* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nieuwsbrief 1, 2005
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
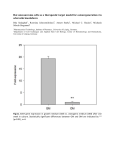
EXAMPLE ABSTRACT Processed Adipose Tissue Cells For Bone Tissue Engineering M. Knippenberg1, M.N. Helder2, S.M. van Ham3, M.J. Oedayrajsingh Varma4, E.H. van Haaren2, P.I.J.M. Wuisman2, J. Klein-Nulend1 1 ACTA-VU, Oral Cell Biology, 2VUmc, Orthopeadics, 3VUmc, Pathology, 4VUmc, Plastic Surgery Background: Autologous adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can provide new and innovative tools in bone tissue engineering. When seeded on synthetic or natural (bioresorbable) scaffolds, these cells may be used to restore or replace tissues and organs. Recently, adipose tissue (AT) has been described as an alternative source for the commonly used bone marrow (BM)-derived MSCs, since the latter cells are available only in limited amounts. Objective: To evaluate the potential use of osteogenically stimulated AT-MSCs for application in a goat spinal fusion model. Methods: Characterization of human and goat AT-MSCs was performed using histotyping and FACS analysis for the lineage-specific markers ASO-2, vimentin, CD166 and CD105. Osteogenic differentiation of MSCs was induced using osteogenic medium containing ascorbic acid, betaglycerophosphate, and 10 nM 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Afterwards, alkaline phosphatase acivity and cbfa-1/runx-2 mRNA expression were determined. Results: Relatively homogenous populations of human and goat AT-MSCs were obtained. Osteogenic stimulation resulted in upregulation of the (pre)osteoblastic marker cbfa-1/runx-2 (human 1.5 fold; goat 3 fold) at day 7. Untreated cultures also showed slightly increased (about 0.1 fold) cbfa-1/runx-2 mRNA expression, possibly due to reaching confluency at day 3-4. In addition osteogenically-stimulated cultures demonstrated increased alkaline phosphatase activity. Conclusion: Adipose Tissue contains a population of mesenchymal stem cells based on histotyping and FACS analysis. These AT-MSCs from human as well as from goat can be pushed into osteogenic differentiation by the osteogenic factor 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, as shown by cbfa-1/runx-2 upregulation and increased alkaline phosphatase activity. Therefore, AT-MSCs are a promising new tool in bone tissue engineering. INSTRUCTIONS FOR ABSTRACT PREPARATION: Prepare abstract similar as the abstract above. Font:Arial 11 (title, authors, affiliations), Arial 9 (the remainder) Title:bold, title case, centered Authors: initial(s) followed by last name, centered Affiliations: indicated by numbers if there is more than 1 author affiliation, indicate University (abbreviated) and department, centered Body abstract (i.e. without title, authors names, and affiliations): MAXIMUM 250 words. SUBMIT ABSTRACT via NVCB website www.NVCB.nl