* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lactic Acid Fermentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
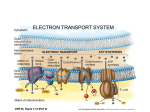
Alcohol Fermentation -necessary in prokaryotes due to no mitochondria and in yeast when the oxygen is gone. As you can see in the above diagram, Glycolysis makes 2 ATP (net) and 2 NADH which would normally be used in the ETC but there are no ETC in prokaryotes and there is no oxygen available for yeast so the NADH builds up and NAD+ runs out. If NAD+ runs out, glycolysis itself will stop and there will be NO ATP made again. This will cause the organism to die. Therefore, a recycling program is needed to get the NADH back to NAD+. In alcohol fermentation, the pyruvate breaks down into Ethanol (alcohol) as it gives off one carbon dioxide (per pyruvate) while accepting two electrons from NADH. This breaks down NADH into NAD+ so that it can be used by Glycolysis again and again. In bacteria (prokaryotes), this has to happen because there are no mitochondria to pass the NADH to for the recycling of NAD+. This is the process that allows beer and wine makers to produce alcoholic beverages by putting yeast in with the fruits and sugars specific to the beverage. Lactic Acid Fermentation -necessary to recycle NADH back into NAD+ when oxygen is not available in humans In animals, especially humans, when there is a high demand for oxygen and it is not getting to the cells fast enough, the NADH builds up and the cell runs out of NAD+ in glycolysis to make ATP. With no oxygen available to the last step of the ETC, then there is no place for the NADH to drop off it’s electrons. This occurs when your activity level exceeds your body’s ability to bring in oxygen fast enough to supply the ETC in the mitochondria. The solution, so that you get at least some ATP from glycolysis, is to skip the mitochondria all together and recycle the NADH into NAD+ through lactic acid fermentation. When pyruvate is made, it is converted into lactic acid (lactate) while accepting 2 electrons from NADH. Once this occurs, the NADH falls apart into NAD+ and H+ thereby making NAD+ available so that at least glycolysis can continue to provide you with some ATP instead of none. The lactic acid is secreted by the cells into the surrounding space where your nerves happen to be which causes you to feel a burning sensation in the areas of the muscles that were in oxygen debt.