ATP Pool and Growth Yield in Selenomonas
... 0.084 h-l and after about 160 h attained a steady state which continued for the next 200 h. The dilution rate was then increased to 0.101for 200 h, a new steady state being reached in about 30 h. The medium was then changed to glucose plus pyruvate. Some granular growth occurred on first changing th ...
... 0.084 h-l and after about 160 h attained a steady state which continued for the next 200 h. The dilution rate was then increased to 0.101for 200 h, a new steady state being reached in about 30 h. The medium was then changed to glucose plus pyruvate. Some granular growth occurred on first changing th ...
Analysis of structural robustness of metabolic
... Wiback and Palsson [34] considered even more of such exchange reactions (with some of them describing consumption inside the cell), which increases the number of elementary modes. Although it is questionable whether such exchange reactions are relevant in erythrocytes, we use the network in this con ...
... Wiback and Palsson [34] considered even more of such exchange reactions (with some of them describing consumption inside the cell), which increases the number of elementary modes. Although it is questionable whether such exchange reactions are relevant in erythrocytes, we use the network in this con ...
CHAPTER 19
... But why do we say a substance is reduced when it gains electrons? Remember, when electrons are gained, their negative electrical charge will cause the overall oxidation number to drop, that is, be reduced. A transfer of electrons causes changes in the oxidation states of one or more elements. Any ch ...
... But why do we say a substance is reduced when it gains electrons? Remember, when electrons are gained, their negative electrical charge will cause the overall oxidation number to drop, that is, be reduced. A transfer of electrons causes changes in the oxidation states of one or more elements. Any ch ...
Oxidation - medscistudents
... Patients with this disease accumulate large quantities of an unusual fatty acid, Phytanic acid derived from phytol, a constituent of chlorophyll Also present in milk and animal fats Phytanic acid cannot undergo - oxidation due to the presence of a methyl group on carbon-3 This fatty acid undergo in ...
... Patients with this disease accumulate large quantities of an unusual fatty acid, Phytanic acid derived from phytol, a constituent of chlorophyll Also present in milk and animal fats Phytanic acid cannot undergo - oxidation due to the presence of a methyl group on carbon-3 This fatty acid undergo in ...
Fatty acid and phospholipid metabolism in prokaryotes
... mole of lipid requires about 32 mole of ATP for its synthesis. Thus, phospholipid synthesis requires significant investment by the cell, and the advantages of maintaining fine control over the pathway are obvious. The pathway in most bacteria is catalyzed by a series of discrete proteins: the enzyme ...
... mole of lipid requires about 32 mole of ATP for its synthesis. Thus, phospholipid synthesis requires significant investment by the cell, and the advantages of maintaining fine control over the pathway are obvious. The pathway in most bacteria is catalyzed by a series of discrete proteins: the enzyme ...
A Study of the Membrane–Water Interface Region of Membrane
... together with other polar residues such as Asn and Ser. These residues have been shown to be efficient turn-promoters when placed in the middle of long transmembrane segments,13 and also serve as helixbreaking or helix-capping residues in globular proteins.14 It has been reported that polar residues ...
... together with other polar residues such as Asn and Ser. These residues have been shown to be efficient turn-promoters when placed in the middle of long transmembrane segments,13 and also serve as helixbreaking or helix-capping residues in globular proteins.14 It has been reported that polar residues ...
Answers - Study of Life
... You extract RNA from liver cells and then carry out an agarose gel electrophoresis of the liver RNA. The RNA fragments are then transferred to an RNA-binding membrane (nitrocellulose or nylon) using capillary action. Next, you hybridize a probe for gene X to the RNA on the membrane. Which of the fol ...
... You extract RNA from liver cells and then carry out an agarose gel electrophoresis of the liver RNA. The RNA fragments are then transferred to an RNA-binding membrane (nitrocellulose or nylon) using capillary action. Next, you hybridize a probe for gene X to the RNA on the membrane. Which of the fol ...
to the full text - David Moore`s World of Fungi: where
... cellobiose oxidoreductases; a cellobiose: quinone oxidoreductase (CBQ) and cellobiose oxidase (CBO). Cellobiose oxidase is able to oxidise cellobiose to the δ-lactone, which can then be converted to cellobionic acid and then glucose + gluconic acid; cellobiose δ-lactone can also be formed by the enz ...
