* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.-lactic-acid-metabolism
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
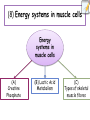
(8) Energy systems in muscle cells Energy systems in muscle cells (A) Creatine Phosphate (B) Lactic Acid Metabolism (C) Types of skeletal muscle fibres (b) Energy systems in muscle cells • State the alternative route of pyruvate and when this occurs • Explain how muscle fatigue develops • Explain what is meant by the term ‘oxygen debt’ and how it can be ‘repaid’ What can you remember about these words? • Lactic acid •Muscle fatigue •Oxygen debt LACTIC ACID METABOLISM (occurs in the absence of oxygen) In the absence of oxygen, neither the citric acid cycle nor the electron transport chain can occur! Therefore a cells only source of ATP is through glycolysis. When glucose is broken down into pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2NADH are made. This is followed by the conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid AND THE TRANSFER OF HYDROGEN from NADH. Since the hydrogen has been removed, therefore regenerating NAD. (NAD must be present for glycolysis to continue). But as more and more lactic acid builds up, muscle fatigue is caused and an oxygen debt is created. NAD Glucose 2 ADP+Pi NADH Pyruvate 2 ATP Oxygen debt builds up Oxygen debt repaid (through aerobic respiration) Lactic Acid 1 • During vigorous exercise, the muscle cells do not 3 get sufficient oxygen to support the electron 2 3 chain. transport • Under these conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactic4 acid. This conversion involves the transfer of 5 hydrogen from the NADH produced during glycolysis to pyruvic acid to produce lactic acid. 6 This regenerates the NAD needed to maintain ATP 7 production through glycolysis. 8 • Lactic acid accumulates in muscle causing fatigue. • The oxygen debt is repaid when exercise is 9 complete, as this allows respiration to provide the 10 acid energy to convert lactic acid back to pyruvic and glucose in the liver. (b) Energy systems in muscle cells • State the alternative route of pyruvate and when this occurs • Explain how muscle fatigue develops • Explain what is meant by the term ‘oxygen debt’ and how it can be ‘repaid’