The 2 fundamental questions: Linneaus and Kirchner
... y 1858 – The Linnaean Society y Wallace’s Ternate paper + y Darwin’s letter to Asa Gray y 1859 – “Origin of Species” ...
... y 1858 – The Linnaean Society y Wallace’s Ternate paper + y Darwin’s letter to Asa Gray y 1859 – “Origin of Species” ...
Developing a Theory of Evolution - biology-rocks
... What is Evolution?? It is a theory explaining the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. ...
... What is Evolution?? It is a theory explaining the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. ...
5_Week_of_February_6-11,_2012__files/Natural Selection PPT
... • Natural selection: the process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do • Adaptation: a characteristic that improves an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment • ...
... • Natural selection: the process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do • Adaptation: a characteristic that improves an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment • ...
EVOLUTION Practice TestHISTORY
... For each type of evidence for evolution listed below, describe what it is, and how it shows change over time in a species. ...
... For each type of evidence for evolution listed below, describe what it is, and how it shows change over time in a species. ...
You Light Up My Life
... First, members of a natural population will compete for limited resources, such as food and shelter, as their size increases. Second, some varieties of the individuals’ heritable traits will improve survival and reproductive chances. Third, those with the adaptive forms of these traits will be m ...
... First, members of a natural population will compete for limited resources, such as food and shelter, as their size increases. Second, some varieties of the individuals’ heritable traits will improve survival and reproductive chances. Third, those with the adaptive forms of these traits will be m ...
Species
... inferred evolution by natural selection. • Darwin had the idea first, but only published his book once he knew Wallace had also arrived at the same conclusion – Darwin had been working on it for over 20 years!! • Darwin explained his theory more completely and with more supporting evidence, and es ...
... inferred evolution by natural selection. • Darwin had the idea first, but only published his book once he knew Wallace had also arrived at the same conclusion – Darwin had been working on it for over 20 years!! • Darwin explained his theory more completely and with more supporting evidence, and es ...
Descent with modification II
... have probably been copied from a common ancestor. • For example, the number of amino acid differences in human hemoglobin when compared to other vertebrates show the same patterns of evolutionary relationships that researchers find based on other proteins or other types of data. ...
... have probably been copied from a common ancestor. • For example, the number of amino acid differences in human hemoglobin when compared to other vertebrates show the same patterns of evolutionary relationships that researchers find based on other proteins or other types of data. ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... evolution. However, Darwin's theory did not explain sources of genetic variation Variations within a species increase the chance of survival when conditions change. ...
... evolution. However, Darwin's theory did not explain sources of genetic variation Variations within a species increase the chance of survival when conditions change. ...
Unit 3 Test Review Solutions File
... 56. Producing large numbers of young means that some will likely survive even if most of them die before they reach adulthood. In many cases, animals do not provide a lot of care to young produced in large numbers. Frogs and turtles are examples. Having a smaller number of young allows for each one ...
... 56. Producing large numbers of young means that some will likely survive even if most of them die before they reach adulthood. In many cases, animals do not provide a lot of care to young produced in large numbers. Frogs and turtles are examples. Having a smaller number of young allows for each one ...
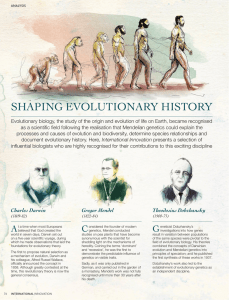
shaping evolutionary history
... Evolutionary biology, the study of the origin and evolution of life on Earth, became recognised as a scientific field following the realisation that Mendelian genetics could explain the processes and causes of evolution and biodiversity, determine species relationships and document evolutionary hist ...
... Evolutionary biology, the study of the origin and evolution of life on Earth, became recognised as a scientific field following the realisation that Mendelian genetics could explain the processes and causes of evolution and biodiversity, determine species relationships and document evolutionary hist ...
Final Test Review
... 18. Natural selection is also known as ____________. 19. The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles for the same gene occurs is ________. 20. All individuals of the same species in a given area form a __________. True/False – make the statemen ...
... 18. Natural selection is also known as ____________. 19. The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles for the same gene occurs is ________. 20. All individuals of the same species in a given area form a __________. True/False – make the statemen ...
