* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reading: AMSCO, pp. 518-525 Key Terms Stimson Doctrine Good
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
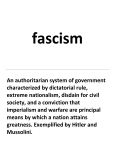
Reading: AMSCO, pp. 518-525 I. Key Terms 1. Stimson Doctrine 2. Good Neighbor Policy 3. fascism 4. Benito Mussolini 5. National Socialist Party (Nazi Party) 6. Adolf Hitler 7. Neutrality Acts 8. America First Committee 9. Munich Conference (1938) II. Reading Questions 1. What aggressive actions did Japan take in the early 1930s? How did the League of Nations and the United States deal with this early Japanese expansionism? 2. What ideas and developments increased Americans’ desire for isolationism in the first half of the 1930s? 3. How did European nations respond to the rise of fascism in Italy and Germany? Why do you think they responded this way? 4. How did President Roosevelt's response to the Japanese invasion of China illustrate the political strength of isolationist sentiment in the US? Reading: AMSCO, pp. 525-529 I. Key Terms 1. blitzkrieg 2. Cash-and-Carry system 3. Selective Training and Service Act (1940) 4. Lend-Lease Act 5. Atlantic Charter II. Reading Questions 1. What German moves and diplomatic failures led to the start of World War II in Europe? 2. How did Roosevelt manage to aid Great Britain in 1939 and 1940 in various ways without officially joining the war? 3. How/why did tensions between Japan and the U.S. increase between 1940 and 1941? 4. Could the U.S. have avoided the attack on Pearl Harbor? What were the consequences of this attack? Reading: AMSCO, pp. 532-535 I. Key Terms 1. Dwight Eisenhower 2. D-Day 3. “island-hopping” 4. Manhattan Project 5. Yalta Conference 6. Potsdam Conference II. Reading Questions 1. What were the two “theaters of operation” in which the fighting of World War II took place? 2. Why did the United States drop atomic bombs on Japan rather than attack Japan with soldiers? Do you think the U.S. made the right decision in using the atomic bombs? Explain I. Map Labeling 1. Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, Japan 2. Allied Powers: Great Britain, Russia, France 3. Poland 4. Austria 5. Czechoslovakia 6. North Africa 7. Midway Island 8. Guadalcanal 9. Iwo Jima 10. Okinawa Reading: Brinkley, pp. 748-756 I. Key Terms 1. Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) 2. Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) 3. “code-talkers” 4. Zoot-suit riots 5. “Rosie the Riveter” 6. War Relocation Authority (WRA) 7. Korematsu v. U.S. (1944) II. Reading Questions 1. Describe the wartime migration and employment of African Americans. Did the war create any new problems for African Americans? Explain. 2. Describe the roles of blacks in the military. What tensions resulted? 3. How were the women who filled war jobs treated? What obstacles did they face? 4. How were Japanese Americans treated during the war? What was done to compensate for this treatment? 5. What did President Roosevelt mean by the shift from "Dr. New Deal" to "Dr. Win-the-War"? How did the war “dismantle many of the achievements of the New Deal?”