Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P
... Gluconeogenesis I • Occurs mainly in liver and kidneys • Not the mere reversal of glycolysis for 2 reasons: – Energetics must change to make gluconeogenesis favorable (delta G of glycolysis = -74 kJ/mol – Reciprocal regulation must turn one on and the other off - this requires something new! ...
... Gluconeogenesis I • Occurs mainly in liver and kidneys • Not the mere reversal of glycolysis for 2 reasons: – Energetics must change to make gluconeogenesis favorable (delta G of glycolysis = -74 kJ/mol – Reciprocal regulation must turn one on and the other off - this requires something new! ...
Synthesis and Degradation of Lipids
... • Released into lymph/blood -> delivered to tissue • Triglyceride made by liver is packaged into VLDL part. -> • Released into blood • TAG hydrolyzed in periphery by lipoprotein lipase -> • FA uptake but glycerol back transport to liver and kidney • TAG in adipose tissue is mobilized by hormon ...
... • Released into lymph/blood -> delivered to tissue • Triglyceride made by liver is packaged into VLDL part. -> • Released into blood • TAG hydrolyzed in periphery by lipoprotein lipase -> • FA uptake but glycerol back transport to liver and kidney • TAG in adipose tissue is mobilized by hormon ...
Chapter 10. Delivering Oxygen.
... nucleus cannot make protein. As they get older, the cells suffer damage and finally after about 120 days the spleen removes old RBC’s. In normal blood, about 1 – 2 % of RBC’s are reticulocytes, the new RBC’s with a nucleus. Under conditions of chronic, long-term O2 deprivation, more capillaries form ...
... nucleus cannot make protein. As they get older, the cells suffer damage and finally after about 120 days the spleen removes old RBC’s. In normal blood, about 1 – 2 % of RBC’s are reticulocytes, the new RBC’s with a nucleus. Under conditions of chronic, long-term O2 deprivation, more capillaries form ...
Amino Acids
... off grass or wood has these specific bacteria in their guts to break the cellulose into digestible disaccharides.] ...
... off grass or wood has these specific bacteria in their guts to break the cellulose into digestible disaccharides.] ...
Energy systems of a runner. Presentation for Level
... adverse by-products (CO2 and lactic acid) that can be taken away Increased ability to store glycogen Increased ability to use fat as a fuel and SPARE glycogen ...
... adverse by-products (CO2 and lactic acid) that can be taken away Increased ability to store glycogen Increased ability to use fat as a fuel and SPARE glycogen ...
Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P
... Gluconeogenesis I • Occurs mainly in liver and kidneys • Not the mere reversal of glycolysis for 2 reasons: – Energetics must change to make gluconeogenesis favorable (delta G of glycolysis = -74 kJ/mol – Reciprocal regulation must turn one on and the other off - this requires something new! ...
... Gluconeogenesis I • Occurs mainly in liver and kidneys • Not the mere reversal of glycolysis for 2 reasons: – Energetics must change to make gluconeogenesis favorable (delta G of glycolysis = -74 kJ/mol – Reciprocal regulation must turn one on and the other off - this requires something new! ...
GOALS FOR LECTURE 7:
... energy (in the form of the Na+ gradient) since glucose is moving from a region where its concentration is low, in the lumen, to a region where its concentration is high, in the intestinal cell cytoplasm. Glucose is released by the cell into the bloodstream by passive transport down its concentration ...
... energy (in the form of the Na+ gradient) since glucose is moving from a region where its concentration is low, in the lumen, to a region where its concentration is high, in the intestinal cell cytoplasm. Glucose is released by the cell into the bloodstream by passive transport down its concentration ...
FATTY ACID OXIDATION Fatty acids are oxidized in several tissues
... Carnitine Acyltransferase (CAT/CPT) Deficiency (Myopathic Form): Although all tissues with mitochondria contain carnitine acyltransferase, the most common form of this genetic deficiency is myopathic and due to a defect in the musclespecific CAT/CPT gene. Hallmarks of this disease include: . Muscl ...
... Carnitine Acyltransferase (CAT/CPT) Deficiency (Myopathic Form): Although all tissues with mitochondria contain carnitine acyltransferase, the most common form of this genetic deficiency is myopathic and due to a defect in the musclespecific CAT/CPT gene. Hallmarks of this disease include: . Muscl ...
Chapter 2: Biochemistry
... also contain one or more chains of amino acids, the structural units of proteins. Glycine and alanine are examples of amino acids. If two amino acids are joined by dehydration synthesis, a peptide bond forms between them. The resulting molecule is a dipeptide. A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids ...
... also contain one or more chains of amino acids, the structural units of proteins. Glycine and alanine are examples of amino acids. If two amino acids are joined by dehydration synthesis, a peptide bond forms between them. The resulting molecule is a dipeptide. A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids ...
biochem notes
... Peptide Bond • Covalent bond linking two amino acids • A condensation reaction (water is formed and released) • Long chains of amino acids has positive and negative regions which fold to give protein molecules unique shapes • The shapes can be denatured when heated ...
