* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rigorous Curriculum Design
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
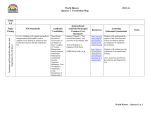
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Grade/Course Unit of Study Unit Title Pacing Social Studies 9th Grade Revolutionary Ideas (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) Unit 8: Changes throughout the World 11 days (block) Conceptual Lenses Changes Unit Overview Points of focus in this unit include changes in government, economics, society and culture. Philosophical and Scientific theories: manifest as changes in the political, economic, and social systems. Political upheaval/revolutions: the transformation of governmental systems as a result of changes in ideas and expectations. Geographic and technological advantages: tied to the rise of industrialism and subsequent environmental consequences. Social and Economic Reforms: as a result of the Industrial Revolution Unit Enduring Understanding(s) Unit Essential Question(s) 1. New ideas, theories and political thought often help engineer foundations for changes in government, economies and societies 2. Changes due to revolution can lead to the establishment of new types of government 3. Technology often leads to the desire for additional resources 4. New economic patterns often result in the need for social and economic reforms 1. How did enlightened ideas influence changes in society? 2. How do revolutions inspire new political systems? 3. How does technology lead to the desire for additional resources? 4. What are the social and political effects of new economic opportunities? 1 Essential State Standards Priority Objectives Supporting Objectives WH.H.6.1 Explain how new ideas and theories of the universe altered political thought and affected economic and social conditions WH.H.6.2 Analyze political revolutions in terms of their causes and impact on independence, governing bodies and church-state relations. WH.H.6.3 Explain how physical geography and natural resources influenced industrialism and changes in the environment WH.H.6.4 Analyze the effects of industrialism and urbanization on social and economic reform “Unpacked” Concepts (students need to know) WH.H.6.1 ideas and theories of the universe altered political thought economic and social conditions WH.H.6.2 political revolutions causes and impact on independence, governing bodies and church-state relations. “Unpacked” Skills (students need to be able to do) WH.H.6.1 Explain WH.H.6.2 Analyze (cause and impact) WH.H.6.3 physical geography and natural resources industrialism and changes in the environment WH.H.6.3 Explain (the influence) WH.H.6.4 industrialism and urbanization social and economic reform WH.H.6.4 Analyze (effects of) COGNITION (RBT Level) WH.H.6.1 Understand WH.H.6.2 Analyze WH.H.6.3 Understand WH.H.6.4 Analyze 2 Unit “Chunking” & Enduring Understandings Philosophical and Scientific theories Intellectual developments often challenge the status quo and may result in societal changes Political upheaval/revolutions The demand for human and civil rights often increases as the demand for economic opportunities increase. Geographic and technological advantages: As technology improves societies often become more urban, demand more commercial goods and labor saving devices. Social and Economic Reforms States increase their spheres of influence often to compete for resources and power Essential Factual Content Suggested Lesson Essential Questions Scientific Revolution Enlightenment Nation-states How is intellectual development a catalyst for change? X X X Rights Freedom Independence Popular sovereignty Revolution Urbanization Industrialization Mass production Markets Factories Population growth Technological and agricultural changes Capital (money) Investments Economic systems Sphere of influence Resources Colonization Imperialism Socialism Communism Capitalism What factors result in the demand for freedom? X X X X X X X X X X How did technological improvements change societies? What are the geopolitical causes of land expansion? H G C E C & G X Sub Concepts 3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY Competition Power Resources Expansion CIVICS & GOVERNMENT Revolution Challenge ECONOMICS CULTURE Economic Opportunities Resources Technological improvements Society Civil Rights Language Objective EXAMPLES Key Vocabulary LO: SWBAT define and explain the terms urbanization, Popular sovereignty, Scientific revolution, capital and revolution. Language Functions LO: SWBAT explain how the enlightened ideas influence changes in society. Language Skills LO: SWBAT read a passage about one enlightened idea and identify the causes and effects of this idea. (Reading passages should be chosen/modified in accordance with the LEP students’ zone of proximal development). Grammar and Language LO: SWBAT write a firsthand account of someone living during these changes and the experiences they encountered. . Lesson Tasks LO: SWBAT read and summarize a passage about the Industrial Revolution and explain this summary to a group. Language Learning Strategy LO: SWBAT develop a cause/effect graphic organizer analyzing and identifying the causes and effects of the Industrial Revolution. (The linguistic load will vary from LEP student to LEP student. Level 1-2 LEP students may need a word bank or other supplement to complete this activity using this strategy). Historical Thinking and Geography Skill Resources ○ “Straight Ahead” □“Uphill” ∆“Mountainous” Historical Thinking Geography Skills . 4 General Unit Resources SAS Curriculum Pathways #386 Scientific Revolution: Galileo on Trial #885 Enlightenment Philosophers #1120 Industrial Revolutions: Inventions #596 Industrial Revolution: Debating Adam Smith and Child Labor Learn 360 Scientific Revolution Enlightenment Industrial Revolution Bridging World History Bridging World History Unit 17: Ideas Shape the World Unit 19: Global Industrialization World History for us All World History for Us All Unit 7: Industrialization and its Consequences The Urban Game The Urban Game 5