* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
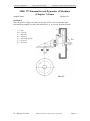
University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 1: Figure1 shows a simple gear train. If the input is provided by gear A and the output is taken off the shaft of gear E, what is the ratio and the sign of out in in terms of the number of teeth on the gears. Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 1 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 2: The compound gear train shown in Figure2 is attached to a motor that drives gear A at in clockwise as viewed from below. What is the expression for the angular velocity of gear H in terms of the number of teeth on the gears? What is the direction of rotation of gear H as viewed from below? Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 2 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 3: Gear A of the gear train in Fig.3 is driven at 200 rpm clockwise as viewed from below. The shafts of all gears are located in grounded bearings. Determine G , K and I given the number of teeth on each gear as indicated in the figure. Determine the direction of rotation of these three gears as viewed from the right. Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 3 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 4: The gear train shown in Fig.4 is arranged to feed lumber between the two 6-in. diameter rollers (R) into a cutting blade for ripping the lumber. The blade is being directly driven at 500 rpm. A power take-off, which consists of the belt system shown, drives the rollers for the purpose of feeding the stock. Determine the speed of the stock in ft/min and the direction of stock movement. Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 4 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 5: Design an ordinary gear train to couple the two shafts in Fig.5 so that the driver will rotate at 30 rpm and the follower at 21,000 rpm in the directions indicated. Design must be based on catalog gears of from 12 to 25 teeth listed every integer, and from 26 to 60 teeth listed every other integer. Prepare a drawing of the train arrangement and label each gear. D 30rpm F 21, 000rpm Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 5 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 6: Figure 6 shows a three-speed transmission with the drive shaft rotating in place at 450 rpm carrying the cluster of gears A, B, and C. The follower shaft is splined and may be shifted along its axis by means of the shift link to bring gears E, G, and H into contact with the gears on the drive shaft. Design the transmission to produce speeds of 150, 350, and 550 rpm, and describe how motion is transmitted in these three speeds. Gear teeth are to be kept within the limits of from 10 to 80 teeth. Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 6 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 7: For each planetary gear train in Figure7, determine the ratio indicated in the following list: (a) By the formula method. (b) By the tabular method. (c) By the instant-center method: Fig. 7(a): 2 3 Fig 7(b): 3 4 Fig 7(c): 2 3 Fig 7(d): 2 4 Fig 7(e): 3 4 Dr. Mostafa S. Habib Fig 7(f): 4 5 MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 7 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 8: (a) Determine the number of teeth on gear E of the gear train hoist in Figure 8 which yields a gear reduction between B and A of B A 25 , given NB = 20, NC = 80, and ND = 30. (b) Determine the numerical value of the mechanical advantage of this gear train hoist, W/Fin , assuming no losses. Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 8 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEG 373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Chapter 7) Gears Student Name: Student No.: Problem 9: The sun gear B of Figure.9 rotates at 100 rpm CW as viewed from the right. Determine the angular velocity and direction of G as viewed from the bottom. A = arm B = 24 teeth C = 60 teeth D = 18 teeth E = 102 teeth (fixed) F = 25 teeth G = 50 teeth Dr. Mostafa S. Habib MEG373 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Page 9