Enzymes & Energy
... Glycolysis - splits a glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvic acid Anaerobic respiration - occurs in the absence of oxygen; reduces pyruvic acid to lactic acid Aerobic respiration - occurs in the presence of oxygen and oxidizes pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water ...
... Glycolysis - splits a glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvic acid Anaerobic respiration - occurs in the absence of oxygen; reduces pyruvic acid to lactic acid Aerobic respiration - occurs in the presence of oxygen and oxidizes pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water ...
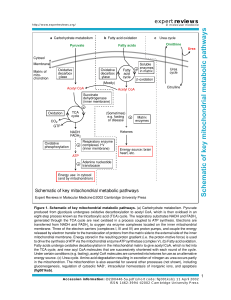
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... Honors Biology Worksheet - Carbohydrates 1. What types of atoms make up carbohydrates? Carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? There are twice as many hydrogens as oxygens. 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? Mon ...
... Honors Biology Worksheet - Carbohydrates 1. What types of atoms make up carbohydrates? Carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? There are twice as many hydrogens as oxygens. 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? Mon ...
2.3 Carbon Compounds
... Living organisms are made up of molecules that consist of carbon and other elements. ...
... Living organisms are made up of molecules that consist of carbon and other elements. ...
2.3_Carbon_Compounds
... that contain bonds between carbon atoms, while inorganic chemistry is the study of all other compounds In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms “organic,” believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. ...
... that contain bonds between carbon atoms, while inorganic chemistry is the study of all other compounds In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms “organic,” believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. ...
Milk Composition
... of fatty acid by weight - contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a potent anti-carcinogen (18:2), cis-9, trans-ll) formed in biohydrogenation of linoleic acid (normally about 0.5% of total fatty acids in milk) - main lipid class is triglycerides (97-98%) - fatty acids made from acetate and butyrat ...
... of fatty acid by weight - contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a potent anti-carcinogen (18:2), cis-9, trans-ll) formed in biohydrogenation of linoleic acid (normally about 0.5% of total fatty acids in milk) - main lipid class is triglycerides (97-98%) - fatty acids made from acetate and butyrat ...
Lecture 7: Metabolic Regulation - University of California, Berkeley
... glucose by the liver enzyme also go up, which allows the liver to take care of excess glucose. If you have lots of glucose, then the liver enzyme will function much faster and take away glucose. Glucagon levels goes down in response to high [glucose]. The opposite regulation of the PFK2/FBPase-2 wil ...
... glucose by the liver enzyme also go up, which allows the liver to take care of excess glucose. If you have lots of glucose, then the liver enzyme will function much faster and take away glucose. Glucagon levels goes down in response to high [glucose]. The opposite regulation of the PFK2/FBPase-2 wil ...
ergogenic aids
... Molecule that transports fatty acids into mitochondria. Research indicates that carnitine provides no ergogenic benefit. Phosphate Some evidence for increased VO 2max and VT. Sodium Bicarbonate Increases blood bicarbonate and buffering potential. Increases performance during intense intermittent exe ...
... Molecule that transports fatty acids into mitochondria. Research indicates that carnitine provides no ergogenic benefit. Phosphate Some evidence for increased VO 2max and VT. Sodium Bicarbonate Increases blood bicarbonate and buffering potential. Increases performance during intense intermittent exe ...
Biochemie jater
... Elevated consumption of ethanol over many years may lead to liver damage (the limit for a man is about 60g daily, and for a woman about 50g); these values are strongly dependent on body weight, health and the use of medication The high levels of NADH and acetyl-CoA inhibit citric acid cycle activi ...
... Elevated consumption of ethanol over many years may lead to liver damage (the limit for a man is about 60g daily, and for a woman about 50g); these values are strongly dependent on body weight, health and the use of medication The high levels of NADH and acetyl-CoA inhibit citric acid cycle activi ...
Lactic Acid System - PhysicalEducationatMSC
... produces lactate and hydrogen ions - for each lactate molecule, one hydrogen ion is formed. The presence of hydrogen ions, not lactate, makes the muscle acidic that will eventually halt muscle function. As hydrogen ion concentrations, increase the blood and muscle become acidic. This acidic environm ...
... produces lactate and hydrogen ions - for each lactate molecule, one hydrogen ion is formed. The presence of hydrogen ions, not lactate, makes the muscle acidic that will eventually halt muscle function. As hydrogen ion concentrations, increase the blood and muscle become acidic. This acidic environm ...