... cellobiose oxidoreductases; a cellobiose: quinone oxidoreductase (CBQ) and cellobiose oxidase (CBO). Cellobiose oxidase is able to oxidise cellobiose to the δ-lactone, which can then be converted to cellobionic acid and then glucose + gluconic acid; cellobiose δ-lactone can also be formed by the enz ...
CoA
... a) fatty acid from which they are derived; b) specific functions of each eicosanoid; c) general pathway of production; effects of glucocorticoids (cortisol) and aspirin ...
... a) fatty acid from which they are derived; b) specific functions of each eicosanoid; c) general pathway of production; effects of glucocorticoids (cortisol) and aspirin ...
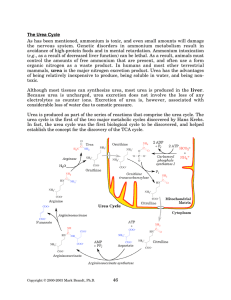
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... kidney. Another pathway for release of ammonium from amino acids is the action of Lamino acid oxidase, a liver enzyme that directly deaminates amino acids. This enzyme is normally present in low levels, and is a relatively minor contributor to the pool of free ammonium. As with glutamate dehydrogen ...
... kidney. Another pathway for release of ammonium from amino acids is the action of Lamino acid oxidase, a liver enzyme that directly deaminates amino acids. This enzyme is normally present in low levels, and is a relatively minor contributor to the pool of free ammonium. As with glutamate dehydrogen ...
Chapter 13 (part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... Regulation of Gluconeogenesis • Reciprocal control with glycolysis • When glycolysis is turned on, gluconeogenesis should be turned off • When energy status of cell is high, glycolysis should be off and pyruvate, etc., should be used for synthesis and storage of glucose • When energy status is low, ...
... Regulation of Gluconeogenesis • Reciprocal control with glycolysis • When glycolysis is turned on, gluconeogenesis should be turned off • When energy status of cell is high, glycolysis should be off and pyruvate, etc., should be used for synthesis and storage of glucose • When energy status is low, ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam II - 2013 Name:________________________
... i) Briefly discuss the major/general feature(s) of allosteric/cooperative behavior (10 pts), your answer should include a discussion of the properties of the tense (T) and relaxed (R) state. ii) then discuss one of (6 pts): Choice A: how this effect optimizes oxygen delivery to the tissues, Choice B ...
... i) Briefly discuss the major/general feature(s) of allosteric/cooperative behavior (10 pts), your answer should include a discussion of the properties of the tense (T) and relaxed (R) state. ii) then discuss one of (6 pts): Choice A: how this effect optimizes oxygen delivery to the tissues, Choice B ...
Reading materials 511/rumen microbes/rumen
... is that they can do this without any oxygen! Most eukaryotes need oxygen; it is needed to generate large amounts of energy in the mitochondria, the biochemical powerhouses of the cell. When human cells run out of oxygen they start fermenting and make lactate to produce energy, which is obvious from ...
... is that they can do this without any oxygen! Most eukaryotes need oxygen; it is needed to generate large amounts of energy in the mitochondria, the biochemical powerhouses of the cell. When human cells run out of oxygen they start fermenting and make lactate to produce energy, which is obvious from ...
Fatty acids with
... +carries the substrate (Ac-CoA) (indicates that two-carbon units & ATP are available for synthesis) ...
... +carries the substrate (Ac-CoA) (indicates that two-carbon units & ATP are available for synthesis) ...
E. coli
... D-lactate, and succinate. A high concentration of fermentation acids limits growth, and acetate induces the RpoS regulon associated with entry into stationary phase. Above pH 7, the favored fermentation products are acetate (with ethanol) and formate. Production of acetate and formate is maximal in ...
... D-lactate, and succinate. A high concentration of fermentation acids limits growth, and acetate induces the RpoS regulon associated with entry into stationary phase. Above pH 7, the favored fermentation products are acetate (with ethanol) and formate. Production of acetate and formate is maximal in ...
BCH 301 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... It maintains the level of intermediates of the citric acid cycle in many tissues. ...
... It maintains the level of intermediates of the citric acid cycle in many tissues. ...
Role of Carnitine in Lipid Metabolism
... In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the role of carnitine in the transport of longchain fatty acids into the matrix of the mitochondria was documented (2,3). Experimental work of the last 20 years has enhanced our knowledge of the role of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, carnitine acylcarnitine tran ...
... In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the role of carnitine in the transport of longchain fatty acids into the matrix of the mitochondria was documented (2,3). Experimental work of the last 20 years has enhanced our knowledge of the role of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, carnitine acylcarnitine tran ...
