02_Lecture_Presentation
... • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell ...
... • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... must each lose or gain electrons in order to become stable. Oxygen has 8 electrons and hence an electron arrangement of 2, 6. This means it has 6 electrons in its valence shell. It must hence ...
... must each lose or gain electrons in order to become stable. Oxygen has 8 electrons and hence an electron arrangement of 2, 6. This means it has 6 electrons in its valence shell. It must hence ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... Our perception of the modern model of the atom has developed over time and allows us to make predictions about how chemicals will act when combined. ...
... Our perception of the modern model of the atom has developed over time and allows us to make predictions about how chemicals will act when combined. ...
Lecture Trends in the Periodic Table - NGHS
... Because of the force of attraction between objects of opposite charge, the most important factor influencing the energy of an orbital is its size and therefore the value of the principal quantum number, n. For an atom that contains only one electron, there is no difference between the energies of th ...
... Because of the force of attraction between objects of opposite charge, the most important factor influencing the energy of an orbital is its size and therefore the value of the principal quantum number, n. For an atom that contains only one electron, there is no difference between the energies of th ...
Lecture 14 1 Entanglement and Spin
... Claim: The ground state of this system is an entangled state! Namely, ¯ψ = 21 ¯0 1 ¯1 2 − ¯1 1 ¯0 2 , a Bell state! How do we show this? It’s the same old quantum story, solving the Schr. equation. So what is Ĥ? We must figure out how these electrons interact with each other. What effect could one ...
... Claim: The ground state of this system is an entangled state! Namely, ¯ψ = 21 ¯0 1 ¯1 2 − ¯1 1 ¯0 2 , a Bell state! How do we show this? It’s the same old quantum story, solving the Schr. equation. So what is Ĥ? We must figure out how these electrons interact with each other. What effect could one ...
Chapters 7, 8, 9 notes - SLCUSD Staff Directory
... opposite ________. Only two electrons can occupy an _____________, and they must have opposite ___. That’s because spinning electrons create a ___________ field. The opposite spins create opposite magnetic fields which are stronger than the ___________________ repulsion that two electrons create. Fo ...
... opposite ________. Only two electrons can occupy an _____________, and they must have opposite ___. That’s because spinning electrons create a ___________ field. The opposite spins create opposite magnetic fields which are stronger than the ___________________ repulsion that two electrons create. Fo ...
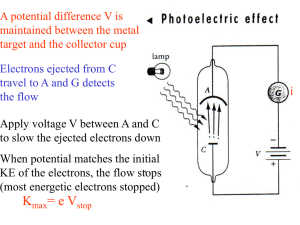
V stop f
... • Vstop does not depend on the intensity of the light source for a given frequency f • => classical physics would predict that if we increase the amplitude of the alternating electric field, then a larger kick would be given to the electron? • => if light is composed of photons, then the maximum ene ...
... • Vstop does not depend on the intensity of the light source for a given frequency f • => classical physics would predict that if we increase the amplitude of the alternating electric field, then a larger kick would be given to the electron? • => if light is composed of photons, then the maximum ene ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... • When Main Group elements react, electrons can be transferred (usually from a metal to a nonmetal) to form ionic bonds. In other cases, pairs of electrons can be shared (usually between nonmetal atoms) to form covalent bonds. In both cases valence electrons are somehow “rearranged” when new chemica ...
... • When Main Group elements react, electrons can be transferred (usually from a metal to a nonmetal) to form ionic bonds. In other cases, pairs of electrons can be shared (usually between nonmetal atoms) to form covalent bonds. In both cases valence electrons are somehow “rearranged” when new chemica ...
collective states of 2d electron-hole system under the influence of
... magnetoexciton ground state energy, and the energy of the single-particle elementary excitations were obtained. The energy per one e–h pair inside the electron-hole droplets found to be situated on the energy scale lower than the value of the chemical potential of the Bose–Einstein condensed magneto ...
... magnetoexciton ground state energy, and the energy of the single-particle elementary excitations were obtained. The energy per one e–h pair inside the electron-hole droplets found to be situated on the energy scale lower than the value of the chemical potential of the Bose–Einstein condensed magneto ...
2015-2016 AP CHEMISTRY MIDTERM EXAM Review
... A) Lattice of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic forces B) Closely packed lattice with delocalized electrons throughout C) Strong single covalent bonds with weak intermolecular forces D) Strong multiple covalent bonds (including π-bonds) with weak intermolecular forces E) Macr ...
... A) Lattice of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic forces B) Closely packed lattice with delocalized electrons throughout C) Strong single covalent bonds with weak intermolecular forces D) Strong multiple covalent bonds (including π-bonds) with weak intermolecular forces E) Macr ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reaction? 88. What does a ca ...
... 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reaction? 88. What does a ca ...
What`s the big idea? - Perimeter Institute
... waves are created by things that oscillate, and there’s nothing oscillating about a rotating ring. A rotating ring of charge would create ...
... waves are created by things that oscillate, and there’s nothing oscillating about a rotating ring. A rotating ring of charge would create ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.