biosynthesis of fatty acids - Academic Research Collections
... a number of possibilities of their being combined with each other. Let us start with number one. Supposing there is one electron, you know it is negatively charged, so it will combine with a positively charged proton to form an atom. To recognize this atom it is given a particular name. The atom or ...
... a number of possibilities of their being combined with each other. Let us start with number one. Supposing there is one electron, you know it is negatively charged, so it will combine with a positively charged proton to form an atom. To recognize this atom it is given a particular name. The atom or ...
emboj2009339-sup
... initio (lane 7), added during the last 10, 20, 30 or 45 minutes of starvation (lanes 3-7) or omitted (lane 2). As control, cells were grown in glucose-rich medium (+ Glc) (lane 1). Equal amounts of protein lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Similar experiment ...
... initio (lane 7), added during the last 10, 20, 30 or 45 minutes of starvation (lanes 3-7) or omitted (lane 2). As control, cells were grown in glucose-rich medium (+ Glc) (lane 1). Equal amounts of protein lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Similar experiment ...
PDF - Agricultural Journals
... fatty acids can be catabolised by α-, β-, and ω-oxidation. The fatty acid (in the form of acyl-CoA thioesters) β-oxidation proceeds in mitochondria and in peroxisomes. It is the preferred degradation that leads to fatty acid by two carbons shorter in length. Mitochondrial oxidation is predominantly ...
... fatty acids can be catabolised by α-, β-, and ω-oxidation. The fatty acid (in the form of acyl-CoA thioesters) β-oxidation proceeds in mitochondria and in peroxisomes. It is the preferred degradation that leads to fatty acid by two carbons shorter in length. Mitochondrial oxidation is predominantly ...
AP Biology Chapter 9.2016
... • The last electron acceptor at the end of the chain is oxygen. • The ½ O2 accepts the 2 electrons and, together with H+ forms water. • NADH provides electrons that have enough energy to phosphorylate approximately 2.5 ADP to 2.5 ATP. ...
... • The last electron acceptor at the end of the chain is oxygen. • The ½ O2 accepts the 2 electrons and, together with H+ forms water. • NADH provides electrons that have enough energy to phosphorylate approximately 2.5 ADP to 2.5 ATP. ...
Disorders of Fatty Acid Oxidation in the Era of Tandem Mass
... homozygous for this common mutation, whereas another 18% are heterozygous for this mutation on one allele.19,47-49,51,52 No other common mutation has been identified.46,53 There appears to be no clear correlation between mutation type (the genetic defect) and clinical phenotype (the physical charact ...
... homozygous for this common mutation, whereas another 18% are heterozygous for this mutation on one allele.19,47-49,51,52 No other common mutation has been identified.46,53 There appears to be no clear correlation between mutation type (the genetic defect) and clinical phenotype (the physical charact ...
Module 2 General principles of metabolism. Мetabolism of carbohy
... E. * All reactions produce some heat. 17. Active holoenzymes are formed from ____________ in the presence of _________. A. Cofactors; proteins B. Proteins; cofactors C. * Apoenzymes; cofactors D. Apoenzymes; proteins E. Apoenzymes; inactive holoenzymes 18. An allosteric inhibitor of an enzyme usual ...
... E. * All reactions produce some heat. 17. Active holoenzymes are formed from ____________ in the presence of _________. A. Cofactors; proteins B. Proteins; cofactors C. * Apoenzymes; cofactors D. Apoenzymes; proteins E. Apoenzymes; inactive holoenzymes 18. An allosteric inhibitor of an enzyme usual ...
CHAPTER 6
... step bypasses the CO2-evolving steps of the TCA cycle to produce succinate and glyoxylate. The malate synthase reaction forms malate from glyoxylate and another acetyl-CoA. The result is that one turn of the cycle consumes one oxaloacetate and two acetyl-CoA molecules but produces two molecules of o ...
... step bypasses the CO2-evolving steps of the TCA cycle to produce succinate and glyoxylate. The malate synthase reaction forms malate from glyoxylate and another acetyl-CoA. The result is that one turn of the cycle consumes one oxaloacetate and two acetyl-CoA molecules but produces two molecules of o ...
What Is the Chemical Logic of the TCA Cycle?
... step bypasses the CO2-evolving steps of the TCA cycle to produce succinate and glyoxylate. The malate synthase reaction forms malate from glyoxylate and another acetyl-CoA. The result is that one turn of the cycle consumes one oxaloacetate and two acetyl-CoA molecules but produces two molecules of o ...
... step bypasses the CO2-evolving steps of the TCA cycle to produce succinate and glyoxylate. The malate synthase reaction forms malate from glyoxylate and another acetyl-CoA. The result is that one turn of the cycle consumes one oxaloacetate and two acetyl-CoA molecules but produces two molecules of o ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis in Protozoan Parasites: Unusual Pathways and
... To get the most out of host supplied fatty acids, parasites encode many pathways for customizing them for parasite-specific uses. Cryptosporidium parvum provides an excellent example of the unusual adaptations to utilize fatty acids from the environment. This intestinal parasite has apparently lost ...
