* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 1 Summary - Team Celebr8
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
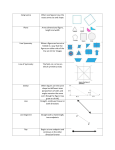
Ch 1 Summary Name ____________________________ Chapter 1: Introduction to Geometry Summary Sheet Undefined Terms General Terms point An undefined term thought of as a location with no size or dimension. It is the most basic building block of geometry. In a two-dimensional coordinate system, a point’s location is represented by an ordered pair of numbers (x, y). line An undefined term thought of as a straight, continuous arrangement of infinitely many points extending forever in two directions. A line has length, but no width or thickness, so it is one-dimensional. plane An undefined term thought of as a flat surface that extends infinitely along its edges. A plane has length and width but no thickness, so it is two-dimensional. intersect To cut or cross. bisect To divide into two congruent parts. counterexample An example that shows a conjecture to be incorrect or a definition to be inadequate. adjacent means next to. adjacent angles Two angles that share a common vertex, share a common side and have no common interior points. consecutive (angles, sides, or vertices of a polygon) Two angles that share a common side, two sides that share a common vertex, or two vertices that are the endpoints of one side. Related Terms collinear On the same line. coplanar In the same plane. Symmetry symmetry The property that a figure coincides with itself under a transformation that preserves size and shape. reflectional symmetry The property that a figure coincides with itself under a reflection. Also called line symmetry or mirror symmetry. line of symmetry The line of reflection of a figure having reflectional symmetry. bilateral symmetry Reflectional symmetry with only one line of symmetry. rotational symmetry The property that a figure coincides with itself under some rotation. If the angle of rotation is 360/n degrees for some positive integer n, the symmetry is called n-fold rotational symmetry. Ch 1 Summary Name ____________________________ Lines and Parts of Lines Angles line segment Two points and all the points between them that are collinear with the two points. Also called a segment. The measure of a line segment is its length. endpoint The point at either end of a segment or arc, or the first point of a ray. midpoint The point on a line segment that is the same distance from both endpoints. The midpoint bisects the segment. ray A point on a line, and all the points of the line that lie on one side of this point. angle Two noncollinear rays having a common endpoint. vertex (of an angle) The common endpoint of the two rays of the angle. side (of an angle) One of the two rays that form an angle. measure of an angle The smallest amount of rotation about the vertex from one ray to the other, measured in degrees. degree A unit of measure for angles and arcs. 360 of a rotation around a circle. (protractor A tool used to measure the size of an angle in degrees.) congruent segments Two or more segments that have the same measure or length. Types of Lines: perpendicular Lines are perpendicular if they meet at 90° angles. Line segments and rays are perpendicular if they lie on perpendicular lines. parallel Lines are parallel if they lie in the same plane and do not intersect. Line segments or rays are parallel if they lie on parallel lines. skew lines Lines that are not in the same plane and do not intersect. congruent angles Two or more angles that have the same measure. angle bisector A ray that has its endpoint at the vertex of the angle and that divides the angle into two congruent angles. adjacent angles Two non-overlapping angles with a common vertex and one common side. Types of Angles: Types of Pairs of Angles: right angle An angle whose measure is 90°. acute angle An angle whose measure is less than 90°. obtuse angle An angle whose measure is greater than 90°, but less than 180°. complementary angles Two angles whose measures have the sum 90°. supplementary angles Two angles whose measures have the sum 180°. vertical angles Two nonadjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines. linear pair (of angles) Two adjacent angles formed by a line and a ray. Ch 1 Summary Name ____________________________ Types of Triangles: Classified by angle: right triangle A triangle with a right angle. acute triangle A triangle with three acute angles. obtuse triangle A triangle with an obtuse angle. Classified by side: scalene triangle A triangle with three sides of different lengths. equilateral triangle A triangle whose sides are congruent. isosceles triangle A triangle with at least two congruent sides. Polygons: Isosceles Triangle Special Vocab. vertex angle (of an isosceles triangle) The angle between the two congruent sides. leg The congruent sides. base (of an isosceles triangle) The side opposite the vertex angle. base angles (of an isosceles triangle) The two angles opposite the two congruent sides. Types of Quadrilaterals: trapezoid A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. kite A quadrilateral with exactly two distinct pairs of congruent consecutive sides. parallelogram A quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. rhombus An equilateral parallelogram. rectangle An equiangular parallelogram. square An equiangular rhombus; equivalently, an equilateral rectangle. Names of polygons Sides Name 3 Triangle 4 Quadrilateral 5 Pentagon 6 Hexagon 7 Heptagon 8 Octagon 9 Nonagon 10 Decagon 11 Undecagon 12 Dodecagon n n-gon polygon A closed figure in a plane, formed by connecting line segments endpoint to endpoint with each segment intersecting exactly two others. side (of a polygon) A line segment connecting consecutive vertices of a polygon. vertex (of a polygon) An endpoint where two sides of the polygon meet. angle (of a polygon) An angle having two adjacent sides of the polygon as its sides. diagonal A line segment connecting two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon or polyhedron. convex polygon A polygon with no diagonal outside the polygon. concave polygon A polygon with at least one diagonal outside the polygon. congruent polygons Two or more polygons with the exact same size and shape. equilateral polygon A polygon whose sides are congruent. equiangular polygon A polygon whose angles are congruent. regular polygon A polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular. perimeter The length of the boundary of a twodimensional figure. For a polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its sides. Ch 1 Summary Name ____________________________ Circles: 3-D Figures: circle The set of all points in a plane at a given distance from a given point. center (of a circle) The coplanar point from which all points of the circle are the same distance. space An undefined term thought of as the set of all points. Space extends infinitely in all directions, so it is three-dimensional. solid A three-dimensional geometric figure that completely encloses a region of space. isometric drawing A drawing of a three-dimensional object that shows three faces in one view. Also called an edge view. net A two-dimensional pattern that can be folded to form a three-dimensional figure. solid of revolution A solid formed by rotating a twodimensional figure about a line. section The intersection of a solid and a plane. radius A line segment from the center of a circle or sphere to a point on the circle or sphere. Also, the length of that line segment. diameter A chord of a circle that contains the center, or the length of that chord. chord A line segment whose endpoints lie on a circle. tangent line A line that lies in the plane of a circle and that intersects the circle at exactly one point. point of tangency The point of intersection of a tangent line and a circle. Types of Solids: congruent circles Two or more circles with the same radius. concentric circles Circles that share the same center. arc Two points on a circle and the continuous part of the circle between them. semicircle An arc of a circle whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter. minor arc An arc of a circle that is less than a semicircle. major arc An arc of a circle that is greater than a semicircle. arc measure The measure of the central angle that intercepts an arc, measured in degrees. central angle An angle whose vertex is the center of a circle and whose sides pass through the endpoints of an arc. Prism Pyramid Cylinder Cone Sphere Hemisphere