Acid - Perkins Science
... Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same atoms in the same sequence, but differ from each other in the way their atoms are arranged three-dimensionally in space. ...
... Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same atoms in the same sequence, but differ from each other in the way their atoms are arranged three-dimensionally in space. ...
ALD
... peroxisomes lead to the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) in tissues of the body, especially the brain and the adrenal glands. Ultimately the myelin sheath surrounding the nerves is destroyed causing neurologic problems, and the adrenal gland malfunction causes Addison’s Disease. W ...
... peroxisomes lead to the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) in tissues of the body, especially the brain and the adrenal glands. Ultimately the myelin sheath surrounding the nerves is destroyed causing neurologic problems, and the adrenal gland malfunction causes Addison’s Disease. W ...
Origin of L-Theanine in the formula LTO3
... L-Theanine is obtained by various processes of fermentation of plants in the laboratory; this is where we get the vegetable source. Now, which kinds of plants are used, that remains a fabrication secret, and there is no reason why anyone needs to return to level of protein and even less on the level ...
... L-Theanine is obtained by various processes of fermentation of plants in the laboratory; this is where we get the vegetable source. Now, which kinds of plants are used, that remains a fabrication secret, and there is no reason why anyone needs to return to level of protein and even less on the level ...
Carbon (Organic) Chemistry
... Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 They are the main source of energy for living things. They have structural purposes in plants and animals Monomers are monosaccharides, Polymers are polysaccharides ...
... Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 They are the main source of energy for living things. They have structural purposes in plants and animals Monomers are monosaccharides, Polymers are polysaccharides ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
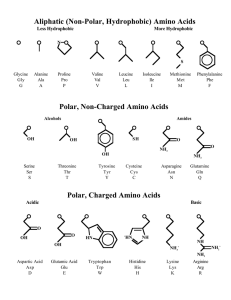
Amino Acid Answers: 1. Determine if the amino acids shown are of
... Compounds containing the carboxylic acid functional group in their side chain are acidic amino acids. Compounds containing amines in their side chair are basic amino acids. Those side chains containing alkyl groups, alcohols, or even sulfur-containing groups are neutral. ...
... Compounds containing the carboxylic acid functional group in their side chain are acidic amino acids. Compounds containing amines in their side chair are basic amino acids. Those side chains containing alkyl groups, alcohols, or even sulfur-containing groups are neutral. ...
Ch 19 reading guide
... transformed into the high energy bond ____________________, which leads to phosphorylation of the enzyme on a ____________ residue, then finally to formation of ___________. 12. Draw the three-reaction transformation of succinate to oxaloacetate. (You need to know this basic pathway well because it ...
... transformed into the high energy bond ____________________, which leads to phosphorylation of the enzyme on a ____________ residue, then finally to formation of ___________. 12. Draw the three-reaction transformation of succinate to oxaloacetate. (You need to know this basic pathway well because it ...
practice exam
... E. is favored when the citric acid cycle is inhibited. 3. ______ Which statement concerning fatty acid synthesis is false? A. Fatty acid synthesis from acetyl CoA requires ATP hydrolysis. B. Fatty acid synthesis requires acetyl CoA to leave the matrix in the form of citrate. C. Fatty acid synthesis ...
... E. is favored when the citric acid cycle is inhibited. 3. ______ Which statement concerning fatty acid synthesis is false? A. Fatty acid synthesis from acetyl CoA requires ATP hydrolysis. B. Fatty acid synthesis requires acetyl CoA to leave the matrix in the form of citrate. C. Fatty acid synthesis ...
Multiple Choice Questions - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... 20. The energy stored in 36 ATP molecules produced by aerobic respiration is 39 percent of the energy available in a six-carbon glucose and the other 61% of the glucose bond energy is lost. The respiration of an 18-carbon fatty acid produces 216 ATP. We can expect that A) the degradation of a fatty ...
... 20. The energy stored in 36 ATP molecules produced by aerobic respiration is 39 percent of the energy available in a six-carbon glucose and the other 61% of the glucose bond energy is lost. The respiration of an 18-carbon fatty acid produces 216 ATP. We can expect that A) the degradation of a fatty ...
levels of the neurotransmitter GABA, which
... ability to restore glutathione levels. Lipoic acid can block damage caused by oxidative molecules and can improve mitochondrial function. Recent research has revealed that lipoic acid can improve memory and protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction. L-phenylalanine: L-Phenylalanine is best k ...
... ability to restore glutathione levels. Lipoic acid can block damage caused by oxidative molecules and can improve mitochondrial function. Recent research has revealed that lipoic acid can improve memory and protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction. L-phenylalanine: L-Phenylalanine is best k ...
hapch2updated2013final
... made up of monomer of amino acids;>50% organic matter in the body,contain C,H,O,and N,~ 20 amino acids,polypeptide is another word for protein (containing fewer than 50 amino acids )and peptide bonds join amino acids-made of an amine (NH2) grp and an acid(COOH) grp,differ in R-grp – Fibrous(or struc ...
