Slide 1
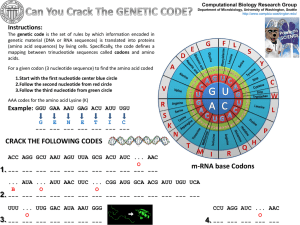
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
Metabolism08
... Protein is only used for energy in the absence of carbohydrate or fat Carbon skeletons: are formed by the deamination of amino acids and can enter the metabolic pathways at several points ...
... Protein is only used for energy in the absence of carbohydrate or fat Carbon skeletons: are formed by the deamination of amino acids and can enter the metabolic pathways at several points ...
Renal Physiology 9 (Acid Base 1)
... BASES (a.k.a. alkalis) – ions or molecules that can ACCEPT H+ (e.g., HCO3- + H+ H2CO3). • STRONG bases – dissociate easily in H2O and quickly bind H+. • WEAK bases – accept H+ more slowly (e.g., HCO3- and NH3) Proteins in body function as weak bases as some constituent AMINO ACIDS have net negat ...
... BASES (a.k.a. alkalis) – ions or molecules that can ACCEPT H+ (e.g., HCO3- + H+ H2CO3). • STRONG bases – dissociate easily in H2O and quickly bind H+. • WEAK bases – accept H+ more slowly (e.g., HCO3- and NH3) Proteins in body function as weak bases as some constituent AMINO ACIDS have net negat ...
Dear Notetaker:
... i. Stroma needs hydration- lots of water—vitamin C is water soluble 6. Cytosolic acetyl CoA comes from: a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understa ...
... i. Stroma needs hydration- lots of water—vitamin C is water soluble 6. Cytosolic acetyl CoA comes from: a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understa ...
chang-hung-chou-china-medical-university-taiwan
... Lung cancer and Apoptosis Lung cancer is the second most frequent type of cancer Nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for ∼80% of primary lung cancers Apoptosis, a major form of cell death, is regulated ...
... Lung cancer and Apoptosis Lung cancer is the second most frequent type of cancer Nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for ∼80% of primary lung cancers Apoptosis, a major form of cell death, is regulated ...
NC-Retinoic acid-2013-06-28
... Based on the current information available to the Office of Controlled Substances, it appears that the above substance is: Controlled Not Controlled ...
... Based on the current information available to the Office of Controlled Substances, it appears that the above substance is: Controlled Not Controlled ...
The Liver cont…..
... • Transamination (or aminotransfer) is the reaction between an amino acid and an alphaketo acid. • The amino group is transferred from the former to the latter; this results in the amino acid being converted to the corresponding α-keto acid, while the reactant α-keto acid is converted to the corresp ...
... • Transamination (or aminotransfer) is the reaction between an amino acid and an alphaketo acid. • The amino group is transferred from the former to the latter; this results in the amino acid being converted to the corresponding α-keto acid, while the reactant α-keto acid is converted to the corresp ...
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... hormones are made a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all j ...
... hormones are made a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all j ...
Ketogenesis (Biosynthesis of ketone bodies)
... Utilization of ketone bodies by peripheral tissues • Liver constantly produces low levels of ketone bodies, but their production becomes much more significant during starvation, when ketone bodies are needed to provide energy to the peripheral tissues. • Liver actively produces ketone bodies, but i ...
... Utilization of ketone bodies by peripheral tissues • Liver constantly produces low levels of ketone bodies, but their production becomes much more significant during starvation, when ketone bodies are needed to provide energy to the peripheral tissues. • Liver actively produces ketone bodies, but i ...
(Acid Base 1).
... pH Scale (Sørensen, 1909) pH INVERSELY related to [H+], i.e. as [H+] ↑, pH falls – acidosis (below 7.35) as [H+] ↓, pH increases – alkalosis (above 7.45) ...
... pH Scale (Sørensen, 1909) pH INVERSELY related to [H+], i.e. as [H+] ↑, pH falls – acidosis (below 7.35) as [H+] ↓, pH increases – alkalosis (above 7.45) ...
ncibi-rcmi-2010-workshop
... Metabolic Assessment. VO2peak, resting metabolic rate (RMR) and R/Q measurement. Oral glucose tolerance tests (for those without a diagnosis of diabetes), Total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides, free fatty acid, insulin (at 0 and 30 and 120 minutes of oGTT), leptin, adiponectin, C-Reactive Prote ...
... Metabolic Assessment. VO2peak, resting metabolic rate (RMR) and R/Q measurement. Oral glucose tolerance tests (for those without a diagnosis of diabetes), Total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides, free fatty acid, insulin (at 0 and 30 and 120 minutes of oGTT), leptin, adiponectin, C-Reactive Prote ...
File
... Name: Period: (1) Explain how monomers are related to polymers. (2) Explain the process that occurs when polymers are broken down into monomers, like for example when carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars. ...
... Name: Period: (1) Explain how monomers are related to polymers. (2) Explain the process that occurs when polymers are broken down into monomers, like for example when carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars. ...