... To get the most out of host supplied fatty acids, parasites encode many pathways for customizing them for parasite-specific uses. Cryptosporidium parvum provides an excellent example of the unusual adaptations to utilize fatty acids from the environment. This intestinal parasite has apparently lost ...
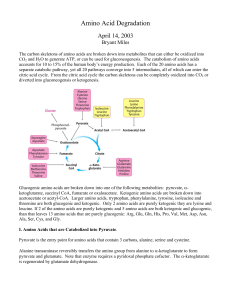
Amino Acid Degradation
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is phosphorylated by a kinase which inactivates the enzyme in a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency i ...
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is phosphorylated by a kinase which inactivates the enzyme in a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency i ...
Full-Text PDF
... systemic insulin resistance [10]. Meanwhile, fructose-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction causes insulin secretion as well, via activating sweet taste receptor (TR) signaling in humans and mice [14]. Impairment of β-cell mass and function inmales with high fructose diets result from dysregulation ...
... systemic insulin resistance [10]. Meanwhile, fructose-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction causes insulin secretion as well, via activating sweet taste receptor (TR) signaling in humans and mice [14]. Impairment of β-cell mass and function inmales with high fructose diets result from dysregulation ...
Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, Third Edition
... The food we eat has a major effect on our physical health and psychological wellbeing. An understanding of the way in which nutrients are metabolized, and hence of the principles of biochemistry, is essential for an understanding of the scientific basis of what we would call a prudent or healthy die ...
... The food we eat has a major effect on our physical health and psychological wellbeing. An understanding of the way in which nutrients are metabolized, and hence of the principles of biochemistry, is essential for an understanding of the scientific basis of what we would call a prudent or healthy die ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... 4. Compare the results of determining formaldehyde, glucose and sucrose by Fehling's reagent. 5. Compare the most important precipitation and colored chemical reactions for detecting proteins. 6. Compare the results of determining glycine and proteins using the ninhindrin reaction. 7. Analyse variou ...
... 4. Compare the results of determining formaldehyde, glucose and sucrose by Fehling's reagent. 5. Compare the most important precipitation and colored chemical reactions for detecting proteins. 6. Compare the results of determining glycine and proteins using the ninhindrin reaction. 7. Analyse variou ...
biochem ch 20 [2-9
... reaction catalyzed by succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase in reverse reaction) Reaction is example of substrate-level phosphorylation (formation of high-energy phosphate bond where none previously existed without use of molecular O2 [not oxidative phosphorylation]) High-energy phosphat ...
... reaction catalyzed by succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase in reverse reaction) Reaction is example of substrate-level phosphorylation (formation of high-energy phosphate bond where none previously existed without use of molecular O2 [not oxidative phosphorylation]) High-energy phosphat ...
Involvement of Polyamine Catabolism in the Regulation of Glucose
... activated polyamine catabolism-mediated depletion in the cellular ATP pool which activated the cellular energy sensor, 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PGC-1D. These results suggest that the enhancement of cellular ATP consumption is an efficient way to reduce body WAT mass and improve glu ...
... activated polyamine catabolism-mediated depletion in the cellular ATP pool which activated the cellular energy sensor, 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PGC-1D. These results suggest that the enhancement of cellular ATP consumption is an efficient way to reduce body WAT mass and improve glu ...
Structure, mechanism and regulation of pyruvate carboxylase
... enter the TCA cycle through PC and the PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) complex, and that these two fluxes are equally important for glucose-induced insulin secretion [32]. However, subsequent experiments using NMR analysis showed that pyruvate entering into mitochondria exists in two different pools. I ...
... enter the TCA cycle through PC and the PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) complex, and that these two fluxes are equally important for glucose-induced insulin secretion [32]. However, subsequent experiments using NMR analysis showed that pyruvate entering into mitochondria exists in two different pools. I ...
Nutrition to Support Recovery from Endurance Exercise: Optimal
... enhance aerobic adaptations during early base training stages (42). As such, these athletes may deliberately restrict carbohydrate intake during the postexercise recovery period to minimize glycogen resynthesis. While this emerging area of research is intriguing, the focus of the present review will ...
... enhance aerobic adaptations during early base training stages (42). As such, these athletes may deliberately restrict carbohydrate intake during the postexercise recovery period to minimize glycogen resynthesis. While this emerging area of research is intriguing, the focus of the present review will ...
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Background - Rose
... isozyme is normally considered to be the TCA cycle enzyme, while the NADPdependent enzyme is largely found in the cytoplasm, and is involved in production of NADPH for biosynthetic reactions. 4. a-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex The a -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is an enzyme complex sim ...
... isozyme is normally considered to be the TCA cycle enzyme, while the NADPdependent enzyme is largely found in the cytoplasm, and is involved in production of NADPH for biosynthetic reactions. 4. a-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex The a -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is an enzyme complex sim ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.