... made up of monomer of amino acids;>50% organic matter in the body,contain C,H,O,and N,~ 20 amino acids,polypeptide is another word for protein (containing fewer than 50 amino acids )and peptide bonds join amino acids-made of an amine (NH2) grp and an acid(COOH) grp,differ in R-grp – Fibrous(or struc ...
ReviewExamIII
... What are the two parts of photosynthesis called (note: the light independent reactions are sometimes called the Calvin Cycle)? What is the function of NAD+ and FAD+ in cellular respiration? Why do glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle stop running when oxygen is lacking? How does fermentation allow glycoly ...
... What are the two parts of photosynthesis called (note: the light independent reactions are sometimes called the Calvin Cycle)? What is the function of NAD+ and FAD+ in cellular respiration? Why do glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle stop running when oxygen is lacking? How does fermentation allow glycoly ...
Protein mteabolism L..
... synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immature RBCs -called megaloblasts- in blood and B.M.). Folic acid is needed for ...
... synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immature RBCs -called megaloblasts- in blood and B.M.). Folic acid is needed for ...
Midterm IV Key
... D. Denatures the primary sequence of the hair protein E. Covalently Bonds additional R-groups 14. In the pentapeptide, Gly-Cys-Ala-Val-Leu, the C-terminal amino acid is ______. A. Ala B. Gly C. Leu D. Val E. None of the above 15. What are the repeating units in a protein like keratin? A. monosachari ...
... D. Denatures the primary sequence of the hair protein E. Covalently Bonds additional R-groups 14. In the pentapeptide, Gly-Cys-Ala-Val-Leu, the C-terminal amino acid is ______. A. Ala B. Gly C. Leu D. Val E. None of the above 15. What are the repeating units in a protein like keratin? A. monosachari ...
File - Craftsbury Science
... Chapter Main Ideas: 1. Carbon’s unique properties as an element make it fundamental in constructing important molecules. 2. Polymerization is the chemical act of building larger molecules of monomers. 3. Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are built from various monomers, which help determine macrom ...
... Chapter Main Ideas: 1. Carbon’s unique properties as an element make it fundamental in constructing important molecules. 2. Polymerization is the chemical act of building larger molecules of monomers. 3. Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are built from various monomers, which help determine macrom ...
BSc in Applied Biotechnology 3 BO0045 ‑ MICROBIOLOGY
... dehydrogenase, followed by the oxidation of 6-phosphoglucono-d-lactone to pentose ribulose 5-phosphate and CO2. • NADPH is produced during these oxidations. The capability of this oxidative metabolic system to bypass glycolysis explains the term shunt. • All cyanobacteria, Acetobacter suboxydans, an ...
... dehydrogenase, followed by the oxidation of 6-phosphoglucono-d-lactone to pentose ribulose 5-phosphate and CO2. • NADPH is produced during these oxidations. The capability of this oxidative metabolic system to bypass glycolysis explains the term shunt. • All cyanobacteria, Acetobacter suboxydans, an ...
ORGANIC ACIDS – Citric Acid Cycle (urine)
... The organic acid test is a nutritional test providing insights into the body's cellular metabolic processes. Urinary organic acids derived from the metabolic conversion of dietary proteins, fats and carbohydrates, in addition to compounds of bacterial origin, provide a unique chemical profile of a p ...
... The organic acid test is a nutritional test providing insights into the body's cellular metabolic processes. Urinary organic acids derived from the metabolic conversion of dietary proteins, fats and carbohydrates, in addition to compounds of bacterial origin, provide a unique chemical profile of a p ...
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I did come up with some nonsense mnemonics on the one-letter abbreviations which helped me to be able to reconstruct the chart: (No, they make no sense. They’re not supposed to. If they made sense, they wouldn’t be mnemonics, eh?) ...
... the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I did come up with some nonsense mnemonics on the one-letter abbreviations which helped me to be able to reconstruct the chart: (No, they make no sense. They’re not supposed to. If they made sense, they wouldn’t be mnemonics, eh?) ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 9. _________________ build living tissue and help in chemical reactions. 10. ________________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called ___________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they ...
... 9. _________________ build living tissue and help in chemical reactions. 10. ________________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called ___________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they ...
Document
... inhibits the hepatocyte surface expression of betachain adenosine triphosphate synthase (a recently ...
... inhibits the hepatocyte surface expression of betachain adenosine triphosphate synthase (a recently ...
D2145 Systems Biology
... Section B comprises short answer questions – please answer all questions, writing your answer clearly in the space provided in this ...
... Section B comprises short answer questions – please answer all questions, writing your answer clearly in the space provided in this ...
chapter 5 large biological molecules
... o Starch – storage form for plants made entirely of glucose monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulos ...
... o Starch – storage form for plants made entirely of glucose monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulos ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.