Fat Metabolism
... • Transport is rate-limiting • Regulation of carnitine acyl transferase – off by fat synth products – high NADH ...
... • Transport is rate-limiting • Regulation of carnitine acyl transferase – off by fat synth products – high NADH ...
COURSE SYLLABUS CHM 521 Biochemistry I 3(3
... Biochemistry by Stryer (4th edition), Freeman and Co., 1995 Principles of Biochemistry by Horton, et al, Neil Patterson Publishers, 1993 Biochemistry by Rawn, Neil Patterson Publishers, 1989 Biochemistry by Voet and Voet, (2nd edition), John Wiley & Sons, 1995 Biochemistry by Zubay (3rd edition), Wm ...
... Biochemistry by Stryer (4th edition), Freeman and Co., 1995 Principles of Biochemistry by Horton, et al, Neil Patterson Publishers, 1993 Biochemistry by Rawn, Neil Patterson Publishers, 1989 Biochemistry by Voet and Voet, (2nd edition), John Wiley & Sons, 1995 Biochemistry by Zubay (3rd edition), Wm ...
Crystal structure of potato tuber ADP‐glucose pyrophosphorylase
... the region around the sulfate 1-binding site in the b subunit does play a role in the allosteric activation of the enzyme. Taken together, these studies indicate that the activator 3-PGA binds at or near the inhibitor-binding site defined in our structure by sulfate 1. Sulfate 2 makes interactions wi ...
... the region around the sulfate 1-binding site in the b subunit does play a role in the allosteric activation of the enzyme. Taken together, these studies indicate that the activator 3-PGA binds at or near the inhibitor-binding site defined in our structure by sulfate 1. Sulfate 2 makes interactions wi ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... Fatty acid synthesis • The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis are packaged together in a complex called as fatty acid synthase (FAS). • The product of FAS action is palmitic acid. (16:0). • Modifications of this primary FA leads to other longer (and shorter) FA and unsaturated FA. • The fatty acid mole ...
... Fatty acid synthesis • The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis are packaged together in a complex called as fatty acid synthase (FAS). • The product of FAS action is palmitic acid. (16:0). • Modifications of this primary FA leads to other longer (and shorter) FA and unsaturated FA. • The fatty acid mole ...
380 KB / 39 pages
... (b) When a match is struck and used to start a barbeque, several chemical reactions occur. There is a chemical reaction that uses the energy of the friction of the match head to initiate the reaction that lights the match (which continues to burn because the energy released in the burning sustains t ...
... (b) When a match is struck and used to start a barbeque, several chemical reactions occur. There is a chemical reaction that uses the energy of the friction of the match head to initiate the reaction that lights the match (which continues to burn because the energy released in the burning sustains t ...
Trafficking of phosphatidylinositol by phosphatidylinositol transfer
... of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity with other known proteins. Previously, a PITP that facilitates the transfer of PtdIns and PtdCho in vitro has been isolated from the cytosol of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisae [3]. This protein is encoded by the SEC14 gene and is required for tr ...
... of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity with other known proteins. Previously, a PITP that facilitates the transfer of PtdIns and PtdCho in vitro has been isolated from the cytosol of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisae [3]. This protein is encoded by the SEC14 gene and is required for tr ...
Relationship between Protein Synthesis and Secretion in Liver Cells
... The effect of rotenone, 2,4-dinitrophenol, fructose and glycerol on the release into the medium of lactate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase, enzymes of the cytoplasm and mitochondria, respectively, was assayed. Enzyme activities were monitored in both total cell suspension and incubation me ...
... The effect of rotenone, 2,4-dinitrophenol, fructose and glycerol on the release into the medium of lactate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase, enzymes of the cytoplasm and mitochondria, respectively, was assayed. Enzyme activities were monitored in both total cell suspension and incubation me ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
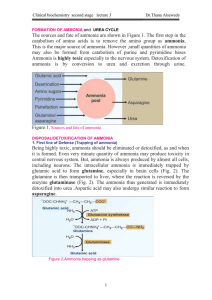
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... Regulation of the Urea Cycle 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where th ...
