Pathways - PharmaStreet
... Shikimic acid is also the glycoside part of some hydrolysable tannins. The shikimate pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by bacteria, fungi, algae, parasites, and plants for the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan). This pathway is not found in anim ...
... Shikimic acid is also the glycoside part of some hydrolysable tannins. The shikimate pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by bacteria, fungi, algae, parasites, and plants for the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan). This pathway is not found in anim ...
Regulation of fatty acid oxidation in cells
... ketone bodies are also made from acetyl-CoA derived from the catabolism of some amino acids and pyruvate oxidation, representing perhaps 10-18% of the amount made from fatty acids [14]. T h e oxidation of one molecule of palmitate to eight acetyl-CoA molecules consumes 14 atoms of oxygen, whereas it ...
... ketone bodies are also made from acetyl-CoA derived from the catabolism of some amino acids and pyruvate oxidation, representing perhaps 10-18% of the amount made from fatty acids [14]. T h e oxidation of one molecule of palmitate to eight acetyl-CoA molecules consumes 14 atoms of oxygen, whereas it ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... D) obtain glyoxylate for cholesterol biosynthesis. E) obtain glyoxylate for pyrimidine synthesis. The glyoxylate cycle is: A) a means of using acetate for both energy and biosynthetic precursors. B) an alternative path of glucose metabolism in cells that do not have enough O2. C) defective in people ...
... D) obtain glyoxylate for cholesterol biosynthesis. E) obtain glyoxylate for pyrimidine synthesis. The glyoxylate cycle is: A) a means of using acetate for both energy and biosynthetic precursors. B) an alternative path of glucose metabolism in cells that do not have enough O2. C) defective in people ...
Oils and Fats
... 3- Alcoholic KOH is used for the S.V. of oils and fats, while aqueous KOH is used for saponification of oils and fats in case of Richert-Meissel value. 4- Iso-oleic acid present in hydrogenated fats, not present in natural oil or fat. 5- During hydrogenation of oils, the mixture of oil, Ni, and hydr ...
... 3- Alcoholic KOH is used for the S.V. of oils and fats, while aqueous KOH is used for saponification of oils and fats in case of Richert-Meissel value. 4- Iso-oleic acid present in hydrogenated fats, not present in natural oil or fat. 5- During hydrogenation of oils, the mixture of oil, Ni, and hydr ...
2 Ionic equilibria - University of Basrah
... • The strength of an acid or a base varies with the solvent. • HCl is a strong acid but it is a weak acid in glacial acetic acid. • Acetic acid, which is a weak acid, is a strong acid in liquid ammonia. • Consequently, the strength of an acid depends not ...
... • The strength of an acid or a base varies with the solvent. • HCl is a strong acid but it is a weak acid in glacial acetic acid. • Acetic acid, which is a weak acid, is a strong acid in liquid ammonia. • Consequently, the strength of an acid depends not ...
Identification, Synthesis and Biological Activity of Galloyl Inhibitors of
... inhibition. Competitive inhibition of LMW-PTP IF2 by known inhibitor pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP) shows a strong inhibition constant (Ki = 7.6 μM at pH 5.0); however, PLP is a cofactor for many other enzymes. In silico screening and in vitro testing identified NSC107022 (Ki = 10.8 ± 1.0) from the Na ...
... inhibition. Competitive inhibition of LMW-PTP IF2 by known inhibitor pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP) shows a strong inhibition constant (Ki = 7.6 μM at pH 5.0); however, PLP is a cofactor for many other enzymes. In silico screening and in vitro testing identified NSC107022 (Ki = 10.8 ± 1.0) from the Na ...
Chapter 6 – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Standard 1.g
... The efficiency of cellular respiration – a typical cell stores around 40% of the chemical energy released in ATP, the rest is released as heat ATP is produced in 2 ways 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons di ...
... The efficiency of cellular respiration – a typical cell stores around 40% of the chemical energy released in ATP, the rest is released as heat ATP is produced in 2 ways 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons di ...
Isomerisms
... sodium lamp) is pass through a polariser which converts it to plane-polarised light. The plane-polarised light is then passes through a tube containing a solution of the sample whose angle of rotation is to be measured. On emerging from the sample tube, the plane polarised light has been rotated eit ...
... sodium lamp) is pass through a polariser which converts it to plane-polarised light. The plane-polarised light is then passes through a tube containing a solution of the sample whose angle of rotation is to be measured. On emerging from the sample tube, the plane polarised light has been rotated eit ...
