lecture6
... appropriately balanced. The reason is that the entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate for the formation of citrate, but the concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable or improperly utilized. Recall that oxaloacetate is ...
... appropriately balanced. The reason is that the entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate for the formation of citrate, but the concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable or improperly utilized. Recall that oxaloacetate is ...
MILK SYNTHESIS ENZYMES AND THEIR ROLES IN MILK QUALITY
... roles compared with SCD. Milk fatty acid data for oleic acid and CLA vs. omega-3 support this conclusion. The similar pattern of expression for key genes involved in milk fat synthesis and desaturation suggests a necessity for coordinated regulation of all those proteins to accomplish the task of sy ...
... roles compared with SCD. Milk fatty acid data for oleic acid and CLA vs. omega-3 support this conclusion. The similar pattern of expression for key genes involved in milk fat synthesis and desaturation suggests a necessity for coordinated regulation of all those proteins to accomplish the task of sy ...
cell respiration notes ap - Wesleyan
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
CITRIC ACID (KREB`S, TCA) CYCLE
... Interconversions of the Citric Acid Cycle (animation available in PowerPoint) ...
... Interconversions of the Citric Acid Cycle (animation available in PowerPoint) ...
Rumen Protected Fat
... Minimize body wt. loss after calving Improve BCS Improve reproductive efficiency ...
... Minimize body wt. loss after calving Improve BCS Improve reproductive efficiency ...
Pathways of Glucose Assimilation in Puccinia graminis
... identify precursors suggest that trehalose was formed via trehalose phosphate, mannitol via fructose, and glucitol via both glucose and fructose. Steady-state specific activities of all free intracellular carbohydrates were much lower (15-5079 than that of the exogenous glucose, indicating that unla ...
... identify precursors suggest that trehalose was formed via trehalose phosphate, mannitol via fructose, and glucitol via both glucose and fructose. Steady-state specific activities of all free intracellular carbohydrates were much lower (15-5079 than that of the exogenous glucose, indicating that unla ...
Nutrition for Strength/Power Athletes
... • Carbohydrate stores in the body are essential for optimal athletic performance. These carbohydrate stores are reduced as a result of exercise; therefore, they must be replenished through your diet. • Athletes should aim to consume 55-60% of their total calorie intake from carbohydrates, keeping in ...
... • Carbohydrate stores in the body are essential for optimal athletic performance. These carbohydrate stores are reduced as a result of exercise; therefore, they must be replenished through your diet. • Athletes should aim to consume 55-60% of their total calorie intake from carbohydrates, keeping in ...
Cell Respiration Notes
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
glucose-6-P - WordPress.com
... The subsequent step is catalyzed by enolase and involves a dehydration, forming phosphoenolpyruvate. Enolase is inhibited by fluoride, and when blood samples are taken for measurement of glucose, it is collected in tubes containing fluoride to inhibit glycolysis. The enzyme is also dependent on the ...
... The subsequent step is catalyzed by enolase and involves a dehydration, forming phosphoenolpyruvate. Enolase is inhibited by fluoride, and when blood samples are taken for measurement of glucose, it is collected in tubes containing fluoride to inhibit glycolysis. The enzyme is also dependent on the ...
Cell Respiration Notes Kelly
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
... Used by microorganisms to make beer/wine Used by yeast to make bread LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Pyruvate → lactic acid + NAD+ Human muscle cells when oxygen is low during exercise ...
ATP Molecules
... shows the coupling of glucose breakdown to ATP buildup. • The breakdown of one glucose molecule results in a maximum of 36 to 38 ATP molecules, representing about 40% of the potential energy within the glucose molecule. ...
... shows the coupling of glucose breakdown to ATP buildup. • The breakdown of one glucose molecule results in a maximum of 36 to 38 ATP molecules, representing about 40% of the potential energy within the glucose molecule. ...
Cellular Energetics
... This creates a proton-motive force and H+ moves back across the membrane thru ATP synthase and ATP is produced ...
... This creates a proton-motive force and H+ moves back across the membrane thru ATP synthase and ATP is produced ...
effect of short time exposure of rats to extreme low temperature on
... activity. OTC is the key enzyme of urea cycle. This enzyme, just as the GDH, is present in the liver mitochondrium and catalyses conversion of carbamoyl phosphate to ornithine (9). Other important urea cycle enzyme, arginase, was also increased during the cryotherapy. The low temperature exert a gre ...
