"thinking acids" handout
... the indicator, the pH will be low at the beginning, so the phenolphthalein will be mostly in the un-ionized or “protonated” “acid” form (we’ll refer to as HIn). As the pH increases over the course of the titration, the pH will eventually get close to the pKa of phenolphthalein, and when pH = pKa, th ...
... the indicator, the pH will be low at the beginning, so the phenolphthalein will be mostly in the un-ionized or “protonated” “acid” form (we’ll refer to as HIn). As the pH increases over the course of the titration, the pH will eventually get close to the pKa of phenolphthalein, and when pH = pKa, th ...
Chem 410 Chapter 11: Polyprotic Acids and Bases Part 1 How
... group (NH2) and the carboxylic acid group. So the carboxylic acid proton is deprotonated while the amine group is protonated as NH3+. This is shown in the figure on the right. The result is a dipolar compound ( one + and one – charge) which is overall a neutral compound. This type of compound is cal ...
... group (NH2) and the carboxylic acid group. So the carboxylic acid proton is deprotonated while the amine group is protonated as NH3+. This is shown in the figure on the right. The result is a dipolar compound ( one + and one – charge) which is overall a neutral compound. This type of compound is cal ...
Cellular Respiration Notes
... • Final Products are: – 2 Pyruvic Acid (C3H4O3) • Compare to original glucose - C6H12O6 ...
... • Final Products are: – 2 Pyruvic Acid (C3H4O3) • Compare to original glucose - C6H12O6 ...
carbonyl group
... Like the aldehydes the Functional group is the carbonyl group C=O Contains an alkyl group on either side of the C=O – In aldehydes one side is an alkyl group the other is H ...
... Like the aldehydes the Functional group is the carbonyl group C=O Contains an alkyl group on either side of the C=O – In aldehydes one side is an alkyl group the other is H ...
BIOS 1700 Dr. Tanda Week 6, Session 3 1. What two subunits made
... 2. This is a hypothetical situation. There is a mouse with a mutation that makes the F0 subunit of ATP synthase less effective. In other words, the F0 subunit let protons go through without efficiently turning its “fan.” This means the conversion of potential energy in the proton gradient across the ...
... 2. This is a hypothetical situation. There is a mouse with a mutation that makes the F0 subunit of ATP synthase less effective. In other words, the F0 subunit let protons go through without efficiently turning its “fan.” This means the conversion of potential energy in the proton gradient across the ...
Liver Function - Wk 1-2
... In order for cells to function normally, their blood glucose levels need to be kept relatively constant (4-5 mmol). The pancreas plays a minor role in regulating blood sugar levels via the production of the hormones Insulin and Glucagon. Insulin is an anabolic hormone that promotes the storage and ...
... In order for cells to function normally, their blood glucose levels need to be kept relatively constant (4-5 mmol). The pancreas plays a minor role in regulating blood sugar levels via the production of the hormones Insulin and Glucagon. Insulin is an anabolic hormone that promotes the storage and ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... pyruvate O2 c) location in cell cytosol mitochondrion d) final products lactic acid, NAD+, EtOH, ATP CO2, H2O, ATP 19. When you exhale, your breath contains carbon dioxide. Where did this come from? 20. Hard (or distilled) liquor is available at concentrations of up to 75% alcohol but the maximum al ...
... pyruvate O2 c) location in cell cytosol mitochondrion d) final products lactic acid, NAD+, EtOH, ATP CO2, H2O, ATP 19. When you exhale, your breath contains carbon dioxide. Where did this come from? 20. Hard (or distilled) liquor is available at concentrations of up to 75% alcohol but the maximum al ...
02 B organic chemistry - macromolecules
... indigestible cellulose is… (can you see it?) [Only certain bacteria make the enzymes to digest cellulose. Generally, any animal living off grass or wood has these specific bacteria in their guts to break the cellulose into digestible disaccharides.] ...
... indigestible cellulose is… (can you see it?) [Only certain bacteria make the enzymes to digest cellulose. Generally, any animal living off grass or wood has these specific bacteria in their guts to break the cellulose into digestible disaccharides.] ...
What is an acid or a base
... ion of the base unite to form water. Acids ___________________________. Even gold, the least active metal, is attacked by an acid, a mixture of acids called 'aqua regia,' or 'royal liquid.' When an acid reacts with a metal, it produces a compound with the cation of the metal and the anion of the aci ...
... ion of the base unite to form water. Acids ___________________________. Even gold, the least active metal, is attacked by an acid, a mixture of acids called 'aqua regia,' or 'royal liquid.' When an acid reacts with a metal, it produces a compound with the cation of the metal and the anion of the aci ...
PBI 3 Student Handout 2
... In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map which contains the nucleotide sequence of the region of the human genome that contains the β-globin gene. In addition to the nucleotide sequence of both strands of DNA, you will find three possible amino acid sequences encoded in th ...
