EFFECT OF NUTRIENTS ON THE GENE EXPRESSION: Nutri
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
1 - WordPress.com
... (E) does not require biotin 42. Which one of the following is a characteristic of the product of the fatty acid synthase complex in the liver? (A) May be elongated to stearic acid (B) May be reduced to form oleic acid (C) May be oxidized directly to palmitic acid (D) May be converted to arachidonic ...
... (E) does not require biotin 42. Which one of the following is a characteristic of the product of the fatty acid synthase complex in the liver? (A) May be elongated to stearic acid (B) May be reduced to form oleic acid (C) May be oxidized directly to palmitic acid (D) May be converted to arachidonic ...
CHAPTER 6
... A special source of fuel and energy for certain tissues • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate ...
... A special source of fuel and energy for certain tissues • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate ...
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
... within mitochondria, organelles with two membranes that produce two compartments – The inner membrane encloses a central compartment containing the fluid matrix – The outer membrane surrounds the ...
... within mitochondria, organelles with two membranes that produce two compartments – The inner membrane encloses a central compartment containing the fluid matrix – The outer membrane surrounds the ...
Monosaccharides
... potent antioxidant properties, is important in antibacterial protection, detoxification, the synthesis of collagen in connective tissue. It insufficiency in the diet causes scurvy, decreases the body's resistance to infectious diseases etc. ...
... potent antioxidant properties, is important in antibacterial protection, detoxification, the synthesis of collagen in connective tissue. It insufficiency in the diet causes scurvy, decreases the body's resistance to infectious diseases etc. ...
Answer
... 45. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be re-used & why? Products are released and the enzyme shape returns to normal. The enzyme is recycled. 46. Besides temperature, what else can affect how an enzyme works by changing the enzyme's shape? Can the reaction still take p ...
... 45. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be re-used & why? Products are released and the enzyme shape returns to normal. The enzyme is recycled. 46. Besides temperature, what else can affect how an enzyme works by changing the enzyme's shape? Can the reaction still take p ...
Biology 105
... 4th stage - takes place in the mitochondria Results in chemiosmosis - formation of ATP as protons diffuse through transmembrane channels. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation Results in 32-34 ATP formed ...
... 4th stage - takes place in the mitochondria Results in chemiosmosis - formation of ATP as protons diffuse through transmembrane channels. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation Results in 32-34 ATP formed ...
Lh6Ch14aGlycolPPP
... – The general thermodynamics of each reaction. – Other sugars entry to glycolysis. – What to do with Pyruvate? ...
... – The general thermodynamics of each reaction. – Other sugars entry to glycolysis. – What to do with Pyruvate? ...
The Central Role of Acetyl-CoA
... ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of coenzymes that ultimately reduce oxygen to H2O • Reduction of oxygen to H2O yields more ATP and oxidised form of coenzymes ...
... ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of coenzymes that ultimately reduce oxygen to H2O • Reduction of oxygen to H2O yields more ATP and oxidised form of coenzymes ...
Approach to Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... Possible Metabolic Acidosis, hyperammonemia **Obtain serum/urine AAs/OAs** Treatment requires rapid removal of Branched chain AAs, often through dialysis. ...
... Possible Metabolic Acidosis, hyperammonemia **Obtain serum/urine AAs/OAs** Treatment requires rapid removal of Branched chain AAs, often through dialysis. ...
Macromolecules biologyjunction
... are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three ...
... are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three ...
File
... are large insoluble molecules that are ideal storage products. Carbohydrates provide a ready easily usable source of food energy for cells. Polysaccharides are long polymers consisting of up to hundreds of glucose ...
... are large insoluble molecules that are ideal storage products. Carbohydrates provide a ready easily usable source of food energy for cells. Polysaccharides are long polymers consisting of up to hundreds of glucose ...
biomolecule ppt
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
Intro powerpoint Energy systems
... This pathway is the first step to the complete breakdown of glucose The amount of ATP produced by this process will allow an athlete to engage in a high level of performance for an additional 1-3 minutes ...
... This pathway is the first step to the complete breakdown of glucose The amount of ATP produced by this process will allow an athlete to engage in a high level of performance for an additional 1-3 minutes ...
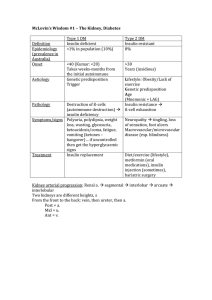
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... place in mitochondria. Occurs in three stages: – Acetyl-CoA binds a fourcarbon molecule and produces a six-carbon molecule. – Two carbons are removed as CO2. – Four-carbon starting material is regenerated. ...
... place in mitochondria. Occurs in three stages: – Acetyl-CoA binds a fourcarbon molecule and produces a six-carbon molecule. – Two carbons are removed as CO2. – Four-carbon starting material is regenerated. ...
C485 Exam I
... 5. (18 Pts) List all the enzyme activities (including transport) required to degrade the C14 fatty acid shown below (either show the reaction at least once, or describe it). Calculate the approximate yield in ATP molecules of the complete oxidation of this molecule. (Show how you arrive at this numb ...
... 5. (18 Pts) List all the enzyme activities (including transport) required to degrade the C14 fatty acid shown below (either show the reaction at least once, or describe it). Calculate the approximate yield in ATP molecules of the complete oxidation of this molecule. (Show how you arrive at this numb ...
Nutrition For Runners
... Too much simple sugar Training on too few calories Not consuming enough calories after workouts Swayed by the “magic bullet” ...
... Too much simple sugar Training on too few calories Not consuming enough calories after workouts Swayed by the “magic bullet” ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.