... activity. OTC is the key enzyme of urea cycle. This enzyme, just as the GDH, is present in the liver mitochondrium and catalyses conversion of carbamoyl phosphate to ornithine (9). Other important urea cycle enzyme, arginase, was also increased during the cryotherapy. The low temperature exert a gre ...
A: Objective type questions: Choose the correct answers Most
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
Vitamins
... Very small amounts are needed by the body (>1 gm) Very small amounts are contained in foods. ...
... Very small amounts are needed by the body (>1 gm) Very small amounts are contained in foods. ...
ZEN - Webnode
... • Please Note: High calorie sugary liquids will sabotage this program as they cause massive amounts of inflammation in the body. Those who ingest more calories or the wrong calories or than what their body has the metabolic capacity to utilize will not see results. This is because some people are in ...
... • Please Note: High calorie sugary liquids will sabotage this program as they cause massive amounts of inflammation in the body. Those who ingest more calories or the wrong calories or than what their body has the metabolic capacity to utilize will not see results. This is because some people are in ...
Document
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Eventually oxaloacetate is reformed and ready to join with another acetyl-CoA. The TCA cycle generates two CO2s, three NADHs, one FADH2, and one GTP for each acetyl- CoA molecule oxidized. TCA cycle enzymes are widely distributed among microorganisms. The complete cy ...
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Eventually oxaloacetate is reformed and ready to join with another acetyl-CoA. The TCA cycle generates two CO2s, three NADHs, one FADH2, and one GTP for each acetyl- CoA molecule oxidized. TCA cycle enzymes are widely distributed among microorganisms. The complete cy ...
CreaPrime™ Blend
... which produces ATP. Adding citric acid and malic acid to Primal N2O aids in ATP production. ...
... which produces ATP. Adding citric acid and malic acid to Primal N2O aids in ATP production. ...
Water Soluble Vitamins 2
... Most exceed RDA in diet Surplus is rapidly lost in urine; non toxic ...
... Most exceed RDA in diet Surplus is rapidly lost in urine; non toxic ...
Paraoxonase-2 Gene (PON2) G148 Variant Associated with
... Serum paraoxonase is associated with high density lipoprotein and hydrolyzes a number of organophosphates (10). In contrast to PON1, which is mainly expressed in the liver, PON2 is expressed in a variety of tissues, including the pancreas (8). Although the physiological role of the PON2 gene product ...
... Serum paraoxonase is associated with high density lipoprotein and hydrolyzes a number of organophosphates (10). In contrast to PON1, which is mainly expressed in the liver, PON2 is expressed in a variety of tissues, including the pancreas (8). Although the physiological role of the PON2 gene product ...
Oxidative degradation of glucose File
... • The high-energy phosphate of phosphoenol pyruvate is transferred to ADP by the enzyme pyruvate kinase to generate, at this stage, two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose oxidized and enolpyruvate is formed. • Enolpyruvate formed is converted spontaneousny to the keto form pyruvate. This is an ...
... • The high-energy phosphate of phosphoenol pyruvate is transferred to ADP by the enzyme pyruvate kinase to generate, at this stage, two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose oxidized and enolpyruvate is formed. • Enolpyruvate formed is converted spontaneousny to the keto form pyruvate. This is an ...
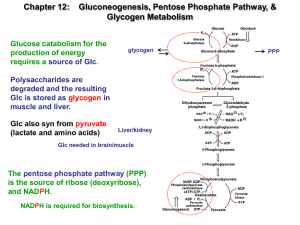
Slide 1
... Primer of 4 to 8 Glc on a Tyr (-OH) of glycogenin. 1st Glc from UDP-Glc via Glc transferase. Remaining Glc’s tranferred by glycogenin. Amylo-(1,4 1,6)-transglycolase catalyzes the branch point. (Alpha 1-6 link) ...
... Primer of 4 to 8 Glc on a Tyr (-OH) of glycogenin. 1st Glc from UDP-Glc via Glc transferase. Remaining Glc’s tranferred by glycogenin. Amylo-(1,4 1,6)-transglycolase catalyzes the branch point. (Alpha 1-6 link) ...
Cellular respiration
... thinking is 32 ATP produced per glucose. This releases 686 kcal of energy. ...
... thinking is 32 ATP produced per glucose. This releases 686 kcal of energy. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.