Basic Atomic Theory
... • Strength of Coulomb forces much larger than gravitational • +ve and –ve charges cause attractive and repulsive interactions. ...
... • Strength of Coulomb forces much larger than gravitational • +ve and –ve charges cause attractive and repulsive interactions. ...
Block 3: Physics of Waves Chapter 12: Sound Skill Goals: • Describe
... Describe features of electromagnetic spectrum Understand all EM waves travel at speed of light Apply the wave equation to EM waves ...
... Describe features of electromagnetic spectrum Understand all EM waves travel at speed of light Apply the wave equation to EM waves ...
Q1. (a) The diagram below shows the path followed by a light ray
... (a) The discovery of photoelectricity and subsequent investigations led to the wave theory of light being replaced by the photon theory. State one feature of photoelectricity that could not be explained using the wave theory of light and describe how it is explained using photon theory. The quality ...
... (a) The discovery of photoelectricity and subsequent investigations led to the wave theory of light being replaced by the photon theory. State one feature of photoelectricity that could not be explained using the wave theory of light and describe how it is explained using photon theory. The quality ...
Solid State Physics
... filled with electrons, while all levels above EF are empty. • Electrons are free to move into “empty” states of conduction band with only a small electric field E, leading to high electrical conductivity! • At T > 0, electrons have a probability to be thermally “excited” from below the Fermi energy ...
... filled with electrons, while all levels above EF are empty. • Electrons are free to move into “empty” states of conduction band with only a small electric field E, leading to high electrical conductivity! • At T > 0, electrons have a probability to be thermally “excited” from below the Fermi energy ...
Meters per second, south
... Gravitational force causes the water to move downstream. There is more potential energy at the top of the mountain than at the bottom. In streams that are flowing very fast, there is a dramatic change (decrease) in the height of the mountain from point A to point B (i.e. there is a bigger drop). The ...
... Gravitational force causes the water to move downstream. There is more potential energy at the top of the mountain than at the bottom. In streams that are flowing very fast, there is a dramatic change (decrease) in the height of the mountain from point A to point B (i.e. there is a bigger drop). The ...
Wavelength-dependent resolution and electron energy distribution
... Variation in the amount of energy lost due to phonon scattering causes a spread of electron energies leaving the photocathode. Electrons generated in the layer do not necessarily travel in the same direction as the initial photon, in fact there is no reason to consider why they should not be release ...
... Variation in the amount of energy lost due to phonon scattering causes a spread of electron energies leaving the photocathode. Electrons generated in the layer do not necessarily travel in the same direction as the initial photon, in fact there is no reason to consider why they should not be release ...
04 Biochemistry
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
GonzalesMestres
... increasing energy. Although the measurements available now are only up to about 55 EeV, the trend suggests that primary CRs are likely to be dominated by heavy nuclei at higher energies. This interpretation of the shower depths is not certain, however. It relies on shower simulations that use hadron ...
... increasing energy. Although the measurements available now are only up to about 55 EeV, the trend suggests that primary CRs are likely to be dominated by heavy nuclei at higher energies. This interpretation of the shower depths is not certain, however. It relies on shower simulations that use hadron ...
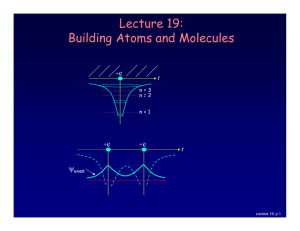
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. ...
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. ...
4-3 Power Point
... the orbital of the first energy level. • The third electron is in an orbital of the second energy level. • If a lithium atom absorbs enough energy, one of its electrons can move to an orbital with a higher energy. • This configuration is referred to as an excited state. An excited state is less stab ...
... the orbital of the first energy level. • The third electron is in an orbital of the second energy level. • If a lithium atom absorbs enough energy, one of its electrons can move to an orbital with a higher energy. • This configuration is referred to as an excited state. An excited state is less stab ...
Bonding
... Q1Q2 (b) Lattice energy can be represented by Coulomb’s law: lattice energy = k ( r ), where Q1 and Q2 are the charges on the ions, in CaO these are +2 and –2 respectively, while in K2O they are +1 and –2. The r (the distance between ions) is slightly smaller in CaO, combined with the larger charges ...
... Q1Q2 (b) Lattice energy can be represented by Coulomb’s law: lattice energy = k ( r ), where Q1 and Q2 are the charges on the ions, in CaO these are +2 and –2 respectively, while in K2O they are +1 and –2. The r (the distance between ions) is slightly smaller in CaO, combined with the larger charges ...
November 11th Electromagnetic Waves - Chapter 34
... materials rotate the plane of polarization ! The rotation angle may depends on the frequency (color) ! This is due to molecular asymmetry e.g. molecules with spiral shapes ! Karo syrup and scotch tape ...
... materials rotate the plane of polarization ! The rotation angle may depends on the frequency (color) ! This is due to molecular asymmetry e.g. molecules with spiral shapes ! Karo syrup and scotch tape ...
Energy Review
... a. A dark light bulb starting to glow b. Food being heated in an oven c. A ball rolling down a hill d. A person lifting weights 32. Describe all the different ways an energy-efficient electric fan converts its electrical energy? 33. Describe the energy transfer that occurs when wind is used to gener ...
... a. A dark light bulb starting to glow b. Food being heated in an oven c. A ball rolling down a hill d. A person lifting weights 32. Describe all the different ways an energy-efficient electric fan converts its electrical energy? 33. Describe the energy transfer that occurs when wind is used to gener ...
Semester 2 review questions
... 4. __________What is the valence electron configuration for any element in group 2? 5. __________ What energy level are Bromine’s valence electrons in? 6. Period:__________ Given the following configuration: [Ar]4s23d104p2; what period and block is the last valence electron found in? ...
... 4. __________What is the valence electron configuration for any element in group 2? 5. __________ What energy level are Bromine’s valence electrons in? 6. Period:__________ Given the following configuration: [Ar]4s23d104p2; what period and block is the last valence electron found in? ...