* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Science with Ms. Tantri
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
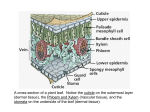
SBI3U: PLANT ORGANS, TISSUES AND CELLS (14.1) Name: ____________________ Read pages 381-390 and answer the following questions. Fill in the blanks. ROOT AND SHOOT SYSTEMS Roots are structures that anchor a plant in the soil, absorbing minerals and water and providing structural support. Monocots Fibrous root system: Examples: Dicots Taproot system: Examples: Shoots are above-ground structures consisting of stems, leaves and flowers. Stems are the parts of a plant that support leaves and flowers. Nodes are the points on the stem which leaves are attached. Internodes are the portions of the stem between nodes. Stems play an important role in ______________________ materials in a plant. _________________________________ runs vertically in the stem and transports __________ and __________________ from the _________ up to the ___________, and _________ from the _____________ to other parts of the plant, such as growing buds, flowers and roots. Undeveloped shoots are called __________. A _____________ bud is found at the tip of a stem. _______________________ buds are found in the ___________ formed by a leaf and the main stem. These angles are called __________. Growth from axillary buds forms the plant’s ________________. THE LEAF Define the following: Leaves: Blade: Petiole: Venation: The vein that runs through the petiole and into the blade consists of _________________________ and ________________________. These veins carry water and nutrients into the leaf, and transport sugars from the leaf to other parts of the plant. Contrast veins in monocots vs. dicots. FLOWERS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION A flower is a specialized __________, unique to __________________. Define the following: Sepals: Petals: Stamens: Pistils: Anther: Ovary: Ovule: Style: Stigma: Endosperm: SEED DEVELOPMENT AND DISPERSAL Read page 384-385 and take notes below: SEED GERMINATION Germination is the process where a plant embryo within a seed begins to grow. Seeds must soak up water in order to germinate. This will expand the seed and split the seed coat. Water also triggers metabolic changes in the embryo that enable it to grow. Look at Figure 14.13, page 386, to compare seed germination of Monocots and Dicots. VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION Many plants are also capable of _________________________________. In plants, this is called vegetative reproduction. The offspring are ______________________________ To the original plant. It can occur naturally or with human help. The simplest way to clone a plant is to __________________ a ________ or _____________ and place the cut end in water or soil. The ______ at the cut end of the petiole or stem become __________________________ and then form new ________________________ and organs. You get a new plant genetically identical to the original one. In many __________ plants, a ______________ from one plant can be grafted onto the ________ of another plant belonging to the same or closely related species. It is widely used by __________________________. See Figure 14.15. MAIN TISSUE SYSTEMS OF A PLANT See Figure 14.16 for a diagram. Dermal Tissue is the ________________________ or skin of the plant. The _____________________, which is the dermal tissue of _________________________, consists of one or more layers of cells. It covers and ____________________ all the young parts of the plant. Some is specialized, leaves and stems can secrete a ___________________________________, that helps plants retain water. Pores called __________________ are located in the epidermis of leaves. ______________________ ___________________ between the environment and the interior of the plant occurs through stoma. Vascular Tissue transports _________________________________________________ ______________________ between roots and shoots. It also contributes to the structural support of the plant. Xylem transports _____________ and ______________________ ___________________ upward from __________ into _______________. Phloem transports ______________ made in mature _____________ to the ___________ and parts of the _______________________ that don’t carry out photosynthesis. Vascular tissue is located in the _________________ of roots, but in the stems it is arranged in many separate ___________ called _______________________________. A monocot stem has vascular bundles scattered throughout the tissue, where a dicot stem have vascular bundles arranged in a ring. Ground Tissue fills the space between the dermal and vascular tissue. It makes up most of the young, non-woody plant and functions in _________________________ in the shoot and in ___________________ and __________________ throughout the plant. The ground tissue of the root consists of a mass of cells called the _______________. TYPES OF PLANT CELLS Define the following: Parenchyma cell- Collenchyma cell- Sclerenchyma cell- CELLULAR STRUCTURE OF A LEAF Leaves are designed to capture sunlight and allow ____________________ between the surrounding air and the __________ inside the leaf that carry out ___________________. See Figure 14.19, pg 389. Describe the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf: What do the guard cells do? The ground tissue of the leaf is made of ___________________, a type of parenchyma cell that is specialized for ________________________. Under the upper epidermis is a layer of elongated _____________________________________ cells that are specialized for capturing ____________________________ and carrying out __________________. Next to the lower epidermis is a layer of loosely packed _________________________ cells . __________________________ within these cells allow ____________________ and ____________________ to circulate within the leaf. COMPARING MONOCOTS AND DICOTS Angiosperms make up ___________ of known plant species. Copy down Table 14.1, page 390.