... Regulation of the Urea Cycle 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where th ...
Lecture_14.pps
... •Different types of glycans have unique degradation pathways •Mutations in different degradative enzymes lead to rare diseases •Limiting glycan synthesis in genetic disorders reduces pathology •Tissue specific differences in salvage/de novo biosynthesis may be important for health and lead to pathol ...
... •Different types of glycans have unique degradation pathways •Mutations in different degradative enzymes lead to rare diseases •Limiting glycan synthesis in genetic disorders reduces pathology •Tissue specific differences in salvage/de novo biosynthesis may be important for health and lead to pathol ...
pentose phosphate pathway
... Utilization of Glucose-6-P Depends on the Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P • Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway • The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism • ATP can be made if G-6-P ...
... Utilization of Glucose-6-P Depends on the Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P • Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway • The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism • ATP can be made if G-6-P ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respiration. In fact, they may not be able to survive at all in the presence of oxygen. ...
... respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respiration. In fact, they may not be able to survive at all in the presence of oxygen. ...
Biochemistry Study Guide NITROGEN METABOLISM
... PROTEIN SYMPORT: Facilitated transport of amino acids is one of two ways that amino acids can get into cells. The other way is via glutathione. Amino Acid comes in as a symport with Na+, with Na+ flowing with its concentration gradient. So, this transport itself does not require energy. Na+ grad ...
... PROTEIN SYMPORT: Facilitated transport of amino acids is one of two ways that amino acids can get into cells. The other way is via glutathione. Amino Acid comes in as a symport with Na+, with Na+ flowing with its concentration gradient. So, this transport itself does not require energy. Na+ grad ...
Chem 356 Structure and Function in Biochemistry
... (b) The value of this ratio in the cell (>100:1) indicates that [glucose 1-P] is far below the equilibrium value. The rate at which glucose 1-P is removed (through entry into glycolysis) is greater than its rate of production (by the glycogen phosphorylase reaction). This indicates that metabolic f ...
... (b) The value of this ratio in the cell (>100:1) indicates that [glucose 1-P] is far below the equilibrium value. The rate at which glucose 1-P is removed (through entry into glycolysis) is greater than its rate of production (by the glycogen phosphorylase reaction). This indicates that metabolic f ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. lactate O dehydrogenase ...
... important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. lactate O dehydrogenase ...
Directed Evolution of ATP Binding Proteins from a Zinc Finger
... A number of different display methods have been employed in combination with new scaffolds to evolve interesting and useful new proteins [9, 11, 15–19]. Phage display has been the most popular method for selecting functional molecules from new scaffolds; the following are examples of successful expe ...
... A number of different display methods have been employed in combination with new scaffolds to evolve interesting and useful new proteins [9, 11, 15–19]. Phage display has been the most popular method for selecting functional molecules from new scaffolds; the following are examples of successful expe ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... A voltaic or electrochemical cell is made by connecting two half-cells using an external circuit and a salt bridge as shown below. The external circuit allows electrons to be transferred from one half cell to the other. A half cell is a piece of a metal immersed in an aqueous salt solution of that m ...
... A voltaic or electrochemical cell is made by connecting two half-cells using an external circuit and a salt bridge as shown below. The external circuit allows electrons to be transferred from one half cell to the other. A half cell is a piece of a metal immersed in an aqueous salt solution of that m ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... A voltaic or electrochemical cell is made by connecting two half-cells using an external circuit and a salt bridge as shown below. The external circuit allows electrons to be transferred from one half cell to the other. A half cell is a piece of a metal immersed in an aqueous salt solution of that m ...
... A voltaic or electrochemical cell is made by connecting two half-cells using an external circuit and a salt bridge as shown below. The external circuit allows electrons to be transferred from one half cell to the other. A half cell is a piece of a metal immersed in an aqueous salt solution of that m ...
Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During Exercise,
... oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular level, but also includes hydration, nutrition, meal timing and maintenance of muscle ...
... oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular level, but also includes hydration, nutrition, meal timing and maintenance of muscle ...