Theory of Evolution FYI…Charles Darwin Theory of Evolution
... Charles Darwin came from a family of doctors, and he almost became one, too. Both his father and grandfather were doctors, and they urged him to follow in their footsteps. Charles started out in medical school but soon found that he did not like it. He then went to theological school to study to bec ...
... Charles Darwin came from a family of doctors, and he almost became one, too. Both his father and grandfather were doctors, and they urged him to follow in their footsteps. Charles started out in medical school but soon found that he did not like it. He then went to theological school to study to bec ...
Darwin presents his case
... 2. Organisms produce more _________________________ than can survive, and many that do survive do not reproduce. 3. Because more organisms are produced than can survive, they ______________________ for limited resources. 4. Individuals best suited to their environment (highest level of _____________ ...
... 2. Organisms produce more _________________________ than can survive, and many that do survive do not reproduce. 3. Because more organisms are produced than can survive, they ______________________ for limited resources. 4. Individuals best suited to their environment (highest level of _____________ ...
Script 3
... [7] This process of purposely influencing which traits are passed on to the next generation is called artificial selection. [8] Darwin thought a similar process might be going on in nature, / but without anyone or anything guiding the process. This idea—which Darwin called natural selection--can be ...
... [7] This process of purposely influencing which traits are passed on to the next generation is called artificial selection. [8] Darwin thought a similar process might be going on in nature, / but without anyone or anything guiding the process. This idea—which Darwin called natural selection--can be ...
Basics of Natural Selection
... 3.) Change is gradual and slow, taking place over a long period of time. 4.) The mechanism of evolutionary change is Natural Selection. ...
... 3.) Change is gradual and slow, taking place over a long period of time. 4.) The mechanism of evolutionary change is Natural Selection. ...
Unit 6 Student Note Packet
... • They often indicate that two or more species share a common __________ • _________ _________- structures that don’t seem to have a __________ • Manatees, snakes, and ________no longer have back _______, but like all animals with legs, they still have a ________ bone • The human ___________ is a ve ...
... • They often indicate that two or more species share a common __________ • _________ _________- structures that don’t seem to have a __________ • Manatees, snakes, and ________no longer have back _______, but like all animals with legs, they still have a ________ bone • The human ___________ is a ve ...
Theory of Natural Selection
... – Individuals within a species are not identical; they have variations. – These variations may affect the individual’s ability to get food, escape predators, find a mate, etc. – These variations can be passed on to offspring ...
... – Individuals within a species are not identical; they have variations. – These variations may affect the individual’s ability to get food, escape predators, find a mate, etc. – These variations can be passed on to offspring ...
Evolution
... • A well-known example of microevolution involves the peppered Moth, Biston betularia in England during the industrial revolution • Prior to the industrial revolution, light variants of the peppered moth survived better than dark variants because they blended well with the light colored trees – caus ...
... • A well-known example of microevolution involves the peppered Moth, Biston betularia in England during the industrial revolution • Prior to the industrial revolution, light variants of the peppered moth survived better than dark variants because they blended well with the light colored trees – caus ...
U6-Topic2_Applying Darwin`s Ideas
... physiological, or behavioral change that improves a population’s ability to survive Fossil The trace or remains of an organism that lived long ago, most commonly preserved in sedimentary rock. Homologous Describes a character that is shared by a group of species because it is inherited from a common ...
... physiological, or behavioral change that improves a population’s ability to survive Fossil The trace or remains of an organism that lived long ago, most commonly preserved in sedimentary rock. Homologous Describes a character that is shared by a group of species because it is inherited from a common ...
Concept 22.1 – The Darwinian revolution challenged traditional
... Ch. 22 Essential Knowledge – bringing it all together. 10. Define natural selection and evolution: _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Homologous structures ...
... Ch. 22 Essential Knowledge – bringing it all together. 10. Define natural selection and evolution: _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Homologous structures ...
Evolution - Cloudfront.net
... Briefly explain what a vaccine is and what it does. Why are transposons called “jumping genes”? What purpose do the insertion sequences play? What is the difference between an oncogene and a tumor ...
... Briefly explain what a vaccine is and what it does. Why are transposons called “jumping genes”? What purpose do the insertion sequences play? What is the difference between an oncogene and a tumor ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.