An Introduction to Metabolism and Energetics
... • To remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecules and transfer them to coenzymes • In the mitochondrion • Pyruvic acid reacts with NAD and coenzyme A (CoA) • Producing 1 CO2, 1 NADH, 1 acetyl-CoA ...
... • To remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecules and transfer them to coenzymes • In the mitochondrion • Pyruvic acid reacts with NAD and coenzyme A (CoA) • Producing 1 CO2, 1 NADH, 1 acetyl-CoA ...
Introduction to Enzymes - Rose
... group of cytochrome P450 enzymes, peroxidases, and hemoglobin is synthesized from amino acids and iron ions. An enzyme lacking its cofactor, coenzyme, or prosthetic group is called an “apoenzyme”; the enzyme with its associated compound is called a “holoenzyme”. Enzymes are specific An enzyme will o ...
... group of cytochrome P450 enzymes, peroxidases, and hemoglobin is synthesized from amino acids and iron ions. An enzyme lacking its cofactor, coenzyme, or prosthetic group is called an “apoenzyme”; the enzyme with its associated compound is called a “holoenzyme”. Enzymes are specific An enzyme will o ...
emboj2009380-sup
... The Cypridina luciferin analog, a specific substrate for the superoxide (Kawano et al, 2002; Nakano, 1990) was used in the chemiluminiscence assay (CLA-CL) to determine the production of superoxide, which represents the POX cycle activity (Jiang et al, 2007). A reaction mixture of 100 µl was assembl ...
... The Cypridina luciferin analog, a specific substrate for the superoxide (Kawano et al, 2002; Nakano, 1990) was used in the chemiluminiscence assay (CLA-CL) to determine the production of superoxide, which represents the POX cycle activity (Jiang et al, 2007). A reaction mixture of 100 µl was assembl ...
Ch. 25
... • Glucose movement from blood into most other body cells occurs via facilitated diffusion transporters (Glu-T molecules). Insulin increases the insertion of Glu-T4 molecules into the plasma membranes, thus increasing the rate of facilitated diffusion of glucose. • Glucose is trapped in the cell when ...
... • Glucose movement from blood into most other body cells occurs via facilitated diffusion transporters (Glu-T molecules). Insulin increases the insertion of Glu-T4 molecules into the plasma membranes, thus increasing the rate of facilitated diffusion of glucose. • Glucose is trapped in the cell when ...
Krebs Cycle
... • Glucose movement from blood into most other body cells occurs via facilitated diffusion transporters (Gly-T molecules). Insulin increases the insertion of Gly-T molecules into the plasma membranes, thus increasing the rate of facilitated diffusion of glucose. • Glucose is trapped in the cell when ...
... • Glucose movement from blood into most other body cells occurs via facilitated diffusion transporters (Gly-T molecules). Insulin increases the insertion of Gly-T molecules into the plasma membranes, thus increasing the rate of facilitated diffusion of glucose. • Glucose is trapped in the cell when ...
Glycolysis
... It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion o ...
... It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion o ...
Photosynthesis - mleonessciencepage
... Electron acceptor donates electrons to a series of molecules located in the thylakoid allowing protons(H+) to move into the thylakoid ...
... Electron acceptor donates electrons to a series of molecules located in the thylakoid allowing protons(H+) to move into the thylakoid ...
File
... Endergonic reactions are those that store energy. During these reactions the reactant has lower free energy than the product. This is expressed by +G (positive Gibbs number). They do not happen spontaneously and need supply of energy to occur. Example would be production of ATP during aerobic respir ...
... Endergonic reactions are those that store energy. During these reactions the reactant has lower free energy than the product. This is expressed by +G (positive Gibbs number). They do not happen spontaneously and need supply of energy to occur. Example would be production of ATP during aerobic respir ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry
... IMPORTANT BIG PICTURE ITEM • Water helps with Temperature Regulation in organisms and on the earth. – Water can act as a huge heat “piggy” bank. (Such as when the sunlight hits the oceans and other water bodies and the water heats up SLOWLY as it absorbs the light energy.) – This property is made p ...
... IMPORTANT BIG PICTURE ITEM • Water helps with Temperature Regulation in organisms and on the earth. – Water can act as a huge heat “piggy” bank. (Such as when the sunlight hits the oceans and other water bodies and the water heats up SLOWLY as it absorbs the light energy.) – This property is made p ...
