use cellular respiration
... • Happens when yeast makes bread dough rise • CO2 bubbles make air spaces in bread ...
... • Happens when yeast makes bread dough rise • CO2 bubbles make air spaces in bread ...
36. ______ layers of ______ make up the cell membrane.
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
Biochemistry - DENTISTRY 2012
... Slide # 15 under normal conditions, palmitic acid after several cycles of beta oxidation will give acetyl coA. The following step (normally) for FA oxidation, is the for acetyl coA to enter the citric acid cycle by oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is hence required as a catalyst. does the citric acid cycl ...
... Slide # 15 under normal conditions, palmitic acid after several cycles of beta oxidation will give acetyl coA. The following step (normally) for FA oxidation, is the for acetyl coA to enter the citric acid cycle by oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is hence required as a catalyst. does the citric acid cycl ...
effect of glucose concentration in the growth medium upon neutral
... (Stadtman, 1963) or glutamate (Buckel and Barker, 1974). However, acetic acid can also arise from glucose via pyruvate. Similarly, butyric acid can readily be formed from acetyl-CoA derived from pyruvate. Two acetyl residues are condensed to yield acetoacetyl-CoA which undergoes /?-reduction to buty ...
... (Stadtman, 1963) or glutamate (Buckel and Barker, 1974). However, acetic acid can also arise from glucose via pyruvate. Similarly, butyric acid can readily be formed from acetyl-CoA derived from pyruvate. Two acetyl residues are condensed to yield acetoacetyl-CoA which undergoes /?-reduction to buty ...
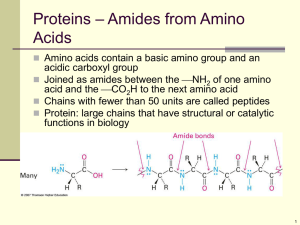
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Denaturation of Proteins The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many ...
... Denaturation of Proteins The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many ...
Energy Systems
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
Metabolism of bilirubin and bile salts synthesis (uronic acid pathway
... Most of URO remains in intestine and is excreted in feces as stercobilinogen Nearly 20% URO is absorbed from the intestine into portal circulation (subsequently excreted via kidneys into urine as urobinlin) A part of URO returns to liver and reaches gut again ...
... Most of URO remains in intestine and is excreted in feces as stercobilinogen Nearly 20% URO is absorbed from the intestine into portal circulation (subsequently excreted via kidneys into urine as urobinlin) A part of URO returns to liver and reaches gut again ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... Biochemistry Quiz Review VI A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. ...
... Biochemistry Quiz Review VI A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. ...
Exam 1
... Identify 2 groups in a protein that can form hydrogen bonds or electrostatic interactions with the amino-terminus at pH 10. Be certain to give not just the name of the amino acid, but ALSO the functional group. For each identify the donor and acceptor. (6 pts) ...
... Identify 2 groups in a protein that can form hydrogen bonds or electrostatic interactions with the amino-terminus at pH 10. Be certain to give not just the name of the amino acid, but ALSO the functional group. For each identify the donor and acceptor. (6 pts) ...
AMINO ACIDS COMPLEX Factsheet
... acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from dietary protein into the constituent amino acid, which the body uses to build the specific protein that it needs. Each person’s ability to break down protein into single amino acids d ...
... acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from dietary protein into the constituent amino acid, which the body uses to build the specific protein that it needs. Each person’s ability to break down protein into single amino acids d ...
Energy Production
... 1) Aerobic metabolism: dependent on oxygen. 2) Anaerobic metabolism: independent of oxygen. The use of which systems depend on: 1) Duration. 2) Intensity. 3) Type of physical activity. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): It is an energy-rich compound that continuously supply fuel for the body used by ener ...
... 1) Aerobic metabolism: dependent on oxygen. 2) Anaerobic metabolism: independent of oxygen. The use of which systems depend on: 1) Duration. 2) Intensity. 3) Type of physical activity. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): It is an energy-rich compound that continuously supply fuel for the body used by ener ...
cellular respiration
... process that: – Primarily occurs in mitochondria – Harvests energy stored in organic molecules ...
... process that: – Primarily occurs in mitochondria – Harvests energy stored in organic molecules ...