... In this exercise, you are given a model of DNA. This model is a Map which contains the nucleotide sequence of the region of the human genome that contains the β-globin gene. In addition to the nucleotide sequence of both strands of DNA, you will find three possible amino acid sequences encoded in th ...
Dietary supplementation of coated butyrate in healthy dogs: effect on
... In piglets, the addition of organic acids (1.8% K-diformate) affected the intestinal flora (Canibe et al., 2001). Similarly, the results of the present study suggest a change in intestinal flora in dogs: the reduction of the bacterial protein suggests a reduction in total bacterial number although, ...
... In piglets, the addition of organic acids (1.8% K-diformate) affected the intestinal flora (Canibe et al., 2001). Similarly, the results of the present study suggest a change in intestinal flora in dogs: the reduction of the bacterial protein suggests a reduction in total bacterial number although, ...
Objectives_Set1
... Identify the enzymes of glycolysis that catalyze steps in which ATP is used or formed, and in which NADH is formed. ...
... Identify the enzymes of glycolysis that catalyze steps in which ATP is used or formed, and in which NADH is formed. ...
Energy Releasing Pathway
... How many CO2 are liberated per acetic acid? Per glucose? As H+’s are removed then a P jumps on only to be removed to form ATP. ...
... How many CO2 are liberated per acetic acid? Per glucose? As H+’s are removed then a P jumps on only to be removed to form ATP. ...
CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
... Understand the structural features that affect relative reactivity in acyl transfer reactions (interconversion of carboxylic acid derivatives via addn- elimination reactions) Predict the missing product and/or reactant in a relevant chemical reaction involving carboxylic acids and carboxylic aci ...
... Understand the structural features that affect relative reactivity in acyl transfer reactions (interconversion of carboxylic acid derivatives via addn- elimination reactions) Predict the missing product and/or reactant in a relevant chemical reaction involving carboxylic acids and carboxylic aci ...
Anaerobic Respiration - County Central High School
... VO2 max values vary between individuals and although you can increase yours through some training, it will decrease as you get older Even though VO2 max can be increased through exercise, lactic acid is also building up at an increased rate which can limit the amount of training and exercise an indi ...
... VO2 max values vary between individuals and although you can increase yours through some training, it will decrease as you get older Even though VO2 max can be increased through exercise, lactic acid is also building up at an increased rate which can limit the amount of training and exercise an indi ...
M. PHARM. 1. Sildenafil is used in the following disorder: A) Systolic
... A) Mevalonic acid and isopentenyl pyrophosphate B) Mevalonic acid and aldosterone C) Isoprenaline and aldosterone D) Isoprenaline and isopentenyl phosphate 13. Which suppository should be moistened with water before insertion A) Hydrogenated vegetable oil ...
... A) Mevalonic acid and isopentenyl pyrophosphate B) Mevalonic acid and aldosterone C) Isoprenaline and aldosterone D) Isoprenaline and isopentenyl phosphate 13. Which suppository should be moistened with water before insertion A) Hydrogenated vegetable oil ...
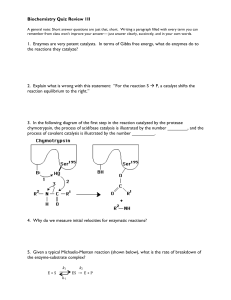
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
acetyl CoA
... • DNP: uncoupler (makes mitochondrial membrane leaky to H+ ions) that results in enormous increase in metabolism and therefore increase in body temperature that can be extreme enough to be fatal • Oligomycin (antibiotic): blocks flow of H+ through ATP synthase • Note that toxins can be useful as pes ...
... • DNP: uncoupler (makes mitochondrial membrane leaky to H+ ions) that results in enormous increase in metabolism and therefore increase in body temperature that can be extreme enough to be fatal • Oligomycin (antibiotic): blocks flow of H+ through ATP synthase • Note that toxins can be useful as pes ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... CoA) produces NADH +H Oxidation of acetyl CoA by the common metabolic ...
... CoA) produces NADH +H Oxidation of acetyl CoA by the common metabolic ...
Fatty acid synthesis
... high when there is adequate acetyl-CoA entering Krebs Cycle. Excess acetyl-CoA is then converted via malonyl-CoA to fatty acids for storage. ...
... high when there is adequate acetyl-CoA entering Krebs Cycle. Excess acetyl-CoA is then converted via malonyl-CoA to fatty acids for storage. ...
Slide 1
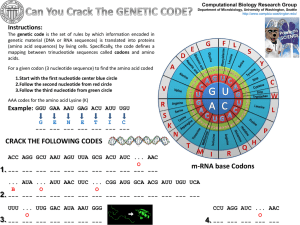
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.