![Biochemistry 2 [1203253] intended learning outcomes DNA, RNA](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002558734_1-17434e4debf95f3be87a42da9306bb2f-300x300.png)
Biochemistry 2 [1203253] intended learning outcomes DNA, RNA
... Gene Expression Can Be Controlled at Posttranscriptional Levels Molecular basis of inherited diseases Restriction Enzymes: Performing Highly Specific DNA-Cleavage Reactions DNA recombinations are helpful in establishing genomic as well as cDNA libraries Antibiotic resistance genes can select ...
... Gene Expression Can Be Controlled at Posttranscriptional Levels Molecular basis of inherited diseases Restriction Enzymes: Performing Highly Specific DNA-Cleavage Reactions DNA recombinations are helpful in establishing genomic as well as cDNA libraries Antibiotic resistance genes can select ...
Lec 11: Fatty acid degradation
... Steps of this ω‐oxidation pathway: 1. P450 dependent oxidation of ω‐ carbon (no ...
... Steps of this ω‐oxidation pathway: 1. P450 dependent oxidation of ω‐ carbon (no ...
Methods of industrial production 1
... Various carbohydrates are utilized individually or as a mixture for the production of L-lysine such as glucose, fructose, sucrose, molasses (sucrose, glucose, fructose etc.), maltose, blackstrap molasses, starch hydrolyzate (glucose, oligosaccharides), lactose, maltose, starch and starch hydrolysate ...
... Various carbohydrates are utilized individually or as a mixture for the production of L-lysine such as glucose, fructose, sucrose, molasses (sucrose, glucose, fructose etc.), maltose, blackstrap molasses, starch hydrolyzate (glucose, oligosaccharides), lactose, maltose, starch and starch hydrolysate ...
The Dna code - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... DNA stores information to build proteins in sequences of nucleotides - DNA nucleotides contain one of 4 nitrogen bases A T C G - there are 20 different amino acids used to build protein ...
... DNA stores information to build proteins in sequences of nucleotides - DNA nucleotides contain one of 4 nitrogen bases A T C G - there are 20 different amino acids used to build protein ...
Student________________ Biochemistry I Homework III Due 10/13
... a). This is the H isozyme of lactate dehydrogenase. What is an isozyme? Isozymes have different quaternary forms that differ in their catalytic ability b). What is the source of this LDH? human heart c). What class of enzymes does LDH belong? oxidoreductase d). What is the cofactor in LDH? NADH e). ...
... a). This is the H isozyme of lactate dehydrogenase. What is an isozyme? Isozymes have different quaternary forms that differ in their catalytic ability b). What is the source of this LDH? human heart c). What class of enzymes does LDH belong? oxidoreductase d). What is the cofactor in LDH? NADH e). ...
Respiration ppt - mleonessciencepage
... • can survive and make use of the energy released from glycolysis itself • Two forms of anaerobes are: – Facultative anaerobes – these can survive in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. – Obligate anaerobes – Survive only as anaerobes. ...
... • can survive and make use of the energy released from glycolysis itself • Two forms of anaerobes are: – Facultative anaerobes – these can survive in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. – Obligate anaerobes – Survive only as anaerobes. ...
26.4 The ureo cyde
... Hyperammonemia is an increasein ammonia in the blood to higher concentrations than the normal30 to 60 mM. This condition is usually caused by the inability of patients to form urea fast enough to keep ammonia in the blood at normal levels. Severalconditions can lead to hlperammonemia. Some newborns ...
... Hyperammonemia is an increasein ammonia in the blood to higher concentrations than the normal30 to 60 mM. This condition is usually caused by the inability of patients to form urea fast enough to keep ammonia in the blood at normal levels. Severalconditions can lead to hlperammonemia. Some newborns ...
READ MORE - MindBody Medicine Center
... myriad chemicals found in all humans at this time on earth, including phalates, parabens, pesticides, styrene, benzene, toluene, and thousands more. For example, medical scientists now widely believe that Al ...
... myriad chemicals found in all humans at this time on earth, including phalates, parabens, pesticides, styrene, benzene, toluene, and thousands more. For example, medical scientists now widely believe that Al ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... include how: Body maintains energy balance (homeostasis) It deals with starvation It responds to the loss of control from diabetes mellitus ...
... include how: Body maintains energy balance (homeostasis) It deals with starvation It responds to the loss of control from diabetes mellitus ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY - Life Sciences 4 All
... • When fermentation is complete the excess yeast is skimmed off and is used to produce yeast extracts such as Marmite ...
... • When fermentation is complete the excess yeast is skimmed off and is used to produce yeast extracts such as Marmite ...
3.2 – Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins
... Ribose is an example of a pentose, or 5-carbon sugars. Deoxyribose is a modified version of ribose, and is known for its role in DNA as part of the sugar phosphate backbone. Its chemical properties are very different to ribose. ...
... Ribose is an example of a pentose, or 5-carbon sugars. Deoxyribose is a modified version of ribose, and is known for its role in DNA as part of the sugar phosphate backbone. Its chemical properties are very different to ribose. ...
Histone Deacetylase 4 Antibody
... members, HDAC-1, 2, 3, and 8, each of which contains a deacetylase domain exhibiting from 45 to 93% identity in amino acid sequence. Class II of the HDAC family comprises HDAC-4, 5, 6, and 7, the molecular weights of which are all about twofold larger than those of the class I members, and the deace ...
