HAPPY WEDNESDAY
... - increase an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce. Humans have thousands of adaptations: large brain, opposable thumbs, excellent sensory organs, light, strong skeleton, etc. ...
... - increase an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce. Humans have thousands of adaptations: large brain, opposable thumbs, excellent sensory organs, light, strong skeleton, etc. ...
Evolution * Natural Selection
... reach tall leaves, this results in a long neck. This trait is then inherited by the kids. ...
... reach tall leaves, this results in a long neck. This trait is then inherited by the kids. ...
H15-R13 - Uplift Education
... environment are more likely to survive and will reproduce more successfully than those that do not have such traits Darwin called this differential rate of reproduction as _____________ ___________________ With time, these favorable characteristics are carried on to the next generation and thus the ...
... environment are more likely to survive and will reproduce more successfully than those that do not have such traits Darwin called this differential rate of reproduction as _____________ ___________________ With time, these favorable characteristics are carried on to the next generation and thus the ...
Ch 3 Lecture
... Divergent evolution • Species w/common ancestor evolve diff structures from a similar original structure • Homologous structuresdiff fxn but similar evolutionary origin • Vestigial organs- parts of body retained but no current fxn ...
... Divergent evolution • Species w/common ancestor evolve diff structures from a similar original structure • Homologous structuresdiff fxn but similar evolutionary origin • Vestigial organs- parts of body retained but no current fxn ...
File
... 12. Why does genetic variation increase the chance that some individuals in a population will survive. The greater the variation of phenotypes in a population, the more likely it is that some individuals can survive a changing environment. 13. Describe two main sources of genetic variation. Mutation ...
... 12. Why does genetic variation increase the chance that some individuals in a population will survive. The greater the variation of phenotypes in a population, the more likely it is that some individuals can survive a changing environment. 13. Describe two main sources of genetic variation. Mutation ...
Evolution Study Guide Answers
... resources, this is known as Overproduction 19. If there are more organisms than resources, Competition will occur between members of the same species. This does not mean animals of the same species will fight one another but simply that some will find enough to eat while others will not. 20. What ar ...
... resources, this is known as Overproduction 19. If there are more organisms than resources, Competition will occur between members of the same species. This does not mean animals of the same species will fight one another but simply that some will find enough to eat while others will not. 20. What ar ...
Study Guide Extra Credit Ch 14
... 10. Describe the habitat of Isabella, Hood and Pinta Island. What is the neck like of each tortoise there? ...
... 10. Describe the habitat of Isabella, Hood and Pinta Island. What is the neck like of each tortoise there? ...
Study Guide Extra Credit 15 16
... 10. Describe the habitat of Isabella, Hood and Pinta Island. What is the neck like of each tortoise there? ...
... 10. Describe the habitat of Isabella, Hood and Pinta Island. What is the neck like of each tortoise there? ...
Evolution quiz
... 5. According to Darwin’s theory of evolution, differences found among the finches of the various Galapagos Islands are the result of a. The accumulation of characteristics acquired by the parents b. The disuse of specific body structure c. The size of the island where the finches live d. The moveme ...
... 5. According to Darwin’s theory of evolution, differences found among the finches of the various Galapagos Islands are the result of a. The accumulation of characteristics acquired by the parents b. The disuse of specific body structure c. The size of the island where the finches live d. The moveme ...
1. Ch. 14 PPT Notes part 1
... • Wild plants and animals have inherited variations • Struggle for existence – only the “fit” survive • Individuals whose characteristics are well-suited to the environment survive. Individuals whose characteristics are not well-suited to their environment either die or leave fewer offspring. (Survi ...
... • Wild plants and animals have inherited variations • Struggle for existence – only the “fit” survive • Individuals whose characteristics are well-suited to the environment survive. Individuals whose characteristics are not well-suited to their environment either die or leave fewer offspring. (Survi ...
Bellwork: January 9
... Evolution: change in heritable traits of a population across generations (over time). ...
... Evolution: change in heritable traits of a population across generations (over time). ...
Question Excerpt From chapter 15 Darwins theory of evolution
... Q.15)these changes over time increase the _________ of a species in its environment Q.16)what are the four indirect evidence of evolution? ( 13 words or 7 words ) ...
... Q.15)these changes over time increase the _________ of a species in its environment Q.16)what are the four indirect evidence of evolution? ( 13 words or 7 words ) ...
Changes Over Time Chapter 5
... The __________ of a radioactive element is the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample to ...
... The __________ of a radioactive element is the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample to ...
Evolution Notes
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
Genus specific epithet
... • Understanding Evolution. University of California Museum of Paleontology ...
... • Understanding Evolution. University of California Museum of Paleontology ...
Name: _______ Per: _____ Notes: Evolution Vocab Builder 1
... Today, we know these variations are the result of mutations. ...
... Today, we know these variations are the result of mutations. ...
Evolution
... Speciation o The isolation of populations can lead to speciation Speciation is the rise of two or more species from one existing species o Populations become isolated when This means their gene pools are separated; there is no more movement of alleles between the populations. Isolated populati ...
... Speciation o The isolation of populations can lead to speciation Speciation is the rise of two or more species from one existing species o Populations become isolated when This means their gene pools are separated; there is no more movement of alleles between the populations. Isolated populati ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Evolution Vocab Card Definitions
... Developed the theory of natural selection which says that the most fit organisms are more likely to survive and reproduce ...
... Developed the theory of natural selection which says that the most fit organisms are more likely to survive and reproduce ...
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations AP Biology Reading
... 6. Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? 7. Several sources of genetic variation are available. What is the ultimate source of new allele ...
... 6. Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? 7. Several sources of genetic variation are available. What is the ultimate source of new allele ...
Ch. 23 The Evolution of Populations Reading Guide 9th Edition
... 6. Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? 7. Several sources of genetic variation are available. What is the ultimate source of new allele ...
... 6. Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? 7. Several sources of genetic variation are available. What is the ultimate source of new allele ...
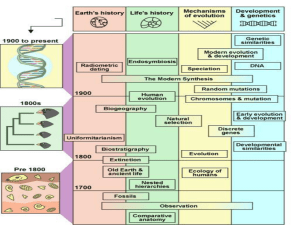
Chapter 2 the Development of Evolutionary Theory
... Copernicus challenged the idea that the earth was the center of the universe. Galileo’s work supported the idea that the universe was a place of motion rather than ...
... Copernicus challenged the idea that the earth was the center of the universe. Galileo’s work supported the idea that the universe was a place of motion rather than ...
MaryPaulEvidence Evolution
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural SelectionThe process by which the organisms whose characteristics are well-suited for their environment survive and reproduce. ...
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural SelectionThe process by which the organisms whose characteristics are well-suited for their environment survive and reproduce. ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.