Sugar Metabolism in Yeasts: an Overview of Aerobic and Anaerobic
... polyols, alcohols, organic acids and amino acids) that can support their growth but preferentially they metabolize sugars. The information related to the metabolism of different carbon sources is huge, the most widely studied being sugars such as hexoses (glucose, fructose, galactose or mannose) and ...
... polyols, alcohols, organic acids and amino acids) that can support their growth but preferentially they metabolize sugars. The information related to the metabolism of different carbon sources is huge, the most widely studied being sugars such as hexoses (glucose, fructose, galactose or mannose) and ...
16.6 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
... By comparing LD50 values, relative toxicities of various laboratory chemicals can be evaluated. For therapeutic use, a compound must show a comfortably wide margin between the dose that produces the desired effect and the dose that produces an acute toxic effect. The LD50 test is controversial; it h ...
... By comparing LD50 values, relative toxicities of various laboratory chemicals can be evaluated. For therapeutic use, a compound must show a comfortably wide margin between the dose that produces the desired effect and the dose that produces an acute toxic effect. The LD50 test is controversial; it h ...
Effects of Heat Stress and Dietary Tryptophan on Performance and
... Effects of Heat Stress and Dietary Tryptophan on Performance and Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations of Broiler Chickens Hayford Y. Tabiri, Kan Sato, Kazuaki Takahashi, Masaaki Toyomizu and Yukio Akiba* Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University, Aoba-Ku, Sendai 981-8555, Japan ABSTRACT ...
... Effects of Heat Stress and Dietary Tryptophan on Performance and Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations of Broiler Chickens Hayford Y. Tabiri, Kan Sato, Kazuaki Takahashi, Masaaki Toyomizu and Yukio Akiba* Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University, Aoba-Ku, Sendai 981-8555, Japan ABSTRACT ...
Document
... There are D-amino acids in many organisms Bacteria incorporate them into structures of their cell walls Makes those structures resistant to standard proteolytic enzymes, which only attack amino acids with L specificity ...
... There are D-amino acids in many organisms Bacteria incorporate them into structures of their cell walls Makes those structures resistant to standard proteolytic enzymes, which only attack amino acids with L specificity ...
Document
... The role of proinsulin seems to be con- extrusion by exocytosis (Rubenstein et al., fined mainly to the biosynthetic process 1969). The C-peptide contains all the since most of it is converted to insulin be- additional amino acids of proinsulin aside fore secretion occurs. However, small from the pa ...
... The role of proinsulin seems to be con- extrusion by exocytosis (Rubenstein et al., fined mainly to the biosynthetic process 1969). The C-peptide contains all the since most of it is converted to insulin be- additional amino acids of proinsulin aside fore secretion occurs. However, small from the pa ...
Microsoft Word
... means in the management of diabetes. In this category, dietary fibers and foods rich in dietary fibers are well accepted to have beneficial functions in the management of diabetes. But there are not many scientific investigations on the role of these dietary fibers in minimizing complications of dia ...
... means in the management of diabetes. In this category, dietary fibers and foods rich in dietary fibers are well accepted to have beneficial functions in the management of diabetes. But there are not many scientific investigations on the role of these dietary fibers in minimizing complications of dia ...
Lactic Acidosis
... Supplementary Appendix). Other disorders associated with elevated epinephrine levels, such as severe asthma (especially with overuse of β2-adrenergic agonists), extensive trauma, cardiogenic or hemorrhagic shock, and pheochromocytoma, can cause hyperlactatemia through this mechanism.9 In inflammator ...
... Supplementary Appendix). Other disorders associated with elevated epinephrine levels, such as severe asthma (especially with overuse of β2-adrenergic agonists), extensive trauma, cardiogenic or hemorrhagic shock, and pheochromocytoma, can cause hyperlactatemia through this mechanism.9 In inflammator ...
Student notes in ppt
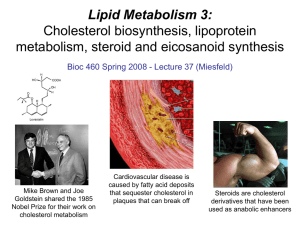
... LDL receptor cycling and cholesterol homeostasis The connection between high serum LDL levels and atherosclerosis was made by Brown and Goldstein when they discovered that a genetic disorder called familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) was due to mutations in the LDL receptor gene. The cholesterol est ...
... LDL receptor cycling and cholesterol homeostasis The connection between high serum LDL levels and atherosclerosis was made by Brown and Goldstein when they discovered that a genetic disorder called familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) was due to mutations in the LDL receptor gene. The cholesterol est ...
Characterization of carnitine and fatty acid metabolism in the long
... deficiency. A profound deficiency of acetylcarnitine was observed in LCAD−/− hearts, which most likely corresponds with low cardiac levels of acetyl-CoA. Since there was no carnitine deficiency and only a marginal elevation of potentially cardiotoxic acylcarnitines, we conclude from these data that ...
