* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis: Part I: Transcription
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
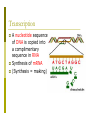
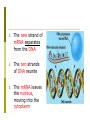
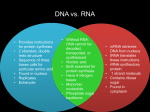
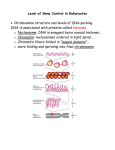
Protein Synthesis: Part I: Transcription Biology Transcription p A nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complimentary sequence in RNA p Synthesis of mRNA p (Synthesis = making) Transcription Overview p DNA is located in the nucleus p mRNA copies DNA p mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome p mRNA complements known as codons n Only 3 nucleotide letters long p Remember RNA has uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)! How does transcription happen? 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA in the nucleus and separates the DNA strands 2. RNA polymerase uses one strand of the DNA as a template and complimentary RNA nucleotides are assembled into single stranded mRNA Base pairing as follows: DNA RNA G C C G T A A U 3. The new strand of mRNA separates from the DNA 4. The two strands of DNA reunite 5. The mRNA leaves the nucleus, moving into the cytoplasm The Genetic Code Polypeptides: long amino acid chains p 20 different AAs that can combine to form a polypeptide The Genetic Code, cont. p RNA code is written in a language that is four letters (A, G, C, U) p Code is read three letters at a time, so each word of the coded message is 3 letters long The Genetic Code, cont. ¨ Codon: 3 consecutive nucleotides on mRNA that specify a single amino acid ¨ 64 possible codons ¨ Certain codons code for start or stop the protein Transcription – Step I A C G T A T C G C G T A T G C A T A G C G C A T Template DNA Strands Transcription – Step II A C G T A T C G C G T A U G C A U A G C G C A U Template DNA is Matched Up with Complementary mRNA Sequences