* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 2 (word)
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
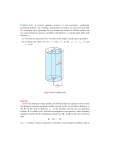
Name_________________________________________ Student number___________________________ Last First I. Multiple Choice (50 pts total) 4 points each unless noted. Please choose the answer that is most correct. 1) An electron is stuck to a neutral blob. The blob, in deep, deep space, (ignore gravity!) moves from left to right and increases speed. The blob has moved from: a) high to low potential b) low to high potential c) no potential difference d) not enough information 2) From 1), what is the direction of the electric field, if any, that the blob moves through? a) to the right b) to the left c) none d) not enough information 3) (2pts) In a capacitor with a dielectric in it, why does the electric field not go to zero due to the induced charges on the dielectric? a) there aren’t enough charged particles in the dielectric to cancel the free charges on the plate b) the charges run into obstacles as they move through the dielectric c) the resonance of the charged dipoles isn’t sustained for a long enough time d) the polarization of the dielectric isn’t enough to cancel the free charges on the plate e) none of the above 4) A parallel plate capacitor, insulated from its surroundings, has a potential of Vo with a separation of d. With all other variables remaining constant, what happens to the potential when d is halved? a) 4Vo b) 2Vo c) Vo d) Vo/2 e) Vo/4 5) A resistor has a potential drop of 5V when a current of 1.25A flows through it. If all other variables remain constant, what is the current through the resistor if its length is tripled? a) 0.104A b) 0.209A c) 0.417A d) 0.833A e) not enough information 6) Can a charged particle be moved through an electric field and have the field do no work on it? a) no, it is impossible since electric fields always apply a force to a charged particle b) no, when you change you position in the field you change your potential which means work was done by the field c) yes, by moving along equipotential lines the field does no work. d) yes, the potential doesn’t necessarily do work if the field has a constant gradient e) not known 7) Three capacitors are connected in series across a battery of potential 12V. If each capacitor has a capacitance of 3F, what is the magnitude of the charge on each plate of the capacitors? a) 3C b) 6C c) 9C d) 12C e) 24C Exam 2 Physics 122A Aut05 1 Name_________________________________________ Student number___________________________ Last First II. Multiple Choice Continued 8) A parallel plate capacitor has a charge of 1.2 C and the plates are separated by a distance of 3mm. The left plate has a potential of 12V and right plate has a potential of 20V. What is the area of the capacitor in 107m2? a) 1.1 b) 2.34 c) 2.54 d) 5.08 e) 10.2 9) In a hydrogen atom, the ionization energy is defined as the energy required to move the electron from the lowest energy (ground) state to infinity. If, in the ground state, the electron is an average distance of 1.5a0, where ao=0.5x10-10m, from the proton, what is the ionization energy of the hydrogen atom in 10-18 joules? (this is actually slightly off from the actual value, quantum mechanics will give the correct value) a) 3.07 b) 4.47 c) 6.67 d) 9.34 10) From 9), with what speed must an electron be started if it is to escape the hydrogen atom, in 10 6m/s? a) 1.2 b) 2.6 c) 3.6 d) 5.5 e) 9.1 11) A current of 1.4A flows through a cylindrical resistor of radius 3mm, what is the current density in the wire in 104 C/m2? a) 2.26 b) 3.56 c) 4.35 d) 4.95 e) 7.75 12) A region of space has a uniform electric field given by E= 13V/mi. Point A is at x=2m, and point B is at x= -2m. Which point has the highest potential? a) A b) B c) Both same potential d) Not enough information 13) From 12) calculate the change in potential from A to B, or VAB. a) 52V b) 26V c) 0V d) -26V e) -52V Exam 2 Physics 122A Aut05 2 Name_________________________________________ Student number___________________________ Last First Written Solutions: Show your work for full credit. III. Cylindrical Conductors (30 pts): A cylindrical conductor with radius a and a cylindrical conducting shell with inner radius b and outer radius c. The inner conductor has a total charge of –Q and the outer conductor has a total charge of +Q and both have a length L, which is much greater than the radius c, L>>c. We will define λ=Q/L All vectors should be in unit vector notation. a) Find the electric field, E, between the cylinders using Gauss’ law. +Q -Q b) Find the potential difference, V, between the cylinders. c) Find the capacitance per unit length, C/l, of the cylinders. l is some arbitrary length along the cylinders. Exam 2 Physics 122A Aut05 3