* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Page 1 of 9 Biology-Ecology Notes and Questions I.What is Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
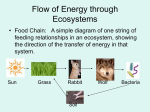
Page 1 of 9 Biology-Ecology Notes and Questions I.What is Ecology? A.Interactions and Interdependence • __________________-scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings. • _________came up with term ecology based on house and economy. • The largest unit is the ______________________ which contains the combined portions of the planet in which all of life exists,inc. water and atmosphere. • Web of interactions in biosphere as organisms and environment ,which are interdependent B.Levels of Organization – 1)_______________level studies interactions between specific organism and surroundings 2)individuals belong to the same species and live in same area. – 3)________________-groups of different populations living in the same area – 4)__________________-collection of all the organisms living in particular place+ nonliving parts – 5)_______________-group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities C. Ecological Methods • Observing-example What species live here?how many?... • Experimenting- • – An _______________________ may test a hypothesis in a lab – field studies in natural ecosystems Modeling may be done because phenomena may occur over a long time/may use mathematical formulas II. Energy Flow • A. Producers – ____________-main source of energy for all life on earth Page 2 of 9 • • – Only <_____% of the sunlight is used by living things ,yet this produces much energy – Some organisms use the energy stored in organic compounds-eg. In _____________and undersea vents – Only ____________________ can take (derive) energy directly from the sun or inorganic compounds…..Theses are called ____________________,which use the energy from the environment to fuel the assembly of simple inorganic compounds into complex organic molecules….finally forming tissue – Because they can make their own food,autotrophs are called __________________. – Both types of producers---those that get energy from sunlight and those that derive energy from inorganic compounds are essential. To the biosphere. 1) Energy from the sun: – Get energy from _______________that converts CO2 and H2O into O2 and glucose,using light energy…..responsible for O2 we breath – On land _______are the main autotrophs and and ______________are the main autotrophs under the water,at the upper layers. In tidal flats and salt marshes,photosynthetic bacteria called _________are the main autotrophs 2. Life w/o Light: • Rely on chemical bonds of such inorganic molecules as hydrogen sulfide • ______________is when chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrates---performed by several type of bacteria • In volcanic vents on the deep ocean floor and hot springs Consumers-also called ____________________rely on other organisms for their food supply Types: • 1)_______________eat only plants.eg-cows,caterpillars and deer • 2)______________eat animals—eg-snakes and owls • 3)__________________-eat both plants and animals • eg-humans,bears • 4)________________________eat plant animal remains,and other dead matter Page 3 of 9 • called detritus—eg-earthworms and snails • _______________________-break down organic matter---eg. Bacteria and fungi C. Feeding Relationships • ____________ flows through an ecosystem in one direction,from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs(producers) and then to various heterotrophs(consumers) .These relationships create feeding networks: 1. The energy stored by producers can be passed through an ecosystem along a ___________________-a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten…shows one way flow of energy The animal plankton is________________________,which devour the phytoplankton and are ,in turn, eaten by small fish 2. ________________________-complex feeding interactions are shown. These show more complex relationships.Producers are either eaten or complete life cycle. Herbivores,omnivores,carivores and producers decompose,turning into detritus,by decomposers and devoured by detritivores and also by consumers Page 4 of 9 3. Each step in a food chain or food web is __________________________Each consumer depends on the trophic level below for energy 4. Ecological Pyramids-shows the relative amount of matter contained w/in each trophic level being a chain or web…There are 3 types: Energy Pyramid-Only about __% of the energy available in one trophic level is transferred to the next…most is released into environment…..only about 1% transferred to humans….the more trophic levels ,the ____energy at the • Biomass Pyramid-represents amount food available @ level – Total amount of living tissue in a trophic level=________________ • expressed in g/unit area Pyramid of Numbers –based on number of individual organisms at each trophic level III. Cycles of Matter • Matter is cycled within and without an ecosystem • Matter is passed from one organism to another through_______________ The Water Cycle Section 3-3 Condensation Precipitation Evaporation Transpiration Runoff Seepage Root Uptake Watergas in EVAPORATION and water enters the air from leaves in TRANSPIRATION Go to Section: All the chemical substances an organism needs for life is a ______________/to build tissues and carry out cell functions Page 5 of 9 4 main types of processes move C through its cycle • Biological processes like Photosynthesis,respiration and decomposition take up and release C and O2 • Geochemical processes,such as erosion and volcanos release CO2 into the atmosphere and oceans. • Mixed Biochemical processes-burial and decomposition and conversion into coal and petroleum store underground C. • Human activities like mining ,cutting and burning forests and fossil fuels release CO2 in the air. Figure 3-13 The Carbon Cycle Section 3-3 CO2 in Atmosphere CO2 in Ocean Go to Section: Page 6 of 9 Figure 3-14 The Nitrogen Cycle N2 in Atmosphere NH3 NO3and NO2- N needed for amino acids and proteins N-fixing bacteria from roots of legumes convert N gas into ammonia in Nitrogen Fixation,also into nitrates and nitrites.Producers use them to make proteins.This is then usable by the consumers to make their own proteins. Denitrification is when organisms die and decomposers return it to soil as ammonia.Other soil bacteria convert Nitrates into N gas,releasing N into air again P forms part of DNA and RNA Page 7 of 9 Nutrient Limitation • Primary productivity is _________________________. • Available nutrients affect this. • When an ecosystem is limited by a single nutrient it is called a______________. • Algal blooms occur due to the increase in a nutrient.the algae may cover the surface of the water and block the sun Chapters 4 ,5,6 1) Name the 3 important characteristics of a population 3--What can affect population density? 4) What factors can affect population size? • Number of births • Number of deaths Page 8 of 9 • Number of individuals that enter or leave a population 5) Compare immigration and emigration. • Immigration is the movement of individuals into an area and emigration is movement OUT OF an area. Immigration can cause a population to grow while emigration can cause a population to decrease .Searching for mates ,changes in resources and food can affect both. 6) What is exponential growth? • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce @ a constant rate….@ first they increase slowly , but eventually they increase approaching an indefinitely large size—This is in the absence of predation and presence of unlimited resources 7)When will a population grow exponentially? • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources 8)What is logistic growth and how does that differ from exponential growth? As resources become less available,the growth slows or stops….This generally is an s-shaped curve….and occurs following a time of exponential growth---Exponential growth occurs @ ideal conditions only 9) Define carrying capacity. • The largest number of individuals that a given environment can support Page 9 of 9 10) What factors may cause carrying capacity to change? Natural disasters,resources limited 11. What are limiting factors and give examples. • Can cause a population growth to decrease----eg.-human disturbances,drought and other 12)List 3 density dependent factors and 3 density-independent factors.climate extremes,parasitism and disease,predation,competition • Density dependent:competition,predation parasitism and disease(are dependent on population) • Density independent :unusual weather,natural disasters,seasonal cycles,human activities 13) How do competition and population size relate? • When populations become larger and more crowded,organisms must compete w/one another for food,water,space,sunlight,and other essential resources. 14) If an entire fox population disappears ,what is likely to happen to the rabbit population? • Explosive growth