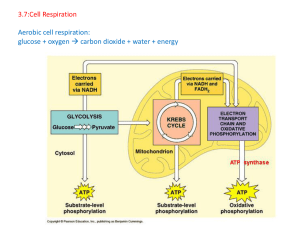
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
Chapter 14: Sports Nutrition
... Needs are easily met by a normal diet ~ sort of – Major Protein supplements are not necessary unless attempting to build muscle mass (protein shakes) – Excessive protein has not been shown to be beneficial ...
... Needs are easily met by a normal diet ~ sort of – Major Protein supplements are not necessary unless attempting to build muscle mass (protein shakes) – Excessive protein has not been shown to be beneficial ...
metabollism ch 8 a.p.
... product. (See Page 141). There are generally of two types of metabolic pathways: 1. Catabolic pathways=Metabolic pathways that release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds (e.g. cellular respiration which degrades glucose to carbon dioxide and water; provides energy for cel ...
... product. (See Page 141). There are generally of two types of metabolic pathways: 1. Catabolic pathways=Metabolic pathways that release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds (e.g. cellular respiration which degrades glucose to carbon dioxide and water; provides energy for cel ...
Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... for the reaction X→Y. The solid line in the energy diagram represents changes in energy as the product is converted to reactant under standard conditions. The dashed line shows changes observed when the same reaction takes place in the presence of a dedicated enzyme. Which equation below indicates h ...
... for the reaction X→Y. The solid line in the energy diagram represents changes in energy as the product is converted to reactant under standard conditions. The dashed line shows changes observed when the same reaction takes place in the presence of a dedicated enzyme. Which equation below indicates h ...
ENERGY
... During chemical reactions, energy can be absorbed (stored) when bonds are made and released when bonds are broken. Usually in a series of steps, yielding small amounts of energy. Enzymes regulate the rates of these reactions ATP Some energy released as heat Some energy from food stored in ATP ...
... During chemical reactions, energy can be absorbed (stored) when bonds are made and released when bonds are broken. Usually in a series of steps, yielding small amounts of energy. Enzymes regulate the rates of these reactions ATP Some energy released as heat Some energy from food stored in ATP ...
VCE PE Unit 3: Preparing Students for the End of Year Exam
... • However, which energy system/s is predominate depends upon the ATP demand of the activity. • Two factors determine ATP demand: • Exercise duration – how long the activity lasts for • Exercise intensity – how hard the exercise is ...
... • However, which energy system/s is predominate depends upon the ATP demand of the activity. • Two factors determine ATP demand: • Exercise duration – how long the activity lasts for • Exercise intensity – how hard the exercise is ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... Glucose Pyruvate Lactate 2. In absence of oxygen, NADH + H+ is not oxidized by the respiratory chain. 3. The conversion of pyruvate to lactate is the mechanism for regeneration of NAD+. 4. This helps continuity of glycolysis, as the generated NAD+ will be used once more for oxidation of another ...
... Glucose Pyruvate Lactate 2. In absence of oxygen, NADH + H+ is not oxidized by the respiratory chain. 3. The conversion of pyruvate to lactate is the mechanism for regeneration of NAD+. 4. This helps continuity of glycolysis, as the generated NAD+ will be used once more for oxidation of another ...
ENZYMES AS CATALYSTS ROLE OF COENZYMES AND METALS
... amount of free energy that provides a degree of stability to the interaction. This energy is called binding energy, GB. Binding energy is a major source of free energy used by enzymes to lower the activation energies of reactions: 1. This binding energy contributes to specificity as well as to catal ...
... amount of free energy that provides a degree of stability to the interaction. This energy is called binding energy, GB. Binding energy is a major source of free energy used by enzymes to lower the activation energies of reactions: 1. This binding energy contributes to specificity as well as to catal ...
Muscle Metabolism - Interactive Physiology
... 19. In the mitochondrion. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and 36 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. 21. a. 2 ATPs b. 36 ATPs 22. a. Creatine phosphate and anaerobic metabolism is more important when sprinting very fast for a short distance because it provides small amounts of ATP quickly, without the ...