... deficiency. A profound deficiency of acetylcarnitine was observed in LCAD−/− hearts, which most likely corresponds with low cardiac levels of acetyl-CoA. Since there was no carnitine deficiency and only a marginal elevation of potentially cardiotoxic acylcarnitines, we conclude from these data that ...
Glucosamine-Induced Insulin Resistance in Primary Rat
... of the insulin signaling pathway that includes PI3-Kinase and Akt-1 (protein kinase B). Phosphorylation of GSK-3 reduces its kinase activity, thereby resulting in reduced phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and an increase in its enzymatic activity (Frame, Cohen etal. 2001). In glycolysis, one mole ...
... of the insulin signaling pathway that includes PI3-Kinase and Akt-1 (protein kinase B). Phosphorylation of GSK-3 reduces its kinase activity, thereby resulting in reduced phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and an increase in its enzymatic activity (Frame, Cohen etal. 2001). In glycolysis, one mole ...
Biochemistry - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... electron transport chain in the form of 3 NADH and 1 FADH2. So these are also formed in the reactions in the Krebs cycle and this NADH and FADH2 is utilized in oxidative phosphorylation for the production of ATP where we require these cofactors in the complexes 1, 2, 3 and 4 also. The citric acid cy ...
... electron transport chain in the form of 3 NADH and 1 FADH2. So these are also formed in the reactions in the Krebs cycle and this NADH and FADH2 is utilized in oxidative phosphorylation for the production of ATP where we require these cofactors in the complexes 1, 2, 3 and 4 also. The citric acid cy ...
Ecstasy-induced toxicity in rat liver
... Abstract: BackgroundAims." The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of single and repeated administration of 3.4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, "ecstasy") on rat liver. Mefllods." Animals were given an acute (20 mg/kg) and repeated (20 mg/kg, b.i.d., for 4 consecutive day's) int ...
... Abstract: BackgroundAims." The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of single and repeated administration of 3.4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, "ecstasy") on rat liver. Mefllods." Animals were given an acute (20 mg/kg) and repeated (20 mg/kg, b.i.d., for 4 consecutive day's) int ...
Engineering Cytosolic Acetyl-CoA Metabolism in
... A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain carrying deletions in all three pyruvate decarboxylase genes (also called Pdc negative yeast) represents a non-ethanol producing platform strain for biochemical production. However, it cannot grow on glucose as the sole carbon source due to the lack of cytosolic ace ...
... A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain carrying deletions in all three pyruvate decarboxylase genes (also called Pdc negative yeast) represents a non-ethanol producing platform strain for biochemical production. However, it cannot grow on glucose as the sole carbon source due to the lack of cytosolic ace ...
Peroxisomes and peroxisomal disorders: The main facts
... thiolytic cleavage. After each cycle, fatty acids are shortened of two carbon atoms which are released as acetyl-CoA (Lazarow and De Duve 1976; Rinaldo et al., 2002; Wanders, 2004) (Figure ...
... thiolytic cleavage. After each cycle, fatty acids are shortened of two carbon atoms which are released as acetyl-CoA (Lazarow and De Duve 1976; Rinaldo et al., 2002; Wanders, 2004) (Figure ...
Trace elements and vitamins - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Esential cofactor acts in posttranslational carboxylation of glutamic acid -Important in coagulation factors (II, VII, IX a X ) and other important proteins (protein C, protein S (Protein S free, Protein S total) -Reaction is inhibited by anticoagulant substances (warfarin) For this reason is Vitami ...
... Esential cofactor acts in posttranslational carboxylation of glutamic acid -Important in coagulation factors (II, VII, IX a X ) and other important proteins (protein C, protein S (Protein S free, Protein S total) -Reaction is inhibited by anticoagulant substances (warfarin) For this reason is Vitami ...
Salai guggal, the oleogum resin of the Boswellia serrata has been
... Sulfur bridges are responsible for the spatial structure of enzymes. Without sulfur bridges, enzymes would lack biological activity due to deviations in their spatial structure. Shortages in sulfur cause reduced production of biologically active enzymes, which result in a reduction of many metabolic ...
... Sulfur bridges are responsible for the spatial structure of enzymes. Without sulfur bridges, enzymes would lack biological activity due to deviations in their spatial structure. Shortages in sulfur cause reduced production of biologically active enzymes, which result in a reduction of many metabolic ...
Activation by Exercise of Human Skeletal Muscle Pyruvate
... preparations of heart and skeletal muscle, both Mgz+ and CaZ+are important activators of the enzyme [41, among other metabolites [21. The energy required for the regeneration of ATP during heavy exercise is largely derived from muscle glycogen, with only a minor proportion coming from fats and amino ...
... preparations of heart and skeletal muscle, both Mgz+ and CaZ+are important activators of the enzyme [41, among other metabolites [21. The energy required for the regeneration of ATP during heavy exercise is largely derived from muscle glycogen, with only a minor proportion coming from fats and amino ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.