Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Pyruvate to Lactate • Under anaerobic (NO Oxygen) conditions, the most important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. lactate O dehydrogenase ...
... Pyruvate to Lactate • Under anaerobic (NO Oxygen) conditions, the most important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. lactate O dehydrogenase ...
Vitamins
... Some parts of animals, like polar bear livers, are unsafe to eat because of the high concentration of vitamin A stored there! ...
... Some parts of animals, like polar bear livers, are unsafe to eat because of the high concentration of vitamin A stored there! ...
Amino Acid Disorders - NewbornScreening.info
... different enzymes are needed to process these amino acids for use by the body. Because of missing or non-working enzymes, people with amino acid disorders cannot process certain amino acids. These amino acids, along with other toxic substances, then build up in the body and cause problems. The sympt ...
... different enzymes are needed to process these amino acids for use by the body. Because of missing or non-working enzymes, people with amino acid disorders cannot process certain amino acids. These amino acids, along with other toxic substances, then build up in the body and cause problems. The sympt ...
Amino Acid Catabolism: C
... Amino Acid Carbon Skeletons Amino acids, when deaminated, yield a-keto acids that, directly or via additional reactions, feed into major metabolic pathways (e.g., Krebs Cycle). Amino acids are grouped into 2 classes, based on whether or not their carbon skeletons can be converted to glucose: gluc ...
... Amino Acid Carbon Skeletons Amino acids, when deaminated, yield a-keto acids that, directly or via additional reactions, feed into major metabolic pathways (e.g., Krebs Cycle). Amino acids are grouped into 2 classes, based on whether or not their carbon skeletons can be converted to glucose: gluc ...
Amino Acid Catabolism: C
... Amino Acid Carbon Skeletons Amino acids, when deaminated, yield a-keto acids that, directly or via additional reactions, feed into major metabolic pathways (e.g., Krebs Cycle). Amino acids are grouped into 2 classes, based on whether or not their carbon skeletons can be converted to glucose: gluc ...
... Amino Acid Carbon Skeletons Amino acids, when deaminated, yield a-keto acids that, directly or via additional reactions, feed into major metabolic pathways (e.g., Krebs Cycle). Amino acids are grouped into 2 classes, based on whether or not their carbon skeletons can be converted to glucose: gluc ...
Download: 7.2 MB PDF
... treatment and prevention of chronic disease. Chronic diseases are often complex and Genova’s system-based testing helps physicians develop targeted treatments for their patients. Easy-to-read color graphic reports synthesize test results into actionable information and facilitate physician-patient c ...
... treatment and prevention of chronic disease. Chronic diseases are often complex and Genova’s system-based testing helps physicians develop targeted treatments for their patients. Easy-to-read color graphic reports synthesize test results into actionable information and facilitate physician-patient c ...
Biochemical Thermodynamics - Illinois Institute of Technology
... Nineteen of the twenty ribosomally encoded amino acids fit this form The only variation is in the identity of the R group (the side chain extending off the alpha carbon) Complexity ranging from glycine (R=H) to tryptophan (R=-CH2-indole) ...
... Nineteen of the twenty ribosomally encoded amino acids fit this form The only variation is in the identity of the R group (the side chain extending off the alpha carbon) Complexity ranging from glycine (R=H) to tryptophan (R=-CH2-indole) ...
Ruminal Acidosis – understandings, prevention and treatment
... logarithmic, not a linear scale. ...
... logarithmic, not a linear scale. ...
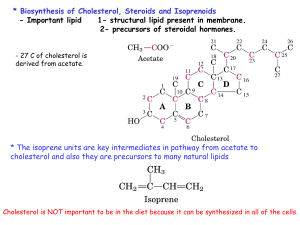
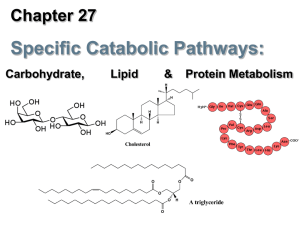
S17 Cholesterol And Steroids Biosynthesis
... - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid soluble for transporting them between organs and also provide efficient mechanism for delivering their ...
... - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid soluble for transporting them between organs and also provide efficient mechanism for delivering their ...
Viva Voce : Orals in Biochemistry
... Saturated fatty acids: All the naturally occuring fatty acids have even number of ‘c’ atoms. Most predominant fatty acids which occur in nature are: (i) Palmitic acid ...
... Saturated fatty acids: All the naturally occuring fatty acids have even number of ‘c’ atoms. Most predominant fatty acids which occur in nature are: (i) Palmitic acid ...
14steriod
... - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid soluble for transporting them between organs and also provide efficient mechanism for delivering their ...
... - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid soluble for transporting them between organs and also provide efficient mechanism for delivering their ...
Metabolism of lactate and sugars by dairy propionibacteria: A
... cycle, but can not grow under normal atmospheric oxygen pressure. The proportions of propionate acetate and CO2 produced vary depending on the strain used and this can be explained, to sorne extent, by their relative ability to utilise pyruvate via reactions of the citrate cycle. The physicochemical ...
... cycle, but can not grow under normal atmospheric oxygen pressure. The proportions of propionate acetate and CO2 produced vary depending on the strain used and this can be explained, to sorne extent, by their relative ability to utilise pyruvate via reactions of the citrate cycle. The physicochemical ...
David Rittenberg - National Academy of Sciences
... amounts and are continually synthesized and destroyed in the animal body presents almost insuperable difficulties. If substances such as natural fatty acids, amino acids, etc., are administered to an animal, we lose track of them the moment they enter the body, since they are mixed with the same sub ...
... amounts and are continually synthesized and destroyed in the animal body presents almost insuperable difficulties. If substances such as natural fatty acids, amino acids, etc., are administered to an animal, we lose track of them the moment they enter the body, since they are mixed with the same sub ...
evaluation of l-methionine bioavailability in nursery pigs
... Protein is an important nutrient in swine production. There have been many studies to define the amino acid (AA) requirement because a deficiency in protein supply to the diet can cause severe reduction in growth and reproduction and an excessive protein supplementation can increase feed cost and N ...
... Protein is an important nutrient in swine production. There have been many studies to define the amino acid (AA) requirement because a deficiency in protein supply to the diet can cause severe reduction in growth and reproduction and an excessive protein supplementation can increase feed cost and N ...
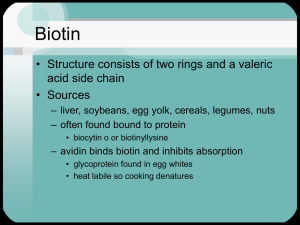
PowerPoint Presentation - Biotin Conclusion and Discussion
... – Deficiency due to inborn error has been documented in infants and children – Clinical features include seizures, ataxia, skin rash, alopecia, acidosis ...
... – Deficiency due to inborn error has been documented in infants and children – Clinical features include seizures, ataxia, skin rash, alopecia, acidosis ...
STRUCTURE-FUNCTION STUDIES OF THE CARNITINE/CHOLINE
... carnitine acyltransferase family were studied. These enzymes play essential roles in fatty acid metabolism by facilitating the transfer of activated fatty acids across intracellular membranes. To understand the mechanism of these enzymes, the structure of human peroxisomal L-carnitine acetyltransfer ...
... carnitine acyltransferase family were studied. These enzymes play essential roles in fatty acid metabolism by facilitating the transfer of activated fatty acids across intracellular membranes. To understand the mechanism of these enzymes, the structure of human peroxisomal L-carnitine acetyltransfer ...
PelleyStep1ReviewInBiochemistry
... Option C (glucagon) is correct. Glucagon is the principal hormone that stimulates liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, which are primarily responsible for maintaining the hyperglycemic state. Incorrect Responses Option A (cortisol) is incorrect. Cortisol functions in the liver to block insulin ...
... Option C (glucagon) is correct. Glucagon is the principal hormone that stimulates liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, which are primarily responsible for maintaining the hyperglycemic state. Incorrect Responses Option A (cortisol) is incorrect. Cortisol functions in the liver to block insulin ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.