* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
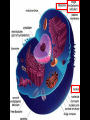
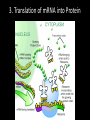
Protein Synthesis Grade 10 EST Recall: DNA • DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid • Composed of nucleotides • Each nucleotide contains – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group (PO4-1) – Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G) • Sequence of bases = gene Recall: Proteins • A gene is piece of DNA that codes to make a protein. • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) Recall: Protein Structure • Protein are made of amino acids. • 20 different amino acids • Average = 100-200 amino acids in a protein chain Protein Synthesis • Protein synthesis is the creation of proteins by cells. • Instructions are in genes inside nucleus. • Protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes, outside the nucleus. RNA • DNA cannot leave the nucleus • Messenger between nucleus and ribosome • mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid • RNA is single-stranded • Thymine (T) Uracil (U) • Ribose sugar Two types of RNA Messenger RNA acts as a messenger between gene and ribosome (mRNA) Transfer RNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasm to ribosome (tRNA) 1. Transcription of DNA into mRNA 2. Attachment of mRNA to Ribosome 3. Translation of mRNA into Protein 4. End of Protein Synthesis UAA, UAG, or UGA nucleotide triplet • • • • Chain is complete. Protein is released. Folds into functional shape. Performs its role. Notes Video HW pp. 181-182 due May 22