A study of archaeal enzymes involved in polar lipid
... Figure 2. List of candidate enzymes for polar lipid synthesis. The classifications and the sources are shown in the first and second columns, respectively. The complete genome sequences of the sources, except for those of M. barkeri and M. burtonii, are available. A candidate enzyme obtained by the ...
... Figure 2. List of candidate enzymes for polar lipid synthesis. The classifications and the sources are shown in the first and second columns, respectively. The complete genome sequences of the sources, except for those of M. barkeri and M. burtonii, are available. A candidate enzyme obtained by the ...
Enzymes - University of Lethbridge
... 1) Which compounds in the cell are metabolites in the pathway? How do we show a metabolite is part of a particular pathway? 2) How do you detect metabolites in the cell? Metabolites are more diverse than proteins/nucleic acids and often present in low concentration. 3) Have all reactions been identi ...
... 1) Which compounds in the cell are metabolites in the pathway? How do we show a metabolite is part of a particular pathway? 2) How do you detect metabolites in the cell? Metabolites are more diverse than proteins/nucleic acids and often present in low concentration. 3) Have all reactions been identi ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Orienting the net hydrophobic moment of each helix to point toward the membrane (phobic orientation): In this procedure (denoted as CoarseRot-H), the helical face with the maximum hydrophobic moment is calculated for the middle section of each helix, denoted as the hydrophobic midregion (HMR). The f ...
... Orienting the net hydrophobic moment of each helix to point toward the membrane (phobic orientation): In this procedure (denoted as CoarseRot-H), the helical face with the maximum hydrophobic moment is calculated for the middle section of each helix, denoted as the hydrophobic midregion (HMR). The f ...
Physics - BC Open Textbooks
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). ...
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). ...
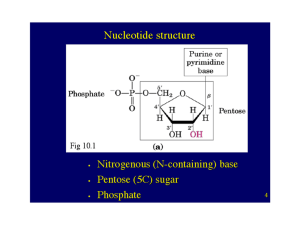
Purine metabolism - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... * when the base is purine, then the nucleoside ends in OSINE (AdenOSINE, GuanOSINE, InOSINE) when the base is pyrimidine, then the nucleoside ends in IDINE (UrIDINE, CytIDINE, ThymIDINE) ...
... * when the base is purine, then the nucleoside ends in OSINE (AdenOSINE, GuanOSINE, InOSINE) when the base is pyrimidine, then the nucleoside ends in IDINE (UrIDINE, CytIDINE, ThymIDINE) ...
Topology and Phosphorylation of Soybean Nodulin
... acids are the primary carbon source supplied to the bacteroids by the plant (see Dilworth and Glenn, 1984). The flow of these compounds is controlled by the PBM. Several carbon and amino acid transport systems have been identiffed in the PBM using isolated peribacteroid units (Day et al., 1990). Non ...
... acids are the primary carbon source supplied to the bacteroids by the plant (see Dilworth and Glenn, 1984). The flow of these compounds is controlled by the PBM. Several carbon and amino acid transport systems have been identiffed in the PBM using isolated peribacteroid units (Day et al., 1990). Non ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (or OXPHOS in short) is the metabolic pathway in which the mitochondria in cells use their structure, enzymes, and energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to reform ATP. Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, ATP is the molecule that supplies energy to metabolism. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is probably so pervasive because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen, in redox reactions. These redox reactions release energy, which is used to form ATP. In eukaryotes, these redox reactions are carried out by a series of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the cell's mitochondria, whereas, in prokaryotes, these proteins are located in the cells' intermembrane space. These linked sets of proteins are called electron transport chains. In eukaryotes, five main protein complexes are involved, whereas in prokaryotes many different enzymes are present, using a variety of electron donors and acceptors.The energy released by electrons flowing through this electron transport chain is used to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, in a process called electron transport. This generates potential energy in the form of a pH gradient and an electrical potential across this membrane. This store of energy is tapped by allowing protons to flow back across the membrane and down this gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase; this process is known as chemiosmosis. This enzyme uses this energy to generate ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP), in a phosphorylation reaction. This reaction is driven by the proton flow, which forces the rotation of a part of the enzyme; the ATP synthase is a rotary mechanical motor.Although oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to disease and, possibly, aging (senescence). The enzymes carrying out this metabolic pathway are also the target of many drugs and poisons that inhibit their activities.