* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fractions
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
John Wallis wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
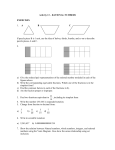
Fractions A fraction is part of an entire object. Fractions consist of two numbers. The top number is called the numerator. The bottom number is called the denominator. numerator denominator 1 4 2 4 One fourth is yellow Two fourths are yellow. One half is yellow. 3 4 Three fourths are yellow. 4 4 Four fourths are yellow. Identifying Equivalent Fractions Equivalent fractions are fractions that have the same value or represent the same part of an object. If a pie is cut into two pieces, each piece is also onehalf of the pie. If a pie is cut into 4 pieces, then two pieces represent the same amount of pie that 1/2 did. We say that 1/2 is equivalent to 2/4. Fractions are determined to be equivalent by multiplying the numerator and denominator of one fraction by the same number. This number should be such that the numerators will be equal after the multiplication. For example if we compare 1/2 and 2/4, we would multiply 1/2 by 2/2 which would result in 2/4 so they are equivalent. To compare 1/2 and 3/7 we would multiply 1/2 by 3/3 to produce 3/6. Since 3/6 is not the same as 3/7, the fractions are not equivalent. Fractions equivalent to 1/2 are 2/4, 3/6, 4/8, 5/10, 6/12 ... Fractions equivalent to 1/3 are 2/6, 3/9, 4/12, 5/15, ... Fractions equivalent to 1/4 are 2/8, 3/12, 4/16, 5/20, ... Fractions equivalent to 1/5 are 2/10, 3/15, 4/20, 5/25, ... Fractions equivalent to 2/5 are 4/10, 6/15, 8/20, 10/25, ... Adding Fractions with the same Denominator To add two fractions with the same denominator, add the numerators and place that sum over the common denominator. Adding Fractions with Different Denominators How to Add Fractions with different denominators: Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) of the fractions Rename the fractions to have the LCD Add the numerators of the fractions Simplify the Fraction Example: Find the Sum of 2/9 and 3/12 Determine the Greatest Common Factor of 9 and 12 which is 3 Either multiply the denominators and divide by the GCF (9*12=108, 108/3=36) OR - Divide one of the denominators by the GCF and multiply the answer by the other denominator (9/3=3, 3*12=36) Rename the fractions to use the Least Common Denominator(2/9=8/36, 3/12=9/36) The result is 8/36 + 9/36 Add the numerators and put the sum over the LCD = 17/36 Simplify the fraction if possible. In this case it is not possible Adding Mixed Numbers with the same Denominator Mixed numbers consist of an integer followed by a fraction. How to add two mixed numbers whose fractions have the same denominator: Add the numerators of the two fractions Place that sum over the common denominator. If this fraction is improper (numerator larger than or equal to the denominator) then convert it to a mixed number Add the integer portions of the two mixed numbers If adding the fractional parts created a mixed number then add its integer portion to the sum. Example: 3 2/3 + 5 2/3 = Add the fractional part of the mixed numbers Convert 4/3 to a mixed number Add the integer portions of the mixed numbers Add the integer from the sum of the fractions State the final answer: 2/3 + 2/3 = 4/3 4/3 = 1 1/3 3+5=8 8+1=9 9 1/3