* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student Handout Book.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
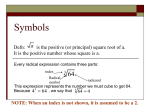
Chapter 4 Roots & Powers Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 1 Table of Perfect Squares, Square Roots, and Cube Roots Root 1 Perfect Square 1x1=1 Perfect Cube 1x1x1=1 2 4 8 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Vocabulary List For each word, provide a definition in your own words and an example. Radicand Radical Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 2 Index Whole Numbers Exact Value Approximate Value Natural Numbers Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 3 Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Integers Mixed radical Entire radical Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 4 Section 4.1: Estimating Roots Estimating Roots: 1) Write the two consecutive (numbers that are in a row like 1 and 2, 5 and 6, etc) perfect squares (or perfect cubes, etc) closest to the radicand. One perfect square (cube, etc) is larger, one is smaller. 2) Complete a table by estimating the square root (cube root, etc) and finding the square (cube, etc) of this value until your answer is within 1 decimal place (or whatever is asked for) of the radicand. a. If the value of the square is too large, reduce the estimated root. b. If the value of the square is too small, increase the estimated root. c. Use your best judgment to figure out how much to increase or decrease by each time. IT IS GUESS AND CHECK! 3) Justify your answer. Example 1: Find the estimated value of 20 within 1 decimal place of 20. 1) Write two consecutive perfect squares closest to 20. ______________ _________________ 2) Fill in the table until the estimate of the square is within 1 decimal place of 20. Estimated Value of its square 20 20 = _____________ 3) Justify your answer. _____________________________ What does it mean to justify your answer? Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 5 Example 2: Find the estimated value of 3 20 within 1 decimal place of 20. 1) Write two consecutive perfect cubes closest to 20. (Hint: Check your reference list). ______________ ___________________ 2) Fill in the table until the estimate of the cube root is within 1 decimal place of 20. Estimated 3 3 Value of its cube 20 20 = ______________ 3) Justify your answer. _____________________________ Question 3: Find the estimated fourth root of 20 within 1 decimal place of 20. 1) Write two consecutive perfect fourth powers closest to 20. _____________________ __________________________ 2) Fill in the table until the estimate of the fourth root is within 1 decimal place of 20. Estimated 4 20 Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Estimates fourth power Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 6 4 20 = ________________ 3) Justify your answer. _____________________________ Question 4: Complete the table below: Radical Value Is the Value Exact or Approximate? 16 4 Exact 27 5.1962 Approximate 16 81 4 9 or 0.4̄ Exact 0.64 3 16 3 27 3 16 81 3 0.64 3 0.64 4 16 4 27 4 4 16 81 0.64 What does it mean to write an equivalent form as a square root? Complete in Vocabulary List: Radicand, Radical, Index, Whole Number, Exact Value, Approximate Value HW: Complete Page 206 #2 - #6 Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 7 4.2 Irrational Numbers What does a decimal number that terminates look like? ____________________ What does a decimal number that repeats look like? _______________________ Steps to determine if a number is irrational or rational: 1) Use your calculator to find the value (approximate or exact) of the number. 2) Determine if it is a repeating or terminating decimal (rational) or not (irrational). Example 1: Classifying Numbers Tell whether each number is rational or irrational. Explain how you know! a) 3 5 b) d) 8 27 e) 3 3 c) 14 1 9 f) 0 Why can’t an irrational number have a 0 in the denominator? Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 8 Together, the rational and irrational numbers form the set of real numbers! Steps to order numbers: 1) First put the numbers all in decimal form. 2) Order the numbers (remember to think about negatives!) Example 2: Ordering Irrational Numbers on a Number Line Use a number line to order these numbers from least to greatest. Also decide if they are rational or irrational (use R and I), exact or approximate (use E and A). Vocabulary List: Natural Numbers, Rational Number, Irrational Numbers, Integers HW: Pg. 211 #3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15 Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 9 4.3 Mixed and Entire Radicals (Day 1) To multiply radicals, you can either multiply the radicands beneath the radical or you can separate these factors into 2 or more radicands. Example: Steps to Simplifying Radicals Using (also referred to as changing an entire radical into a mixed radical) 1) Use prime factorization (from chapter 3) to find the factors of the radical. Then find any repeating factors. a. For square roots, you need 2 of the same factor. (Factor out a perfect square) b. For cube roots, you need 3 of the same factor. (Factor out a perfect cube) c. Etc 2) “Factor” out the perfect square by moving the 2 identical factors from underneath the radical sign to 1 factor outside the radical sign. (similar for cubes, etc) 3) Do this for ALL factors that you can. Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 10 Can a radical always be simplified? Why or why not? HW: Page 218 # 4, 10, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17 Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 11 4.3 Mixed and Entire Radicals (Day 2) Steps for writing mixed radicals as entire radicals. 1) Use the Multiplication Property of Radicals to change the number in front of the radical (called the coefficient) into part of the radicand (number inside the radical symbol). a. To do this, square the number in front if it is a square root. (Cube the number in front if it is a cube root, etc). Vocabulary List: Mixed Radical, Entire Radical HW: Page 218 # 12acegi, 18ac, 8, 22a (no decimals!), 24 Assessment: Quiz (4.1 to 4.3) Foundations and Pre-Cal Math 10 Chapter 4: Roots and Powers 12