CH395 G Exam 3 Fall 2004 - Multiple Choice 1. Which of the
... b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blocking proton translocation. d. binding to the T state of F1 of ATP synthase thereby inhibiting the conformational change necessary to form ATP. e. stim ...
... b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blocking proton translocation. d. binding to the T state of F1 of ATP synthase thereby inhibiting the conformational change necessary to form ATP. e. stim ...
Thoughts on Vitamin A, IBD and PSC
... (RXR) heterodimer in epithelial cells…... Here, we show that several types of RA, including atRA, promote the barrier function of epithelial TJs. Conversely, RA depletion in the cells by overexpressing CYP26s, cytochrome P450 enzymes specifically involved in the metabolic inactivation of RAs, induce ...
... (RXR) heterodimer in epithelial cells…... Here, we show that several types of RA, including atRA, promote the barrier function of epithelial TJs. Conversely, RA depletion in the cells by overexpressing CYP26s, cytochrome P450 enzymes specifically involved in the metabolic inactivation of RAs, induce ...
Types of Protein Hydrolysis
... mixture of min of 3 similar proteins (-, - & casein) 80% of protein present in milk contains the essential amino acids (V P H MATILL) isolated at isoelectric pH (pI), least soluble (isoelectric precipitation) accomplished by addition of dilute acid net charge at pI=0 ...
... mixture of min of 3 similar proteins (-, - & casein) 80% of protein present in milk contains the essential amino acids (V P H MATILL) isolated at isoelectric pH (pI), least soluble (isoelectric precipitation) accomplished by addition of dilute acid net charge at pI=0 ...
Metabolism without Oxygen
... on exposure. It should be noted that all forms of fermentation, except lactic acid fermentation, produce gas. The production of particular types of gas is used as an indicator of the fermentation of specific carbohydrates, which plays a role in the laboratory identification of the bacteria. Various ...
... on exposure. It should be noted that all forms of fermentation, except lactic acid fermentation, produce gas. The production of particular types of gas is used as an indicator of the fermentation of specific carbohydrates, which plays a role in the laboratory identification of the bacteria. Various ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain (highly reduced) and a carboxylic acid polar gro ...
... Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain (highly reduced) and a carboxylic acid polar gro ...
Teacher`s Name: ___Julie
... I can review basic chemistry properties and characteristics: Atoms and subatomic particles; ions, bonding, chemical formulas, water, and pH scale. I can explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. I ca ...
... I can review basic chemistry properties and characteristics: Atoms and subatomic particles; ions, bonding, chemical formulas, water, and pH scale. I can explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. I ca ...
lec---10
... • These components include a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a variable R group (or side chain). General Formula of the ...
... • These components include a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a variable R group (or side chain). General Formula of the ...
doc
... Plants usually make more organic molecules than they need for fuel. This surplus provides material that can be ...
... Plants usually make more organic molecules than they need for fuel. This surplus provides material that can be ...
Study Guide KEY Exam III F 2012
... Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). Secondary structure is maintained by hydrogen bonds formed between a hydrogen (donor) attached to the nitrogen in the b ...
... Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). Secondary structure is maintained by hydrogen bonds formed between a hydrogen (donor) attached to the nitrogen in the b ...
Unit 2 revision ppt - Calderglen High School
... • The calcium salt of a sulphonate is soluble in water unlike the calcium salts of the carboxylate. • Hence no scum is formed ...
... • The calcium salt of a sulphonate is soluble in water unlike the calcium salts of the carboxylate. • Hence no scum is formed ...
THEORY AND PRACTICE OF AEROSOL SCIENCE
... Resarch Station, Station Nord (Feb - Aug 2015), northern Greenland. Both campaigns utilized an Atmospheric Pressure Interface – mass spectrometer (APi-TOF) for measuring the chemical composition of ion clusters and a nitrate ion based Chemical Ionization APi-TOF mass spectrometer for measuring the c ...
... Resarch Station, Station Nord (Feb - Aug 2015), northern Greenland. Both campaigns utilized an Atmospheric Pressure Interface – mass spectrometer (APi-TOF) for measuring the chemical composition of ion clusters and a nitrate ion based Chemical Ionization APi-TOF mass spectrometer for measuring the c ...
chapter-6-rev
... Why is it important to regenerate NAD+ molecules during fermentation? __________ is the only state in glucose metabolism that does not require oxygen to proceed. Two possible end products of fermentation are __________ as is produced by our muscle cell under anaerobic conditions and __________ by ye ...
