* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12-3: Lewis Structures
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
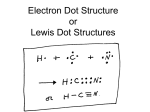
12-3: Lewis Structures Bonding only involves valence electrons Lewis structures—represent valence electrons; use dots placed around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so it is like helium Draw the Lewis structures for: H Ca N F Ar Ionic compounds: draw dots showing where electrons would be after transfer, plus resulting charges Molecules: draw shared electrons as shared dots o A shared pair of electrons can be drawn as a line, representing a bond. (Bonding Pair) The other electrons that are not shared are called unshared pairs or lone pairs Draw Lewis structures for compounds made from these elements: H and Cl Ca and F H2 Cl2 Single Bond—sharing one pair of electrons (Ex: NH3) Double Bond—sharing two pairs of electrons (Ex: CO2) Triple Bond—sharing three pairs of electrons (Ex: C2H2) Finding the Number of Bonds in a Compound: # e- each atom wants to have (noble gas config…) MINUS # e- ea. atom actually has (see atomic #...) DIVIDE (this difference) BY 2 = the # of covalent bonds in the compound o Don’t forget unshared pairs! Double Check!! Some compounds show resonance** o No single structure accurately represents the electron location. (Ex: Benzene, ozone, carbonate ion) Polyatomic Ions: o Negative—add that # of eo Positive—subtract that # of e Draw, then add brackets and charge Try drawing: PO43- Exceptions to the Octet Rule o Compounds with an odd number of valence electrons BF3, SF4, NO, NO2, etc