a wave or the trough to the resting position of a wave. ...