Chapter 15 Darwin and Evolution
... Natural Selection Can Be Witnessed • Darwin had formed his natural selection hypothesis by observing the distribution of tortoises and finches on the Galápagos Islands. • Tortoises with domed shells and short necks live on well-watered islands, where grass is available. Those with shells that flare ...
... Natural Selection Can Be Witnessed • Darwin had formed his natural selection hypothesis by observing the distribution of tortoises and finches on the Galápagos Islands. • Tortoises with domed shells and short necks live on well-watered islands, where grass is available. Those with shells that flare ...
16.4 wkbk KEY - OG
... Therefore, it is reasonable to assume they are descended from a common ancestral form 18. How does the pattern of embryological development provide further evidence that organisms have descended from a common ancestor? The early developmental stages of many vertebrates look very similar. Therefore, ...
... Therefore, it is reasonable to assume they are descended from a common ancestral form 18. How does the pattern of embryological development provide further evidence that organisms have descended from a common ancestor? The early developmental stages of many vertebrates look very similar. Therefore, ...
Ch 2 Notes - Professor Sherry Bowen
... • Collected many fossils and living organisms • Studied geology while reading Principles of Geology by Lyell • Uniformitarianism: observable natural processes responsible for events in the past Of particular note in history is Darwin's observations on the Galapagos Islands located off the coast of E ...
... • Collected many fossils and living organisms • Studied geology while reading Principles of Geology by Lyell • Uniformitarianism: observable natural processes responsible for events in the past Of particular note in history is Darwin's observations on the Galapagos Islands located off the coast of E ...
... Divergent evolution occurs very rapidly and simultaneously in one species resulting in the production of three or more new species. Ground finches migrated from South America (where they ate medium-sized seeds) to the Galapagos Islands. The island did not exhibit much competition, thus the founding ...
Natural Selection
... best suited to survive in their particular circumstances have a greater chance of passing their traits on to the next generation. Plants and animals interact in complex ways with other organisms and their environment; like this hummingbird and flower which have evolved to be perfectly suited to each ...
... best suited to survive in their particular circumstances have a greater chance of passing their traits on to the next generation. Plants and animals interact in complex ways with other organisms and their environment; like this hummingbird and flower which have evolved to be perfectly suited to each ...
An Introduction to Evolution
... trips to the Galapagos Islands, his observations of the finches (and other animals) and the book he wrote: “The Origin of Species”. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution is based on Natural Selection, which is comprised of: 1. Variation exists among individuals in a species. 2. Competition - Individuals of s ...
... trips to the Galapagos Islands, his observations of the finches (and other animals) and the book he wrote: “The Origin of Species”. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution is based on Natural Selection, which is comprised of: 1. Variation exists among individuals in a species. 2. Competition - Individuals of s ...
Study Guide Evolution Test 2016
... reptiles. Which came first: whales or land-dwelling mammals? How do we know? ...
... reptiles. Which came first: whales or land-dwelling mammals? How do we know? ...
Bio - Ch 15 - Darwin and Evolution - BOOK TEST
... c. if all birds on the different islands were finches. d. why all tortoises on the different islands were identical. _____ 3. Which of the following ideas is supported by Darwin’s observation of local variation among tortoises in the Galápagos Islands? a. artificial selection c. acquired characteris ...
... c. if all birds on the different islands were finches. d. why all tortoises on the different islands were identical. _____ 3. Which of the following ideas is supported by Darwin’s observation of local variation among tortoises in the Galápagos Islands? a. artificial selection c. acquired characteris ...
Name: Date - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
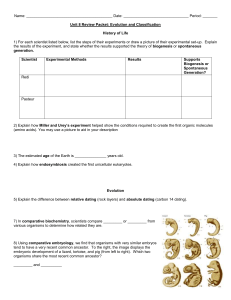
... tend to have a very recent common ancestor. To the right, the image displays the embryonic development of a lizard, tortoise, and pig (from left to right). Which two organisms share the most recent common ancestor? _________ and __________ ...
... tend to have a very recent common ancestor. To the right, the image displays the embryonic development of a lizard, tortoise, and pig (from left to right). Which two organisms share the most recent common ancestor? _________ and __________ ...
Evolution
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Mechanism of evolution- evolution is what happens, natural selection is how it happens • Individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to have more offspring than other individuals which le ...
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Mechanism of evolution- evolution is what happens, natural selection is how it happens • Individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to have more offspring than other individuals which le ...
Glossary - The Teacher-Friendly Guide™ to Evolution Using
... that occurs between generations within one population of a species. This refers of course to change expressed from one individual to another, but we are usually most interested in the changes so great that the later generation is considered a different species. The study of how evolution occurs. An ...
... that occurs between generations within one population of a species. This refers of course to change expressed from one individual to another, but we are usually most interested in the changes so great that the later generation is considered a different species. The study of how evolution occurs. An ...
Blue Print Of Life
... For a new species to evolve, groups of organisms need to become isolated from each other. Usually the organisms become separated by a physical barrier. Within each separate population, different mutations occur, and therefore, different variations are produced. Natural selection acts differently on ...
... For a new species to evolve, groups of organisms need to become isolated from each other. Usually the organisms become separated by a physical barrier. Within each separate population, different mutations occur, and therefore, different variations are produced. Natural selection acts differently on ...
Evolution Study Guide
... 3. Examine the 5 factors Darwin considered in forming his theory of natural selection. a. Genetic Drift, Gene Flow, Mutation, Sexual Selection, Natural Selection 4. Does natural selection act on phenotypes or genotypes? Does natural selection act on existing traits, or can it work directly on DNA ...
... 3. Examine the 5 factors Darwin considered in forming his theory of natural selection. a. Genetic Drift, Gene Flow, Mutation, Sexual Selection, Natural Selection 4. Does natural selection act on phenotypes or genotypes? Does natural selection act on existing traits, or can it work directly on DNA ...
Evolution Notes
... Organism of the Day: Sloth Sloth (Animal) Sloths are extremely slowmoving mammals found in the rainforest canopies of Central and South America. There are two species of sloths:two toed and threetoed. Most sloths are about the size of a small dog and they have short, flat heads. The spen ...
... Organism of the Day: Sloth Sloth (Animal) Sloths are extremely slowmoving mammals found in the rainforest canopies of Central and South America. There are two species of sloths:two toed and threetoed. Most sloths are about the size of a small dog and they have short, flat heads. The spen ...
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... Daily Learning overproduction of offspring, Goal(s): inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. ...
... Daily Learning overproduction of offspring, Goal(s): inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. ...
Isolation and the Evolution of New Species - BioGeoWiki
... Isolation and the Evolution of New Species • The most common way species become isolated is by geographical isolation. • This is when two populations become physically isolated ie, a new river or mountains. ...
... Isolation and the Evolution of New Species • The most common way species become isolated is by geographical isolation. • This is when two populations become physically isolated ie, a new river or mountains. ...
ARTIFICIAL AND NATURAL SELECTION As a human activity
... next generation. Individuals with variations that make them better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce in greater numbers than those without such advantageous adaptations. Speciation. Over many generations, favorable adaptations gradually accumulate in the species and unfavorable ones ...
... next generation. Individuals with variations that make them better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce in greater numbers than those without such advantageous adaptations. Speciation. Over many generations, favorable adaptations gradually accumulate in the species and unfavorable ones ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.