Patterns of nucleotide and amino acid substitution
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
HPTLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION FOR DENSITOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF
... This paper reports new, accurate and precise high performance thin layer chromatographic (HPTLC) method for densitometric determination of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid and β-sitosterol in herbal drug formulation (Madhuveer Liquid). Marketed herbal formulation was suitably diluted with methanol and ultras ...
... This paper reports new, accurate and precise high performance thin layer chromatographic (HPTLC) method for densitometric determination of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid and β-sitosterol in herbal drug formulation (Madhuveer Liquid). Marketed herbal formulation was suitably diluted with methanol and ultras ...
Lactic Acid fermentation
... – Pyruvate becomes acetyl CoA via coenzyme A – Acetyl CoA becomes citric acid – Net Yield 6 CO2, *2 ATP*, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2 ...
... – Pyruvate becomes acetyl CoA via coenzyme A – Acetyl CoA becomes citric acid – Net Yield 6 CO2, *2 ATP*, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2 ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... • Process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 • Provides more energy (ATP) from glucose than Glycolysis • Also captures energy stored in lipids and amino acids • Evolutionary origin: developed about 2.5 billion years ago • Used by animals, plants, and many microorganisms • Occurs in three majo ...
... • Process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 • Provides more energy (ATP) from glucose than Glycolysis • Also captures energy stored in lipids and amino acids • Evolutionary origin: developed about 2.5 billion years ago • Used by animals, plants, and many microorganisms • Occurs in three majo ...
How the decomposers decompose: mineralization of microbial
... adsorbed fractions were analysed by liquid-state NMR. ...
... adsorbed fractions were analysed by liquid-state NMR. ...
File
... – Chlorine: component of stomach acid – Many mineral salts function as electrolytes and govern function of nerve and muscle cells, osmotically regulate the content and distribution of water in the body, and maintain blood volume ...
... – Chlorine: component of stomach acid – Many mineral salts function as electrolytes and govern function of nerve and muscle cells, osmotically regulate the content and distribution of water in the body, and maintain blood volume ...
Document
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...
Krebs cycle
... TCA or Kreb’s cycle, function and regulation. Asymmetric breakdown of a symmetric citrate molecule. “Accounting” of ATP synthesized, from glycolysis to respiratory chain. Murphy’s Law and the missing 10 molecules of ATP per glucose. How to avoid losing your carbons during the exam. ...
... TCA or Kreb’s cycle, function and regulation. Asymmetric breakdown of a symmetric citrate molecule. “Accounting” of ATP synthesized, from glycolysis to respiratory chain. Murphy’s Law and the missing 10 molecules of ATP per glucose. How to avoid losing your carbons during the exam. ...
Cellular Respiration Explained
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
E2 and E11 Acid Deposition Past Paper Questions
... salt particles formed are acidic/have pH lower than 7 salts are washed into the ground; in earth they can be nitrified; nitrification acidifies the soil ...
... salt particles formed are acidic/have pH lower than 7 salts are washed into the ground; in earth they can be nitrified; nitrification acidifies the soil ...
a new equation for calculating the number of atp molecules
... Fatty acids are a sub-class of the lipid macronutrient class. One of the fatty acids major roles is energy production by supplying ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Fatty acids class is considered the highest energy carrier compared to other macronutrient classes such as proteins and carbohydrates. Fatt ...
... Fatty acids are a sub-class of the lipid macronutrient class. One of the fatty acids major roles is energy production by supplying ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Fatty acids class is considered the highest energy carrier compared to other macronutrient classes such as proteins and carbohydrates. Fatt ...
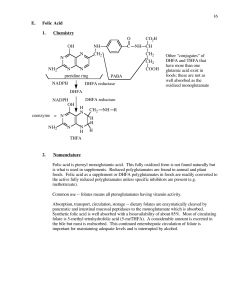
16 E. Folic Acid 1. Chemistry coenzyme DHFA DHFA reductase
... • Deficiency results in megabloblastic anemia. Symptoms include headache, fatigue, weight loss, anemia, nausea, anorexia, diarrhea, insomnia, irritability, forgetfulness. Signs are macrocytic red cells and megaloblasts in the bone marrow. • Deficiency may result in teratogenesis with neural tube def ...
... • Deficiency results in megabloblastic anemia. Symptoms include headache, fatigue, weight loss, anemia, nausea, anorexia, diarrhea, insomnia, irritability, forgetfulness. Signs are macrocytic red cells and megaloblasts in the bone marrow. • Deficiency may result in teratogenesis with neural tube def ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.