* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Krebs Cycle
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
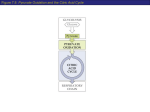
Krebs Cycle: oxidative decarboxylation of the C2 Acetyl group (CH3CO). This cycle has been broken down into 4 steps. The carbons from the original glucose molecule are shown in purple and those of mitochondria molecules in blue. Acetyl CoA joins with the C4(acceptor)group CoA is released to transport more pyruvate into the matrix A C6 fragment is formed (citric acid) C6 (Citric Acid) is oxidatively decarboxylated. A C5 group is formed. The Carbon is given off as Carbon Dioxide NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+ The C5 fragment is oxidised and decarboxylated further to a C4 compound. Again the carbon removed forms carbon dioxide. NAD+ is further reduced to NADH + H+. The final stage in the cycle has the C4 acceptor regenerated. There is a reduction of NAD+ to NADH + H+. FAD (Coenzyme) is reduced to FADH2 . ADP is reduced to ATP The krebs cycle is an example of the metabolic cycles mentioned in section 7.6.1 . Each step in the cycle requires enzymes to reduce the activation energy. The reactions all take place in the matrix of the mitochondria and are usually represented as a circular diagram. Try to overcome the idea that the molecules are going in a circle but more that this reaction is taking place within the confined space of the matrix where each intermediate becomes the substrate for the next step. (a) Pyruvate (3C) (b) Link reaction (c) C4 + C2= C6 (d) Recycling of CoA (e) Decarboxylation C6 to C5 and the reduction of NAD (f) Decarboxylation C5 to C4 and the reduction of NAD (g) C4 to C4 with the reduction of coenzymes FAD and NAD. ATP is made directly. (h) C4 to C4 acceptor This cycle follows one acetyl group. Each glucose that enters glycolysis will produce 2 acetyl groups.