... members, HDAC-1, 2, 3, and 8, each of which contains a deacetylase domain exhibiting from 45 to 93% identity in amino acid sequence. Class II of the HDAC family comprises HDAC-4, 5, 6, and 7, the molecular weights of which are all about twofold larger than those of the class I members, and the deace ...
Partial purification of fatty acid synthetase from Streptomyces
... Thus the synthetase migrated as a single species during these Filamentous bacteria of the genus Streptomyces are extremely procedures (with a consistent recovery of over 80%), and its versatile in making antibiotics, many of which are phenolic activity presumably resides in multifunctional polypepti ...
... Thus the synthetase migrated as a single species during these Filamentous bacteria of the genus Streptomyces are extremely procedures (with a consistent recovery of over 80%), and its versatile in making antibiotics, many of which are phenolic activity presumably resides in multifunctional polypepti ...
EXAM III KEY - the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center
... __T___ 2) Vitamins A, E and K are all isoprenoids. __F___ 3) Transport of ions and small molecules through a bacterial membrane pore requires energy from an ATP to ADP conversion. __T___ 4) The principle advantage of a cascade mechanism in signal transduction is that one molecule of a ligand can aff ...
... __T___ 2) Vitamins A, E and K are all isoprenoids. __F___ 3) Transport of ions and small molecules through a bacterial membrane pore requires energy from an ATP to ADP conversion. __T___ 4) The principle advantage of a cascade mechanism in signal transduction is that one molecule of a ligand can aff ...
Sol: A process of physio
... Mechanism of Electron transport system – Glucose molecule is completely oxidized by the end of the citric acid cycle. The energy is not released unless NADH and FADH are oxidized through the ETS. The oxidation means ‘removal of electrons from it’. Metabolic pathway through which the electron passes ...
... Mechanism of Electron transport system – Glucose molecule is completely oxidized by the end of the citric acid cycle. The energy is not released unless NADH and FADH are oxidized through the ETS. The oxidation means ‘removal of electrons from it’. Metabolic pathway through which the electron passes ...
Exam III - chem.uwec.edu
... 4. Which of the following membranes would be the most fluid (circle the best choice)? a. A bilayer made of lipids with saturated 16 carbon-fatty acids b. A bilayer made of lipids with saturated 18 carbon-fatty acids c. A bilayer made of lipids with polyunsaturated 18 carbon-fatty acids d. A bilayer ...
... 4. Which of the following membranes would be the most fluid (circle the best choice)? a. A bilayer made of lipids with saturated 16 carbon-fatty acids b. A bilayer made of lipids with saturated 18 carbon-fatty acids c. A bilayer made of lipids with polyunsaturated 18 carbon-fatty acids d. A bilayer ...
CH1710 PrEX#2 Sp2013 answers
... 1. Aqueous copper (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to yield solid copper (II) hydroxide and aqueous sodium chloride. ...
... 1. Aqueous copper (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to yield solid copper (II) hydroxide and aqueous sodium chloride. ...
Lecture 35 - Lipid Metabolism 1
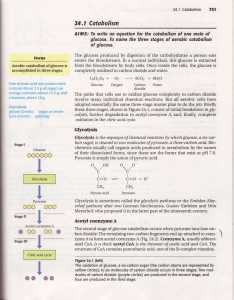
... • Ketogenesis takes place in liver mitochondria when acetyl-CoA levels are high and oxaloacetate levels are low. ...
... • Ketogenesis takes place in liver mitochondria when acetyl-CoA levels are high and oxaloacetate levels are low. ...
homework 3 assigned
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
Reading Guide
... dihydrofolate reductase? Why are these good targets for chemotherapy? 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fu ...
... dihydrofolate reductase? Why are these good targets for chemotherapy? 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fu ...
Midterm Exam Note: Before beginning, please scan the entire exam
... increase in entropy (S) and the products would have less free energy than the reactants. E) The reaction would result in products (C + D) with a greater free-energy content than in the initial reactants (A + B). The next question(s) is based on the following information: A series of enzymes catalyze ...
... increase in entropy (S) and the products would have less free energy than the reactants. E) The reaction would result in products (C + D) with a greater free-energy content than in the initial reactants (A + B). The next question(s) is based on the following information: A series of enzymes catalyze ...
H &
... of chemical reactionsby which glucose,a six-carbon sugar,is cleauedto two moleculesof pyruuate, a three-carbonacid. Biochemists usually call organic acids produced in metabolism by the names of their dissociatedforms, since these are the forms that exist at pH 7.0. P1'ruvateis simply the anion of py ...
... of chemical reactionsby which glucose,a six-carbon sugar,is cleauedto two moleculesof pyruuate, a three-carbonacid. Biochemists usually call organic acids produced in metabolism by the names of their dissociatedforms, since these are the forms that exist at pH 7.0. P1'ruvateis simply the anion of py ...
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Topic 1: Introduction 1. Know the
... Discuss how NAD+ is regenerated in anaerobic glycolysis and why this is so important to the cell under anaerobic conditions. ...
... Discuss how NAD+ is regenerated in anaerobic glycolysis and why this is so important to the cell under anaerobic conditions. ...
Slide 1
... HGD gene. Urine in an infant's diaper may darken and can turn almost black after several hours. However, many persons with this condition may not know they have it until midadulthood (around age 40), when joint and other problems occur. Other symptoms: Arthritis that worsens over time, Darkening o ...
... HGD gene. Urine in an infant's diaper may darken and can turn almost black after several hours. However, many persons with this condition may not know they have it until midadulthood (around age 40), when joint and other problems occur. Other symptoms: Arthritis that worsens over time, Darkening o ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.