Feline Attractant, cis,trans-Nepetalactone: Metabolism in
... acids can be distinguished based on their difference in retention times (4); consequently, we concluded the stereospecific oxidation of nepetalactone results from the action of mammalian enzymes. 13. Supported in part by NSF grant GB5607. We thank Dr. E. J. Eisenbraun for a-nepetalinic acid (2-carbo ...
... acids can be distinguished based on their difference in retention times (4); consequently, we concluded the stereospecific oxidation of nepetalactone results from the action of mammalian enzymes. 13. Supported in part by NSF grant GB5607. We thank Dr. E. J. Eisenbraun for a-nepetalinic acid (2-carbo ...
Ch.3 Fermentation File
... used for beverages and foods based on fruit or vegetable substrates. Yeasts are ideal agents for fermentation of food products as they are generally acceptable to consumers and are rarely toxic or pathogenic. All strains ferment glucose and many ferment other plant-associated carbohydrates such as ...
... used for beverages and foods based on fruit or vegetable substrates. Yeasts are ideal agents for fermentation of food products as they are generally acceptable to consumers and are rarely toxic or pathogenic. All strains ferment glucose and many ferment other plant-associated carbohydrates such as ...
Biochemistry PP
... form polymers is called Dehydration synthesis (removing water, putting together) – For each bond, a water molecule needs to be pulled out to join the 2 monomers together. – It is a building up process, going from simple to more ...
... form polymers is called Dehydration synthesis (removing water, putting together) – For each bond, a water molecule needs to be pulled out to join the 2 monomers together. – It is a building up process, going from simple to more ...
Lab 11
... into oxaloacetate and pyruvate. These organisms are forced to utilize ammonium salts as the nitrogen source producing alkaline ammonia waste. Results: Prussian blue slant and or butt = positive for _ ...
... into oxaloacetate and pyruvate. These organisms are forced to utilize ammonium salts as the nitrogen source producing alkaline ammonia waste. Results: Prussian blue slant and or butt = positive for _ ...
Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is a ______(metabolic
... B. fructose 6-P. b. In the process of glycolysis: A. one enzyme converts glucose into NADH. B. two enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to ten pyruvate molecules. C. ten enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to two pyruvate molecules c. Glycolysis results in the breakdown of a gluco ...
... B. fructose 6-P. b. In the process of glycolysis: A. one enzyme converts glucose into NADH. B. two enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to ten pyruvate molecules. C. ten enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to two pyruvate molecules c. Glycolysis results in the breakdown of a gluco ...
pH Properties of Buffer Solutions
... • Forensic analysis of DNA by electrophoresis requires a buffer that will keep the charge on the DNA molecules relatively constant so that their migration in an electric field will depend only on their size. Research, prepare and study the pH profiles of electrophoresis buffers. ...
... • Forensic analysis of DNA by electrophoresis requires a buffer that will keep the charge on the DNA molecules relatively constant so that their migration in an electric field will depend only on their size. Research, prepare and study the pH profiles of electrophoresis buffers. ...
Mag-Malate Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate
... adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphate is the predominant reaction used to create energy for physiological processes. Thus, generation of ATP is the central goal of energy production There are numerous routes of ATP production. Three primary methods for generating ATP in skeletal muscle include i ...
... adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphate is the predominant reaction used to create energy for physiological processes. Thus, generation of ATP is the central goal of energy production There are numerous routes of ATP production. Three primary methods for generating ATP in skeletal muscle include i ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
An overview on effective parameters in production of single cell oil
... season aclimateasier to scale up. The main aim of this review was to explain the last records about effective parameters on production of single cell oil by microorganisms especially the fungus Mortierella isabellina. Keyword: single cell oil, fermentation, Mortierella isabellina ___________________ ...
... season aclimateasier to scale up. The main aim of this review was to explain the last records about effective parameters on production of single cell oil by microorganisms especially the fungus Mortierella isabellina. Keyword: single cell oil, fermentation, Mortierella isabellina ___________________ ...
CH395 G Exam 3 Fall 2004 - Multiple Choice 1. Which of the
... b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blocking proton translocation. d. binding to the T state of F1 of ATP synthase thereby inhibiting the conformational change necessary to form ATP. e. stim ...
... b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blocking proton translocation. d. binding to the T state of F1 of ATP synthase thereby inhibiting the conformational change necessary to form ATP. e. stim ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.