Esterification Lab - mrs. leinweber`s wiki
... 1. Set up a 250mL beaker on a hot plate, filling the beaker about 2/3 full of water. 2. Use a clamp to support a 18x150mm test tube. Lower the test tube into the water bath. 3. Check the odor of acetic acid and ethanol. WAFT! DON’T SNORT! 4. Put about 2mL of acetic acid into the supported test tube. ...
... 1. Set up a 250mL beaker on a hot plate, filling the beaker about 2/3 full of water. 2. Use a clamp to support a 18x150mm test tube. Lower the test tube into the water bath. 3. Check the odor of acetic acid and ethanol. WAFT! DON’T SNORT! 4. Put about 2mL of acetic acid into the supported test tube. ...
Pyruvate to ACETYL coA CC
... Beta oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of Acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria to generate Acetyl-CoA, a. Activation of fatty acids in the cytosol b. Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria a. Fatty acids are transported across the outer mitochondrial membr ...
... Beta oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of Acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria to generate Acetyl-CoA, a. Activation of fatty acids in the cytosol b. Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria a. Fatty acids are transported across the outer mitochondrial membr ...
SYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACID Acetyl
... Double bonds are introduced into long-chain acyl-CoAs through an electron-transfer process coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen Reaction catalyzed by a complex of membrane-bound enzymes Double bonds inserted such that the new double bond is three carbons closer to the CoA group, and never be ...
... Double bonds are introduced into long-chain acyl-CoAs through an electron-transfer process coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen Reaction catalyzed by a complex of membrane-bound enzymes Double bonds inserted such that the new double bond is three carbons closer to the CoA group, and never be ...
NAME: Chemistry 232 Analytical Chemistry
... 3. Back on the last test you had a problem with where you were trying to calculate the concentrations of a mixture of CaCl2 and 0.5M phosphoric acid at pH 8. This was a complicated problem because Phosphoric acid is a multiprotic acid (H3A) with Ka’s of 7.11x10-3, 6.32x10-8 and 7.1x10-13. Today you ...
... 3. Back on the last test you had a problem with where you were trying to calculate the concentrations of a mixture of CaCl2 and 0.5M phosphoric acid at pH 8. This was a complicated problem because Phosphoric acid is a multiprotic acid (H3A) with Ka’s of 7.11x10-3, 6.32x10-8 and 7.1x10-13. Today you ...
Does System xc- Increase Excitotoxicity?
... Cystine and Quisqualic Acid • Cystine is an amino acid. • Cystine is transported by the amino acid transport system called system xc- in exchange for glutamate which causes overexcitement of neurons and cell death. • Quisqualic acid is a neurotoxin, found in certain plants. • Quisqualic acid or Qui ...
... Cystine and Quisqualic Acid • Cystine is an amino acid. • Cystine is transported by the amino acid transport system called system xc- in exchange for glutamate which causes overexcitement of neurons and cell death. • Quisqualic acid is a neurotoxin, found in certain plants. • Quisqualic acid or Qui ...
Metabolism Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions within an
... isolated from RBCs care must be taken to minimize the opportunities for hemolysis. Hemolysis may arise because of. ...
... isolated from RBCs care must be taken to minimize the opportunities for hemolysis. Hemolysis may arise because of. ...
Water soluble vitamins
... and protein synthesis, inhibition of growth and cell division Symptoms: -hyperchromic megaloblastic anemia -leucopenia -thrombocytopenia -glossitis, conjuctivitis, gastritis (disorders of epithelium proliferation) -growth inhibition -impairment of the wound healing -immunodeficiency ...
... and protein synthesis, inhibition of growth and cell division Symptoms: -hyperchromic megaloblastic anemia -leucopenia -thrombocytopenia -glossitis, conjuctivitis, gastritis (disorders of epithelium proliferation) -growth inhibition -impairment of the wound healing -immunodeficiency ...
Macromolecules in Organisms
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... All except glycine are optically active, and normally only one of the enantiomers is found in nature. If the side-chain has another functional group, like cysteine above, it may be possible to cross-link a protein chain, tying the molecule up into a specific three-dimensional shape. An amino acid re ...
... All except glycine are optically active, and normally only one of the enantiomers is found in nature. If the side-chain has another functional group, like cysteine above, it may be possible to cross-link a protein chain, tying the molecule up into a specific three-dimensional shape. An amino acid re ...
Phytochemistry 1
... -Acetylenic compounds are basically alkyne compounds that have C-C triple bonds in their structures. -Polyacetylene term is often used interchangeably to describe this class of natural products, although they are not polymers and many precursors and metabolites contain only a single acetylenic bond. ...
... -Acetylenic compounds are basically alkyne compounds that have C-C triple bonds in their structures. -Polyacetylene term is often used interchangeably to describe this class of natural products, although they are not polymers and many precursors and metabolites contain only a single acetylenic bond. ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.