* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.6 Inequalities in Two Triangles and Indirect Proof
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
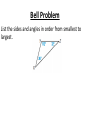
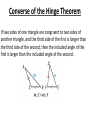
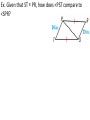
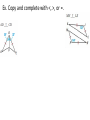
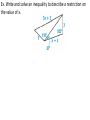
Bell Problem List the sides and angles in order from smallest to largest. 5.6 Inequalities in Two Triangles Standards: 1. Develop mathematical arguments and proofs 2. Use types of reasoning/methods of proof Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the included angle of the first is larger than the included angles of the second, then the third sides of the first is longer than the third side of the second. Converse of the Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the third side of the first is longer than the third side of the second, then the included angle of the first is larger than the included angle of the second. Ex. Given that ST ≅ PR, how does <PST compare to <SPR? Ex. Use the diagram. a. If PR = PS and m<QPR > m<QPS, which is longer, SQ or RQ? a. If PR = PS and RQ < SQ, which is larger, <RPQ or <SPQ? Ex. Copy and complete with <, >, or =. Ex. Write and solve an inequality to describe a restriction on the value of x. Homework 5.6 Practice B worksheet