* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
Survey
Document related concepts
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
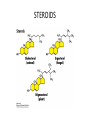
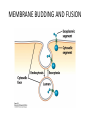
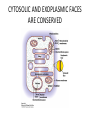
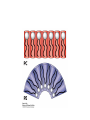
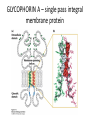
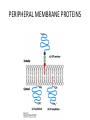
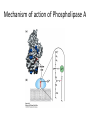
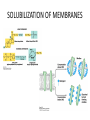
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE LECTURE 4 CHAPTER 10 LIPID CLASSIFICATION • PHOSPHOGLYCERIDES • SPHINGOLIPIDS • STEROIDS PHOSPHOGLYCERIDES SPHINGOLIPIDS STEROIDS MEMBRANE BILAYER BILAYER STRUCTURE OF BIOMEMBRANRANES FORMATION OF PURE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYERS PROPERTIES OF MEMBRANES • HYDROPHOBIC CORE IS AN IMPERMEABLE BARRIER • STABILITY – Van der Waals interaction, and hydrophobic interaction stabilize the fatty acyl groups whereas ionic and hydrogen bonds stabilize the polar head groups • PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYERS SPONTANEOUSLY FORM CLOSED SEALED COMPARTMENTS MEMBRANE BUDDING AND FUSION CYTOSOLIC AND EXOPLASMIC FACES ARE CONSERVED LIPID COMPOSITION IN THE EXOPLASMIC AND CYTOSOLIC FACES OF THE MEMBRANES HOW LIPIDS AFFECT CURVATURE AND THICKNESS OF MEMBRANES PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER- lateral and rotational movement FRAP EXPERIMENTS FRAP EXPERIMENT (cont’d) MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS Integral membrane proteins • Contain membrane spanning α- helices • 20-25 hydrophobic uncharged amino acids (3.75 nm) • Segment is perpendicular to the membrane or is at an oblique angle • Amino peptide bonds in the interior of the αhelix • Hydrophobic side chains interact with fatty acyl groups GLYCOPHORIN A – single pass integral membrane protein Multipass Transmembrane Protein Multiple membrane spanning β strands • Porins • Gram-negative bacteris, outer membrane of mitochondria and chloroplasts • Trimers of identical subunits • Each subunit – 16 beta strands that twist to form a barrel-shaped structure • Barrel - Hydrophilic interior and hydrophobic exterior Single subunit of outer membrane Porin from E.coli PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS HOW IS BLOOD GROUP DETERMINED? Mechanism of action of Phospholipase A SOLUBILIZATION OF MEMBRANES BINDING OF FATTY ACID TO THE FATTY – ACID-BINDING PROTEIN PHOSPHOLIPID BIOSYNTHESIS CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS MECHANISM OF CHOLESTEROL AND PHOSPHOLIPID TRANSPORT