Conservation of the metabolomic response to starvation across two divergent microbes.
... consisting of nitrogen decreases. Elemental analysis of nitrogenstarved yeast revealed this to be the case (Fig. 2C). None of the other starvation conditions resulted in substantial changes in cellular elemental composition [see supporting information (SI) Table 1]. Thus, a major metabolic differenc ...
... consisting of nitrogen decreases. Elemental analysis of nitrogenstarved yeast revealed this to be the case (Fig. 2C). None of the other starvation conditions resulted in substantial changes in cellular elemental composition [see supporting information (SI) Table 1]. Thus, a major metabolic differenc ...
Vitamins
... • Tolerable upper intake: 1,500 IU/d (1,000 mg/d) • Side effects: impaired blood clotting/ risk of hemorrhage seen in adults with vit. E < 2,000 mg/d • Large oral supplements of vit. E have been associated with – Necrotizing enterocolitis in infants – Higher mortality due to hemorrhagic strokes in ...
... • Tolerable upper intake: 1,500 IU/d (1,000 mg/d) • Side effects: impaired blood clotting/ risk of hemorrhage seen in adults with vit. E < 2,000 mg/d • Large oral supplements of vit. E have been associated with – Necrotizing enterocolitis in infants – Higher mortality due to hemorrhagic strokes in ...
the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in glucose and ketone
... knockout (KO), PDK4 KO, and PDK2/PDK4 double knockout (DKO) mice were generated. PDK2 deficiency caused higher PDC activity and lower blood glucose levels in the fed state while PDK4 deficiency caused similar effects in the fasting state. DKO intensified these effects in both states. PDK2 deficiency ...
... knockout (KO), PDK4 KO, and PDK2/PDK4 double knockout (DKO) mice were generated. PDK2 deficiency caused higher PDC activity and lower blood glucose levels in the fed state while PDK4 deficiency caused similar effects in the fasting state. DKO intensified these effects in both states. PDK2 deficiency ...
Redox balances in the metabolism of sugars by yeasts
... be observed between different yeasts, especially with respect to the ability to utilise various sugars and the regulation of respiration and fermentation. Fundamental knowledge of the physiology of yeasts is a prerequisite for the successful use of these organisms. This holds both for improvements i ...
... be observed between different yeasts, especially with respect to the ability to utilise various sugars and the regulation of respiration and fermentation. Fundamental knowledge of the physiology of yeasts is a prerequisite for the successful use of these organisms. This holds both for improvements i ...
Redox balances in the metabolism of sugars by yeasts
... be observed between different yeasts, especially with respect to the ability to utilise various sugars and the regulation of respiration and fermentation. Fundamental knowledge of the physiology of yeasts is a prerequisite for the successful use of these organisms. This holds both for improvements i ...
... be observed between different yeasts, especially with respect to the ability to utilise various sugars and the regulation of respiration and fermentation. Fundamental knowledge of the physiology of yeasts is a prerequisite for the successful use of these organisms. This holds both for improvements i ...
Chapter 3
... • Others can be converted to metabolic intermediates – Contribute as a fuel in muscle • Overall, protein is not a primary energy source during exercise ...
... • Others can be converted to metabolic intermediates – Contribute as a fuel in muscle • Overall, protein is not a primary energy source during exercise ...
5. TCA Cycle
... Looking back at glycolysis Glucose + 2Pi + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ -> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O ...
... Looking back at glycolysis Glucose + 2Pi + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ -> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O ...
Environmental enteric dysfunction is associated with carnitine
... Fig. 1. The carnitine shuttle. Carnitine enters the cell through active transport by the high affinity carnitine transporter, organic cation transporter novel 2 (OCTN2). Long-chain fatty acidCoA in the cytosol exchanges CoA for carnitine by the action of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) in the ...
... Fig. 1. The carnitine shuttle. Carnitine enters the cell through active transport by the high affinity carnitine transporter, organic cation transporter novel 2 (OCTN2). Long-chain fatty acidCoA in the cytosol exchanges CoA for carnitine by the action of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) in the ...
Heart Failure and Loss of Metabolic Control
... Amino Acid Metabolism Amino acids are also important substrates for energy production in heart. Through transamination and deamination reactions, various amino acids generate metabolic intermediates and feed into the citric acid cycle. Early studies have shown that alanine is effectively secreted fr ...
... Amino Acid Metabolism Amino acids are also important substrates for energy production in heart. Through transamination and deamination reactions, various amino acids generate metabolic intermediates and feed into the citric acid cycle. Early studies have shown that alanine is effectively secreted fr ...
13synthesis
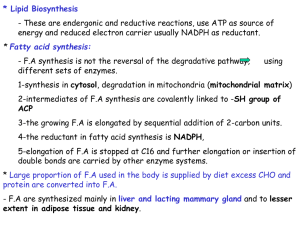
... * Excess of CHO stored as fats, While fats can’t used for glucose synthesis. * TG and phospholipids have the same precursors “Glycerol 3-phosphate” ...
... * Excess of CHO stored as fats, While fats can’t used for glucose synthesis. * TG and phospholipids have the same precursors “Glycerol 3-phosphate” ...
2-Phospho
... product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
How to deal with oxygen radicals stemming from mitochondrial fatty
... high FADH2/NADH ratios. Clockwise: 1. Development of mechanisms to induce (regulated) mild uncoupling (e.g. uncoupling proteins). 2. Segregation of fatty acid oxidation (completely in neurons, plants and some yeasts, limited to VLCFAs only in most mammalian cells). 3. Evolving specific mitophagy pat ...
... high FADH2/NADH ratios. Clockwise: 1. Development of mechanisms to induce (regulated) mild uncoupling (e.g. uncoupling proteins). 2. Segregation of fatty acid oxidation (completely in neurons, plants and some yeasts, limited to VLCFAs only in most mammalian cells). 3. Evolving specific mitophagy pat ...
Malonyl-CoA and AMP-activated protein kinase: An expanding
... The observations that the concentration of malonyl CoA diminishes by 50% within 20 min when an isolated soleus is deprived of glucose [2] and even more rapidly during electrically-induced contractions [5] suggests that malonyl CoA utilization as well as synthesis may be regulated. Since muscle does ...
... The observations that the concentration of malonyl CoA diminishes by 50% within 20 min when an isolated soleus is deprived of glucose [2] and even more rapidly during electrically-induced contractions [5] suggests that malonyl CoA utilization as well as synthesis may be regulated. Since muscle does ...
Cellular Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy
... The energy-investing reactions of glycolysis require ATP Using Figure 7.6, let us work our way through the glycolytic pathway. The first five reactions of glycolysis are endergonic; that is, the cell is investing free energy in the glucose molecule, rather than releasing energy from it. In two separ ...
... The energy-investing reactions of glycolysis require ATP Using Figure 7.6, let us work our way through the glycolytic pathway. The first five reactions of glycolysis are endergonic; that is, the cell is investing free energy in the glucose molecule, rather than releasing energy from it. In two separ ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.