* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription_12_Teacher
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
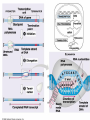
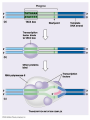
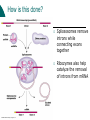
Transcription Chapter 25 Objectives Understand the process of transcription Recognize the role of RNA Polymerase Recognize the significance of promoter and terminator regions of DNA Explain how transcribed RNA is modified prior to exiting the nucleus. Understand the significance of this process Transcription Consists of three stages Initiation: attachment of RNA Polymerase to the promotor region on DNA Elongation: building of the mRNA from the 3’ end of the DNA Termination: release of RNA polymerase and mRNA following transcription of the terminator region of the DNA Initiation Genes on the DNA begin with a promoter region -- a sequence of A & T (TATA box) Transcription initiation complex: transcription factors & RNA polymerase are bound to the promoter region on the DNA Elongation Once initiation is complete the 2 strands of the DNA unwind to be copied into mRNA Termination RNA polymerase builds a mRNA strand complimentary to the DNA Once the RNA Polymerase (Transcriptase) is done copying, the DNA strands zips back up to form their double helix When the RNA Polymerase reaches the terminator region of the DNA, it lets go and releases the mRNA The transcribed termination sequence on the mRNA is AAUAAA Modification of mRNA Transcribed mRNA (pre-mRNA) must be modified before leaving the nucleus There are special “dividers” in the mRNA that need to be cut out. They are not part of the genetic information, just organizers. Further Modifications Transcribed mRNA is too long and is shortened before it leaves the nucleus by a special cutting process Exons are segments of the pre-mRNA that contain genetic information that will be create proteins Introns are just divisions between the EXONS How is this done? Spliceosomes remove introns while connecting exons together Ribozymes also help catalyze the removal of introns from mRNA Why bother with introns? Introns may regulate gene activity and the passage of mRNA into the cytoplasm Genes may play roles in multiple proteins, introns may enable a gene to be diverse in function May increase recombination of genetic material (easier to cut and paste)