Ch06Test_File - Milan Area Schools
... Fill in the Blank 1. Cells cannot create energy because _______. Answer: energy cannot be created or destroyed 2. Variations of enzymes that allow organisms to adapt to changing environments are termed _______. Answer: isozymes 3. Although some enzymes consist entirely of one or more polypeptide cha ...
... Fill in the Blank 1. Cells cannot create energy because _______. Answer: energy cannot be created or destroyed 2. Variations of enzymes that allow organisms to adapt to changing environments are termed _______. Answer: isozymes 3. Although some enzymes consist entirely of one or more polypeptide cha ...
anabolic and catabolic reactions. Energetics of bacterial growth
... Some textbooks of microbiology still indicate that glucose oxidation involves three coupling sites, with the complete oxidation of glucose producing 38 ATP mol per mol (8), but bacteria do not usually have three phosphorylation sites (37, 39). In E. coli there are several pathways of respiration, an ...
... Some textbooks of microbiology still indicate that glucose oxidation involves three coupling sites, with the complete oxidation of glucose producing 38 ATP mol per mol (8), but bacteria do not usually have three phosphorylation sites (37, 39). In E. coli there are several pathways of respiration, an ...
Purine nucleotide synthesis De novo
... • In earlier times gout was thought to be associated with rich diets and excessive consumption of alcoholic drinks • Lead salts used to be added as preservatives in alcoholic drinks; ...
... • In earlier times gout was thought to be associated with rich diets and excessive consumption of alcoholic drinks • Lead salts used to be added as preservatives in alcoholic drinks; ...
Glucose
... carbohydrate: Oxidation of fuel The main function of carbohydrates is to provide your body with energy and carbon. Source of material for anabolism e.g. Carbohydrate provides material for synthesis of amino acid, nucleotide, ...
... carbohydrate: Oxidation of fuel The main function of carbohydrates is to provide your body with energy and carbon. Source of material for anabolism e.g. Carbohydrate provides material for synthesis of amino acid, nucleotide, ...
Restriction Enzymes Brochure
... (HF) Restriction Enzymes to address two short-comings of traditional restriction enzymes: buffer compatibility and star activity. HF restriction enzymes have 100% activity in CutSmart™ Buffer; singlebuffer simplicity means more straightforward and streamlined sample processing. HF enzymes also exhib ...
... (HF) Restriction Enzymes to address two short-comings of traditional restriction enzymes: buffer compatibility and star activity. HF restriction enzymes have 100% activity in CutSmart™ Buffer; singlebuffer simplicity means more straightforward and streamlined sample processing. HF enzymes also exhib ...
heme
... ● globin → AAs → metabolism ● heme → bilirubin 2+ → transport with transferrin and used in the next ● Fe heme biosynthesis ...
... ● globin → AAs → metabolism ● heme → bilirubin 2+ → transport with transferrin and used in the next ● Fe heme biosynthesis ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (or OXPHOS in short) is the metabolic pathway in which the mitochondria in cells use their structure, enzymes, and energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to reform ATP. Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, ATP is the molecule that supplies energy to metabolism. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is probably so pervasive because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen, in redox reactions. These redox reactions release energy, which is used to form ATP. In eukaryotes, these redox reactions are carried out by a series of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the cell's mitochondria, whereas, in prokaryotes, these proteins are located in the cells' intermembrane space. These linked sets of proteins are called electron transport chains. In eukaryotes, five main protein complexes are involved, whereas in prokaryotes many different enzymes are present, using a variety of electron donors and acceptors.The energy released by electrons flowing through this electron transport chain is used to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, in a process called electron transport. This generates potential energy in the form of a pH gradient and an electrical potential across this membrane. This store of energy is tapped by allowing protons to flow back across the membrane and down this gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase; this process is known as chemiosmosis. This enzyme uses this energy to generate ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP), in a phosphorylation reaction. This reaction is driven by the proton flow, which forces the rotation of a part of the enzyme; the ATP synthase is a rotary mechanical motor.Although oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to disease and, possibly, aging (senescence). The enzymes carrying out this metabolic pathway are also the target of many drugs and poisons that inhibit their activities.