Carbohydrates
... • Energy rich molecules that can be used for energy – typically occurs when there is an absence of usable carbohydrates in the body • Major molecule that provides structure to biological membranes • Used as signaling molecules for communication between cells (steroid hormones) ...
... • Energy rich molecules that can be used for energy – typically occurs when there is an absence of usable carbohydrates in the body • Major molecule that provides structure to biological membranes • Used as signaling molecules for communication between cells (steroid hormones) ...
- Our Schools
... monomers known as Glycerol and fatty acids – Each monomer has 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids ...
... monomers known as Glycerol and fatty acids – Each monomer has 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids ...
Glycolysis I
... • Glucose is the only substrate for the brain and some skeletal muscle cells • In situations in which the glucose supply might become limiting, liver and kidney cells can indulge in regeneration of glucose from more oxidized starting materials • This process carries an energetic penalty; energy must ...
... • Glucose is the only substrate for the brain and some skeletal muscle cells • In situations in which the glucose supply might become limiting, liver and kidney cells can indulge in regeneration of glucose from more oxidized starting materials • This process carries an energetic penalty; energy must ...
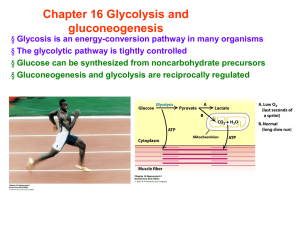
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... generate ATP and provide building blocks, such as fatty acid synthesis ...
... generate ATP and provide building blocks, such as fatty acid synthesis ...
Macromolecules - Issaquah Connect
... Macromolecules 1. Draw the functional groups for alcohols, carboxylic acids, and amines. 2. Most carbohydrates eaten by humans are in which two forms? (sugar and starch) 3. What is the function of starch? (storage in plants) 4. A starch molecule is a chain of what simple sugar units? (glucose) 5. Wh ...
... Macromolecules 1. Draw the functional groups for alcohols, carboxylic acids, and amines. 2. Most carbohydrates eaten by humans are in which two forms? (sugar and starch) 3. What is the function of starch? (storage in plants) 4. A starch molecule is a chain of what simple sugar units? (glucose) 5. Wh ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
Document
... Chemical properties of monosaccharides Reductive properties –only when free aldehyde or ketone group in saccharide molecule is present. In alkaline environment saccharides have reductive properties and ring can be opened In acidic environment saccharides are in cyclic form and there is no =CO gro ...
... Chemical properties of monosaccharides Reductive properties –only when free aldehyde or ketone group in saccharide molecule is present. In alkaline environment saccharides have reductive properties and ring can be opened In acidic environment saccharides are in cyclic form and there is no =CO gro ...
outlines
... -Tense state has low affinity for substrate -Relaxed state has high affinity for substrate -A change in a single subunit makes it easier for a change in another subunit Regulation by Phosphorylation -Ser, Thr, and Tyr residues can be phosphorylated by kinases (usually uses ATP) -Phosphorylation can ...
... -Tense state has low affinity for substrate -Relaxed state has high affinity for substrate -A change in a single subunit makes it easier for a change in another subunit Regulation by Phosphorylation -Ser, Thr, and Tyr residues can be phosphorylated by kinases (usually uses ATP) -Phosphorylation can ...
Document
... her friends tell her she is too skinny, but she is sure they are wrong because she still thinks of herself as chubby. She wants to lose even more weight. Melanie has an eating disorder called anorexia nervosa. Her body is not getting the nutrition it needs. She could die the the situation ...
... her friends tell her she is too skinny, but she is sure they are wrong because she still thinks of herself as chubby. She wants to lose even more weight. Melanie has an eating disorder called anorexia nervosa. Her body is not getting the nutrition it needs. She could die the the situation ...
Lecture 36
... if carbohydrate metabolism is properly balanced. When fatty acid oxidation produces more acetyl-CoA than can be combined with OAA to form citrate, then the "extra" acetyl-CoA is converted to acetoacetyl-CoA and ketone bodies, including acetone. Ketogenesis (synthesis of ketone bodies) takes place pr ...
... if carbohydrate metabolism is properly balanced. When fatty acid oxidation produces more acetyl-CoA than can be combined with OAA to form citrate, then the "extra" acetyl-CoA is converted to acetoacetyl-CoA and ketone bodies, including acetone. Ketogenesis (synthesis of ketone bodies) takes place pr ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.