... Peptide Bond • Covalent bond linking two amino acids • A condensation reaction (water is formed and released) • Long chains of amino acids has positive and negative regions which fold to give protein molecules unique shapes • The shapes can be denatured when heated ...
งานนำเสนอ PowerPoint
... permit its substrate and product to equilibrate • most of other reactions in a pathway function close to equilibrium • committed step = rate-limiting step ...
... permit its substrate and product to equilibrate • most of other reactions in a pathway function close to equilibrium • committed step = rate-limiting step ...
Nutrition Brief
... Protein and fat should replace the vast majority of grains in your diet. Protein contains an appetite inhibitor called PYY. Helps maintain healthy weight. Try to consume close to one ...
... Protein and fat should replace the vast majority of grains in your diet. Protein contains an appetite inhibitor called PYY. Helps maintain healthy weight. Try to consume close to one ...
Ch. 2 Notes Organic Chemistry
... are a special type of protein that acts as a biological catalyst. Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the Ea but are not affected themselves. * (This means that they do not become part of the product.) Enzymes can be affected by: changes in pH, temperature ...
... are a special type of protein that acts as a biological catalyst. Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the Ea but are not affected themselves. * (This means that they do not become part of the product.) Enzymes can be affected by: changes in pH, temperature ...
Fatty acid
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
[j26]Chapter 5#
... perform routine functions. These include such vital functions as the transport of materials across cell membranes; generating membrane potentials (chapter 6) and transmitting these electrical impulses (chapters 7-10); the synthesis and secretion of hormones (chapter 11); and muscle contraction (chap ...
... perform routine functions. These include such vital functions as the transport of materials across cell membranes; generating membrane potentials (chapter 6) and transmitting these electrical impulses (chapters 7-10); the synthesis and secretion of hormones (chapter 11); and muscle contraction (chap ...
Metabolism of Glycerol
... • lipases hydrolyze triacylglycerols, forming glycerol and free fatty acids, which are oxidized to acetyl CoA molecules for ATP synthesis. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... • lipases hydrolyze triacylglycerols, forming glycerol and free fatty acids, which are oxidized to acetyl CoA molecules for ATP synthesis. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Main concepts Carbohydrates Fats, Proteins and Enzymes
... are not consumed in a reaction do not affect the position of equilibrium are reaction-specific operate under mild conditions (especially temperature and pH). 41. In an enzyme-catalysed reaction the enzyme forms specific bonds with the particular reactant or (substrate) molecule(s) at the enzyme’s ac ...
... are not consumed in a reaction do not affect the position of equilibrium are reaction-specific operate under mild conditions (especially temperature and pH). 41. In an enzyme-catalysed reaction the enzyme forms specific bonds with the particular reactant or (substrate) molecule(s) at the enzyme’s ac ...
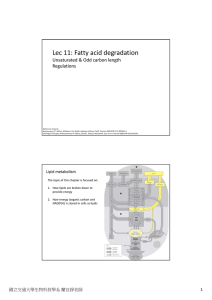
Lec 11: Fatty acid degradation
... Steps of this ω‐oxidation pathway: 1. P450 dependent oxidation of ω‐ carbon (no ...
... Steps of this ω‐oxidation pathway: 1. P450 dependent oxidation of ω‐ carbon (no ...
Guided Practice
... The set up contains an aquatic plant in a sealed test tube filled with water. The gas levels in the water were measured. The oxygen level measured at the beginning of the experiment is 50% and the carbon dioxide level is also 50%. After 24 hours of light, the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels are mea ...
... The set up contains an aquatic plant in a sealed test tube filled with water. The gas levels in the water were measured. The oxygen level measured at the beginning of the experiment is 50% and the carbon dioxide level is also 50%. After 24 hours of light, the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels are mea ...
Lipids and Proteins
... - Proteins are made up of small carbon compounds called ______________ ________. - There are __________ types of amino acids. Our bodies naturally make __________, but we must eat certain foods to obtain the other __________. - Proteins are different from carbs and lipids because they contain the el ...
... - Proteins are made up of small carbon compounds called ______________ ________. - There are __________ types of amino acids. Our bodies naturally make __________, but we must eat certain foods to obtain the other __________. - Proteins are different from carbs and lipids because they contain the el ...
Title: Hormones of the Pancreas
... hyperglycemia, glycosuria, ketosis ( → acetone breath ), acidosis ( → coma ) 14. Diagnosis of diabetes: a. Determination of urinary sugar b. Determination of blood glucose level c. The glucose tolerance test. 15. Types of diabetes: a. Insulin - dependent diabetes mellitus IDDM (type 1) - 10% • body ...
... hyperglycemia, glycosuria, ketosis ( → acetone breath ), acidosis ( → coma ) 14. Diagnosis of diabetes: a. Determination of urinary sugar b. Determination of blood glucose level c. The glucose tolerance test. 15. Types of diabetes: a. Insulin - dependent diabetes mellitus IDDM (type 1) - 10% • body ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.














![[j26]Chapter 5#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013325615_1-93c4a55e793afe312f3604738fdd639e-300x300.png)