Bioenergetics Key
... 7. Explain why hydrolysis of a thioester releases more energy than hydrolysis of an ester. a thioester has no resonance between the sulfur and the oxygen while an ester does. Therefore an ester has lower energy. when either is hydrolyzed, the result is a resonance stabilized carboxylate ion. 8. What ...
... 7. Explain why hydrolysis of a thioester releases more energy than hydrolysis of an ester. a thioester has no resonance between the sulfur and the oxygen while an ester does. Therefore an ester has lower energy. when either is hydrolyzed, the result is a resonance stabilized carboxylate ion. 8. What ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... The atomic mass of an element is the mass average of the atomic masses of the different isotopes of an element. For example, naturally occurring carbon, for example, is a mixture of two isotopes, 12C (98.89%) and 13C (1.11 %). Individual carbon atoms therefore have a mass of either 12.000 or 13.0335 ...
... The atomic mass of an element is the mass average of the atomic masses of the different isotopes of an element. For example, naturally occurring carbon, for example, is a mixture of two isotopes, 12C (98.89%) and 13C (1.11 %). Individual carbon atoms therefore have a mass of either 12.000 or 13.0335 ...
Exam 3 Key
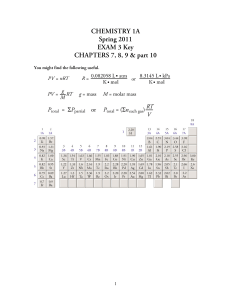
... CHEMISTRY 1A Spring 2011 EXAM 3 Key CHAPTERS 7, 8, 9 & part 10 You might find the following useful. ...
... CHEMISTRY 1A Spring 2011 EXAM 3 Key CHAPTERS 7, 8, 9 & part 10 You might find the following useful. ...
Quantum Theory of Light. Matter Waves.
... aspects of the reality. However, the physical reality arises from small-scale world of atoms and molecules, electrons and nuclei. Electrons behave as particles because they have charge and mass, but moving electrons also show evidence of behaving as waves (diffraction, interference). The wave-partic ...
... aspects of the reality. However, the physical reality arises from small-scale world of atoms and molecules, electrons and nuclei. Electrons behave as particles because they have charge and mass, but moving electrons also show evidence of behaving as waves (diffraction, interference). The wave-partic ...
Chemistry Scavenger Hunt
... 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter are made from _______________________ of these atoms. A material in which ...
... 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter are made from _______________________ of these atoms. A material in which ...
Unit 1
... 1. To know that chemical bonds, the forces that hold atoms together (text definition), are the lowering of energy when atoms come together (additional definition). 2. To describe, differentiate, and give examples of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. 3. To use Lewis dot symbols for atoms and ions ...
... 1. To know that chemical bonds, the forces that hold atoms together (text definition), are the lowering of energy when atoms come together (additional definition). 2. To describe, differentiate, and give examples of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. 3. To use Lewis dot symbols for atoms and ions ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... In the Stern-Gerlanch experiment,as it is now know,silver is vaporized in an oven, and some of the atoms in that vapor escape through a narrow slit in the oven wall,into an evacuated tube.Some of those escaping atoms then pass through a second narrow slit,to form a narrow beam of atoms. The beam pas ...
... In the Stern-Gerlanch experiment,as it is now know,silver is vaporized in an oven, and some of the atoms in that vapor escape through a narrow slit in the oven wall,into an evacuated tube.Some of those escaping atoms then pass through a second narrow slit,to form a narrow beam of atoms. The beam pas ...
P1_8 Muonic Atoms - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... kg, and the mass of a proton (the positive nucleus) is taken as 1.672621777 , since these are the current recommended values [4]. Substituting the appropriate values into Eq. 2 yields a reduced mass of a muon of 186 times larger than the reduced mass of an electron. On substituting electrons for muo ...
... kg, and the mass of a proton (the positive nucleus) is taken as 1.672621777 , since these are the current recommended values [4]. Substituting the appropriate values into Eq. 2 yields a reduced mass of a muon of 186 times larger than the reduced mass of an electron. On substituting electrons for muo ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... 3. The arrangement of the elements in groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of th ...
... 3. The arrangement of the elements in groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of th ...
Electron Arrangement
... Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents, like water. Covalent compounds (like candle wax) dissolve in covalent solvents (like hexane). Electrical Conductivity Metals conduct when solid or liquid. Covalent compounds don’t conduct at all. Ionic compounds only conduct when molten (liquid) or in solu ...
... Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents, like water. Covalent compounds (like candle wax) dissolve in covalent solvents (like hexane). Electrical Conductivity Metals conduct when solid or liquid. Covalent compounds don’t conduct at all. Ionic compounds only conduct when molten (liquid) or in solu ...
Microsoft Word
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
n-1 - KAIST
... The kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to give the quantized energies of the system and the form of the wavefunction so that other properties may be calculated. The wave nature of the electron has been clearly shown in experiments lik ...
... The kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to give the quantized energies of the system and the form of the wavefunction so that other properties may be calculated. The wave nature of the electron has been clearly shown in experiments lik ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – C Carbon b atoms have h different diff chemical h i l andd physical h i l properties than sulfur atoms. ...
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – C Carbon b atoms have h different diff chemical h i l andd physical h i l properties than sulfur atoms. ...
PPT File
... The kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to give the quantized energies of the system and the form of the wavefunction so that other properties may be calculated. The wave nature of the electron has been clearly shown in experiments lik ...
... The kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to give the quantized energies of the system and the form of the wavefunction so that other properties may be calculated. The wave nature of the electron has been clearly shown in experiments lik ...
Chapter: 12 - Physics365.com
... the energy of the electron continuously decreases and it must spiral down into the nucleus. Thus, the atom cannot be stable. But, it is well known that most of the atoms are stable. (ii) According to classical electromagnetic theory, the accelerating electron must radiate energy continuously . This ...
... the energy of the electron continuously decreases and it must spiral down into the nucleus. Thus, the atom cannot be stable. But, it is well known that most of the atoms are stable. (ii) According to classical electromagnetic theory, the accelerating electron must radiate energy continuously . This ...
Document
... ii. subatomic particles and their relation to the atom and each other. a. proton, neutron & electron b. quarks and other subatomic particles C. Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass, & Isotopes i. know meaning of each and how to use to find out information about the structure of the atom. (such as ...
... ii. subatomic particles and their relation to the atom and each other. a. proton, neutron & electron b. quarks and other subatomic particles C. Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass, & Isotopes i. know meaning of each and how to use to find out information about the structure of the atom. (such as ...
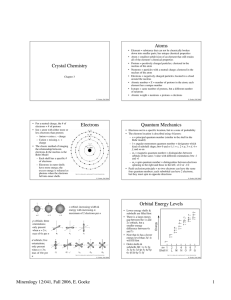
Crystal Chemistry Atoms Electrons Quantum Mechanics Orbital
... • The electron location is described using 4 factors: – n = principal quantum number (similar to the shell in the Bohr model) – l = angular momentum quantum number = designates which kind of subshell shape; btw 0 and n-1; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d, 4 = f, and so on – ml = magnetic quantum number = disting ...
... • The electron location is described using 4 factors: – n = principal quantum number (similar to the shell in the Bohr model) – l = angular momentum quantum number = designates which kind of subshell shape; btw 0 and n-1; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d, 4 = f, and so on – ml = magnetic quantum number = disting ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms
... Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vertical column on periodic table Isotopes- atoms of the same element with a ...
... Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vertical column on periodic table Isotopes- atoms of the same element with a ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.