Fast evolutionary rates associated with functional loss in class I
... to glycolysis in the presence of glucose immediately after invading the human host. This metabolic switch is dependent on extracellular glucose concentration. Four glucose transporters are encoded in the genome of S. mansoni, however, only two were shown to facilitate glucose diffusion. Results: By ...
... to glycolysis in the presence of glucose immediately after invading the human host. This metabolic switch is dependent on extracellular glucose concentration. Four glucose transporters are encoded in the genome of S. mansoni, however, only two were shown to facilitate glucose diffusion. Results: By ...
Medical Physiology
... Same functions as GH Synthesized in placenta Function during fetal period Placental lactogen Similar to GH Weaker affinity to GH receptor 100-1000 fold weaker Prolactin Pituitary produced 19-20% homologous to GH No growth promoting function GH binding protein 40% GH bound (inactive) 60% GH free (act ...
... Same functions as GH Synthesized in placenta Function during fetal period Placental lactogen Similar to GH Weaker affinity to GH receptor 100-1000 fold weaker Prolactin Pituitary produced 19-20% homologous to GH No growth promoting function GH binding protein 40% GH bound (inactive) 60% GH free (act ...
accelerated glucose discoloration method
... The non-enzymatic browning of glucose was investigated by accelerating the glucose degradation with or without heating glucose solutions for 1 h at 100°C with different reagents. Evaluation of the glucose degradation was performed using two types of glucose, glucose A and glucose B, in order to inve ...
... The non-enzymatic browning of glucose was investigated by accelerating the glucose degradation with or without heating glucose solutions for 1 h at 100°C with different reagents. Evaluation of the glucose degradation was performed using two types of glucose, glucose A and glucose B, in order to inve ...
Unraveling Biochemical Pathways Affected by Mitochondrial
... In addition to the degradation of glutamine, mitochondria are also involved in the metabolism of three other hydrophobic amino acids: valine, leucine and isoleucine (also known as branched amino acids [BCAAs]). Even if every tissue is virtually able to catabolize BCAAs, this activity is more importa ...
... In addition to the degradation of glutamine, mitochondria are also involved in the metabolism of three other hydrophobic amino acids: valine, leucine and isoleucine (also known as branched amino acids [BCAAs]). Even if every tissue is virtually able to catabolize BCAAs, this activity is more importa ...
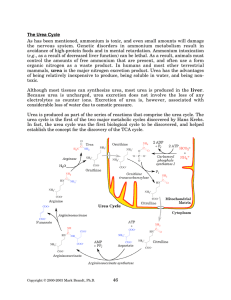
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... As mentioned previously, the major enzyme used for incorporating free ammonium into organic compounds, glutamine synthetase is also regulated. Glutamine synthetase activity is stimulated by a-ketoglutarate. This allows glutamine synthetase to some extent counter the effects of glutamate dehydrogenas ...
... As mentioned previously, the major enzyme used for incorporating free ammonium into organic compounds, glutamine synthetase is also regulated. Glutamine synthetase activity is stimulated by a-ketoglutarate. This allows glutamine synthetase to some extent counter the effects of glutamate dehydrogenas ...
Acetyl L-Carnitine
... ou may not think that your good health is related to the vitality of your cells, but it is. Your body is comprised of billions and billions of cells that work together in complex systems to keep you healthy. But each of these cells also has a unique life. A primary role of your body is to keep these ...
... ou may not think that your good health is related to the vitality of your cells, but it is. Your body is comprised of billions and billions of cells that work together in complex systems to keep you healthy. But each of these cells also has a unique life. A primary role of your body is to keep these ...
Chapter 9: Pathways that Harvest Chemical
... chemical fuel is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6). Other molecules, including other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, can also supply energy. However, to release their energy they must be converted into glucose or intermediate compounds that can enter into the various pathways of glucose metabolism. In ...
... chemical fuel is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6). Other molecules, including other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, can also supply energy. However, to release their energy they must be converted into glucose or intermediate compounds that can enter into the various pathways of glucose metabolism. In ...
On the role of gut microbiota in intestinal physiology and
... devoid of bacteria. This idea was conceived in 1885 by Pasteur, who postulated that germ-free (GF) life would be impossible5. Rearing GF animals is technically challenging, and historical documentation reveals several attempts that did not succeed in creating viable GF animals. The omnipresence of t ...