... 19. In the mitochondrion. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and 36 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. 21. a. 2 ATPs b. 36 ATPs 22. a. Creatine phosphate and anaerobic metabolism is more important when sprinting very fast for a short distance because it provides small amounts of ATP quickly, without the ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... 18. myoglobin 19. In the mitochondrion. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and 36 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. 21. a. 2 ATPs b. 36 ATPs 22. a. Creatine phosphate and anaerobic metabolism is more important when sprinting very fast for a short distance because it provides small amounts of ATP quickl ...
... 18. myoglobin 19. In the mitochondrion. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and 36 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. 21. a. 2 ATPs b. 36 ATPs 22. a. Creatine phosphate and anaerobic metabolism is more important when sprinting very fast for a short distance because it provides small amounts of ATP quickl ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... b) Which of these reactions, 1, 2, or 3 is most likely to proceed in the forward direction in the absence of an enzyme? If you do not have enough information to answer this question, write “Can’t tell” below. Explain your answer. Reaction 1 is most likely to proceed in the forward direction in the a ...
... b) Which of these reactions, 1, 2, or 3 is most likely to proceed in the forward direction in the absence of an enzyme? If you do not have enough information to answer this question, write “Can’t tell” below. Explain your answer. Reaction 1 is most likely to proceed in the forward direction in the a ...
Cancer_JC_presentation_2009
... EGFR levels decrease upon matrix detachment and forced expression rescues downstream signaling and allows cell survival Reginato MJ, et al Nat Cell Biol (2003) ...
... EGFR levels decrease upon matrix detachment and forced expression rescues downstream signaling and allows cell survival Reginato MJ, et al Nat Cell Biol (2003) ...
Lesson Overview - Midland Park School
... Alcoholic Fermentation Yeast and a few other microorganisms use alcoholic fermentation that results in the production of ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Pyruvic acid + NADH Alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ ...
... Alcoholic Fermentation Yeast and a few other microorganisms use alcoholic fermentation that results in the production of ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Pyruvic acid + NADH Alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ ...
Structure of mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier in complex with
... ATP, the principal energy currency of the cell, fuels most biosynthetic reactions in the cytoplasm by its hydrolysis into ADP and inorganic phosphate. Because resynthesis of ATP occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, ATP is exported into the cytoplasm while ADP is imported into the matrix. The exchange ...
... ATP, the principal energy currency of the cell, fuels most biosynthetic reactions in the cytoplasm by its hydrolysis into ADP and inorganic phosphate. Because resynthesis of ATP occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, ATP is exported into the cytoplasm while ADP is imported into the matrix. The exchange ...
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Cardiac
... This is a pore with a large maximal conductance (12 000 pS) but with multiple subconductance states, and an estimated pore diameter of 2 nm (Crompton and Costi 1990), apparently concentrated at the contact sites between the mitochondrial inner and outer membranes. First discovered by the observation ...
... This is a pore with a large maximal conductance (12 000 pS) but with multiple subconductance states, and an estimated pore diameter of 2 nm (Crompton and Costi 1990), apparently concentrated at the contact sites between the mitochondrial inner and outer membranes. First discovered by the observation ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (or OXPHOS in short) is the metabolic pathway in which the mitochondria in cells use their structure, enzymes, and energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to reform ATP. Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, ATP is the molecule that supplies energy to metabolism. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is probably so pervasive because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen, in redox reactions. These redox reactions release energy, which is used to form ATP. In eukaryotes, these redox reactions are carried out by a series of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the cell's mitochondria, whereas, in prokaryotes, these proteins are located in the cells' intermembrane space. These linked sets of proteins are called electron transport chains. In eukaryotes, five main protein complexes are involved, whereas in prokaryotes many different enzymes are present, using a variety of electron donors and acceptors.The energy released by electrons flowing through this electron transport chain is used to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, in a process called electron transport. This generates potential energy in the form of a pH gradient and an electrical potential across this membrane. This store of energy is tapped by allowing protons to flow back across the membrane and down this gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase; this process is known as chemiosmosis. This enzyme uses this energy to generate ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP), in a phosphorylation reaction. This reaction is driven by the proton flow, which forces the rotation of a part of the enzyme; the ATP synthase is a rotary mechanical motor.Although oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to disease and, possibly, aging (senescence). The enzymes carrying out this metabolic pathway are also the target of many drugs and poisons that inhibit their activities.