Document
... • What type of bond connects Amino Acids? • What are lipids composed of? • What are three of the macromolecules of carbohydrates? What is the sugar ...
... • What type of bond connects Amino Acids? • What are lipids composed of? • What are three of the macromolecules of carbohydrates? What is the sugar ...
Biomolecules
... • What type of bond connects Amino Acids? • What are lipids composed of? • What are three of the macromolecules of carbohydrates? What is the sugar ...
... • What type of bond connects Amino Acids? • What are lipids composed of? • What are three of the macromolecules of carbohydrates? What is the sugar ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicants responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writt ...
... Public Health Nutrition. Applicants should use this form to self declare any relevant prior study which can be used as part of the admissions process and as outlined in the admissions requirement information. It is the applicants responsibility to ensure this form is completed sufficiently and writt ...
Biochemistry Metabolic pathways - Limes-Institut-Bonn
... • Only the liver and kidneys contain glucose-6-phosphatase Glucose regulation in the liver • When blood glucose is high (fed state), FA are synthesized by the liver, converted into triacylglycerols and packaged into VLDL that are secreted into the blood. • When blood glucose is low (fasting state), ...
... • Only the liver and kidneys contain glucose-6-phosphatase Glucose regulation in the liver • When blood glucose is high (fed state), FA are synthesized by the liver, converted into triacylglycerols and packaged into VLDL that are secreted into the blood. • When blood glucose is low (fasting state), ...
4.Lect Carbon skeleton intro
... AMINO ACID CATABOLISM Accounts for ~ 10% of energy requirement of adults Degradation exceeds demand for new protein When: There is excess protein in diet (amino acids are not stored) and also during starvation when carbohydrates are not available. ...
... AMINO ACID CATABOLISM Accounts for ~ 10% of energy requirement of adults Degradation exceeds demand for new protein When: There is excess protein in diet (amino acids are not stored) and also during starvation when carbohydrates are not available. ...
REGULATION OF BODY WEIGHT
... PROTEINS INVOLVED IN WEIGHT REGULATION STARVATION OBESITY DIABETES: TYPES I AND II ...
... PROTEINS INVOLVED IN WEIGHT REGULATION STARVATION OBESITY DIABETES: TYPES I AND II ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... Alcohol fermentation is carried a number of bacteria & yeasts. Organisms that produce lactic acid other acids or alcohols are known as heterolactic (or heterofermentative); often use the pentose phosphate pathway. Glucose + ADP + P —>Lactic acid + Ethanol + CO2+ ATP ...
... Alcohol fermentation is carried a number of bacteria & yeasts. Organisms that produce lactic acid other acids or alcohols are known as heterolactic (or heterofermentative); often use the pentose phosphate pathway. Glucose + ADP + P —>Lactic acid + Ethanol + CO2+ ATP ...
Document
... The ETC couples the transfer of electrons between a donor (like NADH) and an electron acceptor (like O2) with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, enabling the process of oxidative phosphorylation. In the presence of oxygen, energy is passed, stepwise, through t ...
... The ETC couples the transfer of electrons between a donor (like NADH) and an electron acceptor (like O2) with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, enabling the process of oxidative phosphorylation. In the presence of oxygen, energy is passed, stepwise, through t ...
Q01to05
... ATP = 4.8, ADP = 0.2, AMP in uM The total adenine nucleotide pool ([ATP] + [ADP] + [AMP]) in cells is about 5 mM ATP = 4.8, ADP = 0.2, AMP in uM ...
... ATP = 4.8, ADP = 0.2, AMP in uM The total adenine nucleotide pool ([ATP] + [ADP] + [AMP]) in cells is about 5 mM ATP = 4.8, ADP = 0.2, AMP in uM ...
3rd Fall - rci.rutgers.edu
... C) The free fatty acid must be carboxylated in the β position by a biotin-dependent reaction before the process of β oxidation commences; D) The free fatty acid must be converted to a thioester before the process of β oxidation commences; E) Two NADH are produced for each acetyl-CoA 18. Ketone bodie ...
... C) The free fatty acid must be carboxylated in the β position by a biotin-dependent reaction before the process of β oxidation commences; D) The free fatty acid must be converted to a thioester before the process of β oxidation commences; E) Two NADH are produced for each acetyl-CoA 18. Ketone bodie ...
Nutrients and the structure of macromolecules File
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular - Rose
... These tissues are tightly controlled by external signals: the levels of the pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon, the adrenal hormones epinephrine and cortisol, and, in the case of skeletal muscle, the neuronal signals that govern muscle contraction. The following description of events simplifie ...
... These tissues are tightly controlled by external signals: the levels of the pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon, the adrenal hormones epinephrine and cortisol, and, in the case of skeletal muscle, the neuronal signals that govern muscle contraction. The following description of events simplifie ...
1.2 organic molecules supplemental worksheet
... Standard: 1.2 - Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). ...
... Standard: 1.2 - Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... through production of more acid via metabolism elevated [H+] concentration inhibits PFK1 to slow acid production Inhibition by citrate - citrate is a feedback inhibitor of glycolysis by allosterically inactivating PFK-1 - fed state citrate derived from glucose carbons for fat production; excess ...
... through production of more acid via metabolism elevated [H+] concentration inhibits PFK1 to slow acid production Inhibition by citrate - citrate is a feedback inhibitor of glycolysis by allosterically inactivating PFK-1 - fed state citrate derived from glucose carbons for fat production; excess ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism - LSU School of Medicine
... Occurs only in the mitochondrial matrix First step - is reverse thiolase Second reaction makes HMG-CoA These reactions are mitochondrial analogues of the (cytosolic) first two steps of cholesterol synthesis Third step - HMG-CoA lyase - is similar to the reverse of citrate synthase ...
... Occurs only in the mitochondrial matrix First step - is reverse thiolase Second reaction makes HMG-CoA These reactions are mitochondrial analogues of the (cytosolic) first two steps of cholesterol synthesis Third step - HMG-CoA lyase - is similar to the reverse of citrate synthase ...
gluconeogenesis
... sucrose in germinating seeds begins in glyoxysomes, which produce succinate and export it to mitochondria. There it is converted to oxaloacetate by enzymes of the citric acid cycle. ...
... sucrose in germinating seeds begins in glyoxysomes, which produce succinate and export it to mitochondria. There it is converted to oxaloacetate by enzymes of the citric acid cycle. ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... What are the subunits of fats? Fatty acids ...
... What are the subunits of fats? Fatty acids ...
The Chemistry of Life
... 3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. 3.2.6 State three functions of lipids. 3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydra ...
... 3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. 3.2.6 State three functions of lipids. 3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydra ...
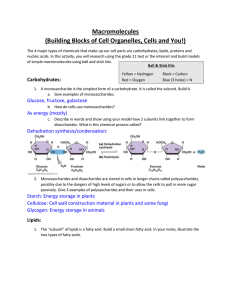
Macromolecules
... different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
... different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
Regulation of Glycolysis - Valdosta State University
... • Both mobilization and synthesis of glycogen are regulated by hormones and allosterically • Insulin, glucagon and epinephrine regulate mammalian glycogen metabolism (hormones) • Ca2+ and [AMP]/[ATP] (muscle glycogen ...
... • Both mobilization and synthesis of glycogen are regulated by hormones and allosterically • Insulin, glucagon and epinephrine regulate mammalian glycogen metabolism (hormones) • Ca2+ and [AMP]/[ATP] (muscle glycogen ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.