... devoid of bacteria. This idea was conceived in 1885 by Pasteur, who postulated that germ-free (GF) life would be impossible5. Rearing GF animals is technically challenging, and historical documentation reveals several attempts that did not succeed in creating viable GF animals. The omnipresence of t ...
3. BIOMOLECULES I. CARBOHYDRATES
... 4. 12.4. The fate of dietary proteins in heterotrophic organisms ............................................. 82 4.1. 12.4.1. The quality of proteins ................................................................................ 82 4.2. 12.4.2. The protein balance of the organism ................ ...
... 4. 12.4. The fate of dietary proteins in heterotrophic organisms ............................................. 82 4.1. 12.4.1. The quality of proteins ................................................................................ 82 4.2. 12.4.2. The protein balance of the organism ................ ...
Glycogen branches out: new perspectives on the role of glycogen
... in the exercise intensity of the protocols. In the studies where moderate-intensity exercise without fatigue is used, the observed increases in fat oxidation may compensate for the reduction in muscle glycogenolysis in the low-starting-glycogen groups, such that glucose transport into the muscle was ...
... in the exercise intensity of the protocols. In the studies where moderate-intensity exercise without fatigue is used, the observed increases in fat oxidation may compensate for the reduction in muscle glycogenolysis in the low-starting-glycogen groups, such that glucose transport into the muscle was ...
NVC Bio 120 lect 9 cell respiration
... Gycolysis and the citric acid cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
... Gycolysis and the citric acid cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
Chapter 9 Powerpoint
... energy extracted from the glucose. The electron escorts link glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the machinery of oxidative phosphorylation, which uses energy released from the electron transport chain to power ATP synthesis. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjam ...
... energy extracted from the glucose. The electron escorts link glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the machinery of oxidative phosphorylation, which uses energy released from the electron transport chain to power ATP synthesis. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjam ...
ATP
... Intestinal epithelial cells – mitochondria beneath the microvilli to release energy for the absorption of digested food by active transport Inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded to form cristae which are lined with stalked particles for oxidative phosphorylation while the enzymes of the Kreb ...
... Intestinal epithelial cells – mitochondria beneath the microvilli to release energy for the absorption of digested food by active transport Inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded to form cristae which are lined with stalked particles for oxidative phosphorylation while the enzymes of the Kreb ...
Cellular Respiration
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
LESSON 1. COMMON PATHWAY OF AMINO ACIDS
... liver diseases, the concentration of ammonia in the peripheral blood rises to toxic levels. Intestinal bacteria putrefy nitrogenous substances to form ammonia which is absorbed into Neomycin by its anti-bacterial action. This reduces the quantity of ammonia transported from the large intestine to th ...
... liver diseases, the concentration of ammonia in the peripheral blood rises to toxic levels. Intestinal bacteria putrefy nitrogenous substances to form ammonia which is absorbed into Neomycin by its anti-bacterial action. This reduces the quantity of ammonia transported from the large intestine to th ...
The Metabolism of Cellulose, Glucose and Starch by
... removed; Coleman, 1958) increased the protozoal population density by 60 % (100 % in one experiment) after 2 d. At most times there were fewer protozoa in the presence of rice starch than cellulose suggesting that with protozoa grown in vitro on dried grass as the sole source of food, cellulose was ...
... removed; Coleman, 1958) increased the protozoal population density by 60 % (100 % in one experiment) after 2 d. At most times there were fewer protozoa in the presence of rice starch than cellulose suggesting that with protozoa grown in vitro on dried grass as the sole source of food, cellulose was ...
to - HealthFitLabs
... Vitamin D (or the sunshine vitamin as its often referred to) is the only vitamin produced naturally by the human body, and technically classified as a hormone. Our superior combination has been formulated to work synergistically within the body, primarily to aid in the development and maintenance of ...
... Vitamin D (or the sunshine vitamin as its often referred to) is the only vitamin produced naturally by the human body, and technically classified as a hormone. Our superior combination has been formulated to work synergistically within the body, primarily to aid in the development and maintenance of ...
Reactions of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... phosphates are consumed per mole of glucose synthesized by gluconeogenesis. ...
... phosphates are consumed per mole of glucose synthesized by gluconeogenesis. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.