* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
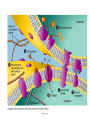
Download Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
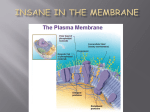
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
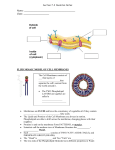
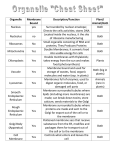
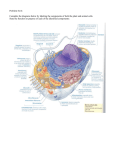
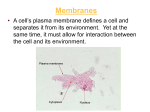
Membranes of the Cell • Plasma membrane – cell’s outer membrane • Endomembranes – smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria Membrane Features • Semi-permeable (selectively permeable) – allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions Membrane Structure • Two layer membrane called phospholipid bilayer – composed of protein and lipids – Lipids are called phospholipids – Contain 2 fatty acids instead of 3 • Fatty acids are hydrophobic – Water fearing – Avoid water – Contain a phosphate group in place of 3rd fatty acid • Phosphate group is charged making this hydrophilic – Water loving – Mixes with water • Specific proteins are inserted into the phospholipid bilayer to… a. b. c. d. Attach to cytoskeleton Cell signaling Enzymatic activity Transport Passive and Active e. Intercellular joining f. Cell-cell recognition Membranes and Proteins Fig. 4.23 Flexibility • Membranes are not rigid • Proteins move freely in the plane of the membrane • Called the Fluid Mosaic model Fluid = molecular wanderings Mosaic = diversity of protein