* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fellmann et al/Human Geography, 8/e
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
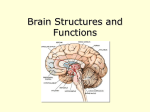
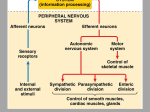
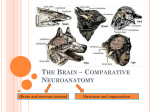
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site Chapter 44 Test Yourself Questions 1. A nerve net consists of a. bilateral neurons that extend from the head of the animal to the tail. b. a group of neurons that are interconnected and are activated all at once. c. a single nerve cord with ganglia in each body segment. d. a central nervous system with peripheral nerves associated with different body structures. e. none of the above. Answer: b. A nerve net consists of a group of neurons that are interconnected and are activated all at once. 2. The division of the vertebrate brain that includes the cerebellum is a. the hindbrain. b. the telencephalon. c. the midbrain. d. the forebrain. e. the diencephalon. Answer: a. The hindbrain is the division of the vertebrate brain that includes the cerebellum, as well as the medulla oblongata and pons. 3. In general, the brains of more complex vertebrates a. are larger. b. have fewer neurons. c. have more folds in the cerebral cortex. d. use less oxygen. e. both a and c. Answer: e. In general, the brains of more complex vertebrates are larger and have more folds. 4. The white matter of the CNS is composed of a. dendrites. b. unmyelinated axons. c. myelinated axons. d. cell bodies. e. a and b only. Answer: c. The white matter is composed of myelinated axons. 5. The division of the nervous system that controls voluntary muscle movement is a. the autonomic nervous system. b. the sensory division. c. the somatic nervous system. d. the parasympathetic division. e. the sympathetic division. Answer: c. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary muscle movement. 6. Which of the following is not a characteristic response to the activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system? a. increased breathing rate b. decreased heart rate c. increased blood flow to the skeletal muscles d. increased blood glucose levels e. all of the above are characteristic responses to activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. Answer: b. When the sympathetic division is activated, heart rate increases. 7. The ___ acts as a relay for the cerebrum. a. medulla b. pons c. hypothalamus d. midbrain e. thalamus Answer: e. The thalamus acts as a relay for the cerebrum. 8. The _______ is a portion of the limbic system that is important for memory formation. a. amygdala b. hippocampus c. pons d. thalamus e. mesencephalon Answer: b. The hippocampus is a portion of the limbic system that is important for memory formation. 9. In humans, the ________ hemisphere of the cerebrum is dominant in nonverbal processing. a. right b. left c. both a and b Answer: a. In humans the right hemisphere of the cerebrum is dominant in nonverbal processing. 10. _____________ is a progressive disease that causes a loss of memory and intellectual and emotional function. a. Meningitis b. Parkinson’s disease c. Amnesia d. Alzheimer’s disease e. Stroke Answer: d. Alzheimer’s disease causes a loss of memory and intellectual and emotional function. Conceptual Questions 1. List the three major divisions of the brain of vertebrates and briefly describe the function of each. Answer: The hindbrain is an extension of the spinal cord that includes the medulla oblongata, pons and the cerebellum. The medulla oblongata coordinates many basic reflexes and bodily functions. The cerebellum and pons are responsible for monitoring and coordinating body movements. The midbrain processes several types of sensory inputs, including vision, smell and hearing. The forebrain consists of a group of structures that are responsible for the higher functions of conscious thought, planning and emotion. The cerebrum handles many of these functions. The basal nuclei and hippocampus contribute to learning motor and cognitive skills. The thalamus relays sensory information to appropriate parts of the cerebrum, and the hypothalamus controls the function of the gastrointestinal and reproductive systems. 2. Explain what makes white matter white. Answer: Myelinated axons are bundled together in large tracts and the myelin is white. 3. What are the two subdivisions of the efferent pathways of the autonomic nervous system and what are their functions. Answer: The sympathetic division is responsible for rapidly activating systems that provide immediate energy to the body in response to stress or danger. The parasympathetic system is involved in maintaining and restoring body functions. Experimental Questions 1. What was the hypothesis proposed by Gaser and Schlaug? Answer: Gaser and Schlaug hypothesized that repeated exposure to musical training would increase the size of certain areas of the brain associated with motor, auditory and visual skills. All three skills are commonly used in reading and performing musical pieces. 2. How did Gaser and Schlaug test this hypothesis? What were the results of their experiment? Answer: The researchers used MRI to examine the areas of the brain associated with motor, auditory and visual skills in three groups of individuals: professional musicians, amateur musicians and nonmusicians. The researchers found that certain areas of the brain were larger in the professional musicians compared to the other groups, and larger in the amateur musicians compared to the nonmusicians. 3. How did the research of Schmithorst and Holland impact the findings of Gaser and Schlaug? How did their experiments differ from that of Gaser and Schlaug? Answer: Schmithorst and Holland found that, when exposed to music, certain regions of the brains of musicians were activated differently compared to non-musicians. This study supports the hypothesis that there is a difference in the brains of musicians compared to non-musicians. The experiment conducted by Gaser and Schlaug compared the size of certain regions of the brain among professional musicians, amateur musicians and non-musicians. Schmithorst and Holland, however, were also able to detect functional differences between musicians and non-musicians. Collaborative Questions 1. Discuss two different types of nervous systems found in animals. Answer: Almost all animals have a nervous system ranging from very simple to very complex. The simplest type of nervous system is the nerve net which is found in the cnidarians. In this type of nervous system, all nerves are connected to each other in a network and can be activated at once. As a result of this, cnidarians can contract and move large areas of its body and its tentacles at the same time in response to a predator. Other types of nervous systems concentrate neurons into ganglia. The function of the ganglia is to integrate inputs from the sense organs and control motor outputs such as moving. In addition to having ganglia, nerve cords in some invertebrates run along the ventral portion of the body starting with the ganglia in the head and ending in the tail region. These cords receive stimuli and allow the animal to respond to those stimuli if necessary. 2. Discuss the parts of the human brain. Answer: Like all vertebrates, the three main divisions of the human brain are the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. The hindbrain - This is an extension of the spinal cord and it includes the cerebellum and pons which are responsible for monitoring and coordinating body movements. The medulla oblongata is also part of the hindbrain and is responsible for coordinating and controlling many of the body’s functions such as breathing and maintaining homeostasis. The midbrain - This part of the brain acts as a processing center for many of the sensory inputs such as vision, smell, and hearing. In addition, it also has tracts that pass information on to other parts of the brain for interpretation. The forebrain - This is the part of the brain that is responsible for the higher functions of consciousness and emotion. The thalamus plays a major role in relaying sensory information to appropriate parts of the cerebrum and, in turn, sending outputs from the cerebrum to other parts of the brain. The hypothalamus controls functions of the gastrointestinal and reproductive systems, and regulates many basic behaviors such as eating and drinking. This area has great importance for homeostasis of the body and the control of behavior. Most of the forebrain consists of a part called the cerebrum which is the largest part of the vertebrate brain. It also consists of areas that contribute to learning, motor, and cognitive skills. The basal nuclei are involved in planning and learning movements. They also function via a complex circuitry to initiate or inhibit movements. The limbic system is primarily involved in the formation and expression of emotions, and also plays a role in learning, memory, and the perception of smells. The cerebral cortex is involved with processing many complex sensory inputs and relaying motor outputs. These functions are also associated with learning and memory.