* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Vocabulary File
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
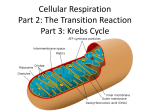
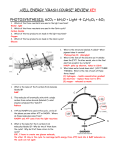
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Vocabulary: 1) Energy = the ability to do work 2) ATP = (adenosine triphosphate); energy storing molecule 3) ADP = adenosine diphosphate 4) Photosynthesis = the process that provides energy for almost all life 5) Autotroph = organisms that make their own food 6) Chlorophyll = green pigment in chloroplasts that traps sunlight 7) Light Reactions = Light energy is converted to chemical energy; Energy is captured from sunlight in the chlorophyll of the chloroplasts of plant cells. 8) Dark Reactions = (Calvin Cycle); Carbon dioxide (CO2) and the chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH powers the formation of carbohydrate molecules (sugars, starch and cellulose) 9) Stroma = specific location on a chloroplast where the dark reactions occur 10) Glycolysis = Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell Starting molecule: ONE molecule of glucose (C6H12O6) Produces: TWO pyruvic acids or pyruvates (C3H6O3); 2 ATP molecules Attaches H’s to NAD+ (electron carrier) and forms NADH (high energy molecule) 11) Aerobic = requires oxygen 12) Pyruvic Acid = (pyruvate) C3H6O3 13) Kreb Cycle = also called the citric acid cycle Aerobic process (requires oxygen) Occurs in the mitochondrion Starting molecules: 2 pyruvates and oxygen Produces: NADH and FADH2, CO2 and 2 ATP molecules 14) ETC = Electron Transport Chain Aerobic process (requires oxygen) Occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Starting molecules: NADH and FADH2 and oxygen o Uses the NADH and FADH2 from the Kreb’s Cycle and another NADH from Glycolysis. Produces: Water and 32 ATP’s o FADH2 and NADH, release H’s so they can attach to oxygen and produce water 15) NADH & FADH = high energy molecules 16) Anaerobic = no oxygen present 17) Alcoholic Fermentation = Occurs in plants Starting molecules: 2 pyruvates and NADH (from glycolysis) Produces: ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Bakers use alcoholic fermentation of YEAST to make bread. Used to make wine and beer 18) Lactic Acid Fermentation = Occurs in animals Starting molecules: 2 pyruvates and NADH (from glycolysis) Produces: lactic acid Lactic acid fermentation by microorganisms plays an essential role in the manufacturing of food products such as yogurt and cheese.