... Why is it important to regenerate NAD+ molecules during fermentation? __________ is the only state in glucose metabolism that does not require oxygen to proceed. Two possible end products of fermentation are __________ as is produced by our muscle cell under anaerobic conditions and __________ by ye ...
Teacher`s Name: ___Julie
... I can review basic chemistry properties and characteristics: Atoms and subatomic particles; ions, bonding, chemical formulas, water, and pH scale. I can explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. I ca ...
... I can review basic chemistry properties and characteristics: Atoms and subatomic particles; ions, bonding, chemical formulas, water, and pH scale. I can explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. I ca ...
Photosynthesis & Respiration
... Light Independent Cycle (Calvin) Uses enzymes to speed the reaction to use CO2, ATP, and NADPH to produce high E compounds that can be stored for a long time (Glucose) Intermediates are important to cellular metabolism ...
... Light Independent Cycle (Calvin) Uses enzymes to speed the reaction to use CO2, ATP, and NADPH to produce high E compounds that can be stored for a long time (Glucose) Intermediates are important to cellular metabolism ...
IIIb
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
The Neuroscience of Psychiatry
... • Actions mediated mostly at ligand-gated ion channel type receptors – rapid, short-lasting alterations in membrane potential ...
... • Actions mediated mostly at ligand-gated ion channel type receptors – rapid, short-lasting alterations in membrane potential ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 1 yellow or green sphere Place the two carbons in a chain with the nitrogen [blue] Place an oxygen and a hydroxyl group on the end carbon Place two hydrogens on the nitrogen Place a hydrogen and the yellow or green sphere on the central carbon You have made an amino acid ...
... 1 yellow or green sphere Place the two carbons in a chain with the nitrogen [blue] Place an oxygen and a hydroxyl group on the end carbon Place two hydrogens on the nitrogen Place a hydrogen and the yellow or green sphere on the central carbon You have made an amino acid ...
Homework
... California State Polytechnic University, Pomona Organic Chemistry CHM 201 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey Acid Strength Homework Name:______________________________________ Section: ____________ (day/time) For each of the following pairs compounds, determine which is the stronger acid (A or B) WITHOUT referri ...
... California State Polytechnic University, Pomona Organic Chemistry CHM 201 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey Acid Strength Homework Name:______________________________________ Section: ____________ (day/time) For each of the following pairs compounds, determine which is the stronger acid (A or B) WITHOUT referri ...
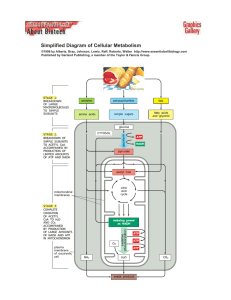
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Unit 2A Macromolecule PPT
... – Starch- Polysaccharide, basically same as glycogen but IN PLANTS, stores energy (glucose) *polymer • i.e. potato (just a big wad of sugar) – Cellulose- polysaccharide in plants as well, used for STRUCTURE in cell walls *polymer ...
... – Starch- Polysaccharide, basically same as glycogen but IN PLANTS, stores energy (glucose) *polymer • i.e. potato (just a big wad of sugar) – Cellulose- polysaccharide in plants as well, used for STRUCTURE in cell walls *polymer ...
D. Transfer of activated acetaldehyde to
... _______________________. Section III: Matching. Each term on the left has a phrase or term on the right which best describes or matches it. Place the letter of the term/phrase on the right in the blank before the term on the left that it best matches. Only one letter is appropriate in the blank. Not ...
... _______________________. Section III: Matching. Each term on the left has a phrase or term on the right which best describes or matches it. Place the letter of the term/phrase on the right in the blank before the term on the left that it best matches. Only one letter is appropriate in the blank. Not ...
PDF UNIT 2A Macromolecule PPT
... – Starch- Polysaccharide, basically same as glycogen but IN PLANTS, stores energy (glucose) *polymer • i.e. potato (just a big wad of sugar) – Cellulose- polysaccharide in plants as well, used for STRUCTURE in cell walls *polymer ...
... – Starch- Polysaccharide, basically same as glycogen but IN PLANTS, stores energy (glucose) *polymer • i.e. potato (just a big wad of sugar) – Cellulose- polysaccharide in plants as well, used for STRUCTURE in cell walls *polymer ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.