lect19-20
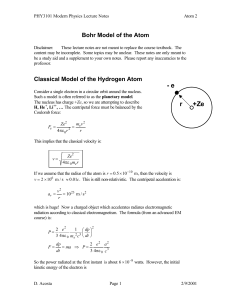
... reduces the repulsion and hence a lower energy solution results, ie. to take the electron from the state described by (y1+y2) and take it to infinite distance costs energy. It also follows that E+total < E-total The total energy is given by E+total = E+ + Up, where E+ is the energy of the electron i ...
... reduces the repulsion and hence a lower energy solution results, ie. to take the electron from the state described by (y1+y2) and take it to infinite distance costs energy. It also follows that E+total < E-total The total energy is given by E+total = E+ + Up, where E+ is the energy of the electron i ...
File
... Group 1 and Group 2 metals form 1+ and 2+ ions respectively, whereas oxygen and sulfur form 2 ions and the halogens 1 ions. (2) ...
... Group 1 and Group 2 metals form 1+ and 2+ ions respectively, whereas oxygen and sulfur form 2 ions and the halogens 1 ions. (2) ...
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
... produces continuous spectrum • Low-density hot gas produces emission spectrum • Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas produces absorption spectrum ...
... produces continuous spectrum • Low-density hot gas produces emission spectrum • Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas produces absorption spectrum ...
chapter 3 notes for power point
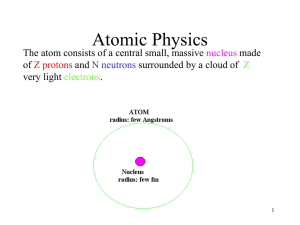
... greater the force between them. • The repulsive force between two protons is large when two protons are close together. • Protons form stable nuclei despite the repulsive force between them. • A strong attractive force between these protons overcomes the repulsive force at small distances. • Because ...
... greater the force between them. • The repulsive force between two protons is large when two protons are close together. • Protons form stable nuclei despite the repulsive force between them. • A strong attractive force between these protons overcomes the repulsive force at small distances. • Because ...
my Work 4 U
... This led to the idea that there may be sub-shells within each energy level. Further evidence for this comes from the lines in the emission spectra of atom. Some of the lines consist of two or more lines close together (i.e., at very similar energy levels). ...
... This led to the idea that there may be sub-shells within each energy level. Further evidence for this comes from the lines in the emission spectra of atom. Some of the lines consist of two or more lines close together (i.e., at very similar energy levels). ...
Energy Spectra for Fractional Quantum Hall
... E-mail: [email protected] Fractional quantum Hall states (FQHS) with the filling factor ν = p/q of q < 21 are examined and their energies are calculated. The classical Coulomb energy is evaluated among many electrons; that energy is linearly dependent on 1/ν. The residual binding energies are als ...
... E-mail: [email protected] Fractional quantum Hall states (FQHS) with the filling factor ν = p/q of q < 21 are examined and their energies are calculated. The classical Coulomb energy is evaluated among many electrons; that energy is linearly dependent on 1/ν. The residual binding energies are als ...
The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to
... The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to be a guide to the level and breadth of treatment expected. I. Structure of Matter A. Atomic theory and atomic structure 1. Evidence for the atomic theory 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic nu ...
... The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to be a guide to the level and breadth of treatment expected. I. Structure of Matter A. Atomic theory and atomic structure 1. Evidence for the atomic theory 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic nu ...
Atomic number
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
Word document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... “…determination of the stable motion of electrons in the atom introduces integers, and up to this point the only phenomena involving integers in physics were those of interference and of normal modes of vibration. This fact suggested to me the idea that electrons too could not be considered simply a ...
... “…determination of the stable motion of electrons in the atom introduces integers, and up to this point the only phenomena involving integers in physics were those of interference and of normal modes of vibration. This fact suggested to me the idea that electrons too could not be considered simply a ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 1. The atomic number of an element is __________________________? Does this number ever change for atoms of the same element? 2. The atomic mass number of an element is ___________________________? If this number changes for an atom of a specific element you have an (ion, isotope) __________________ ...
... 1. The atomic number of an element is __________________________? Does this number ever change for atoms of the same element? 2. The atomic mass number of an element is ___________________________? If this number changes for an atom of a specific element you have an (ion, isotope) __________________ ...
Hydrogen`s Atomic Orbitals
... Four d orbitals have identical shapes but different orientations. However, the fifth, dz2 orbital is shaped and oriented differently from the other four. ...
... Four d orbitals have identical shapes but different orientations. However, the fifth, dz2 orbital is shaped and oriented differently from the other four. ...
Quantum Numbers (and their meaning)
... m states is always odd (2 + 1) and should produce odd number of ...
... m states is always odd (2 + 1) and should produce odd number of ...
Electrons
... • Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. • The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy level ...
... • Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. • The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy level ...
CP Chemistry Final Exam Review Sheet
... e. Lewis/Electron dot structures show what type of electrons? Valence electrons in the valence (outermost) shell (s and p sublevels) *remember: group # = # valence electrons (for group A elements) 31. What is the name of the lowest, most stable energy level an electron occupies within an atom? groun ...
... e. Lewis/Electron dot structures show what type of electrons? Valence electrons in the valence (outermost) shell (s and p sublevels) *remember: group # = # valence electrons (for group A elements) 31. What is the name of the lowest, most stable energy level an electron occupies within an atom? groun ...
course materials
... Ria Broer and Remco Havenith, Theoretical Chemistry, University of Groningen This course considers the theoretical treatment of the geometrical and electronic structure of solids and surfaces and of molecule-surface interactions. For molecules a much-used approximation is molecular orbital (MO) theo ...
... Ria Broer and Remco Havenith, Theoretical Chemistry, University of Groningen This course considers the theoretical treatment of the geometrical and electronic structure of solids and surfaces and of molecule-surface interactions. For molecules a much-used approximation is molecular orbital (MO) theo ...
organic chemistry i
... Bond strength can be predicted using the orbital overlap model. Which makes the stronger bond, a face-to-face overlap or a sideways overlap? Explain your choice of answer ...
... Bond strength can be predicted using the orbital overlap model. Which makes the stronger bond, a face-to-face overlap or a sideways overlap? Explain your choice of answer ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.